Abstract
Purpose/objective(s)
Radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT) has been reported to be useful for patients with ≤ 4 brain metastases (BM), but we hypothesized that similar treatment may be applicable to patients with ≥ 5 BM with or without meningeal dissemination. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and toxicity of low-dose Gamma Knife (GK) followed by WBRT for patients with advanced BM.
Materials/methods
Major eligibility criteria for this phase II study were: (1) ≥ 5 BM with or without meningeal dissemination and (2) the largest tumor diameter ≤ 4 cm. During 2013–2016, 40 patients (13 men and 27 women) entered the study. Nineteen had meningeal dissemination. The GK dose was 12 Gy at the periphery when the longest diameter was 3–4 cm and 14 Gy when it was < 3 cm. The WBRT dose to the isocenter was 30 Gy in 10 fractions, or 37.5 Gy in 15 fractions for two patients, with an expected survival of > 12 months. The median number of target BM was 17.5.
Results
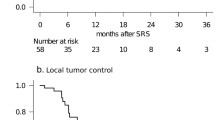
After GK plus WBRT for 40 patients, 31 did not develop further intracranial recurrence until death or last follow-up, whereas 9 developed recurrence. With a follow-up period up to 24 months, the overall survival rate was 36% at 12 months and median survival time was 8 months. The cumulative incidence of intracranial recurrence was 25% at 12 months. Toxicity was considered acceptable.
Conclusion
Treatment with low-dose GK followed by WBRT for advanced-stage BM appeared to contribute to local control.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shibamoto Y, Sugie C, Iwata H (2009) Radiotherapy for metastatic brain tumors. Int J Clin Oncol 14:281–288
Ohira S, Ueda Y, Akino Y et al (2018) HyperArc VMAT planning for single and multiple brain metastases stereotactic radiosurgery: a new treatment planning approach. Radiat Oncol 13:13
El Gantery MM, Abd El Baky HM, El Hossieny HA et al (2014) Management of brain metastases with stereotactic radiosurgery alone versus whole brain irradiation alone versus both. Radiat Oncol 9:116
Sperduto PW, Shanley R, Luo X et al (2014) Secondary analysis of RTOG 9508, a phase 3 randomized trial of whole-brain radiation therapy versus WBRT plus stereotactic radiosurgery in patients with 1–3 brain metastases; poststratified by the graded prognostic assessment (GPA). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 90:526–531
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M et al (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 295:2483–2491
Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Shuto T et al (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): a multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol 15:387–395
Nagai A, Shibamoto Y, Yoshida M et al (2014) Treatment of single or multiple brain metastases by hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy using helical tomotherapy. Int J Mol Sci 15:6910–6924
Ogura M, Mitsumori M, Okumura S et al (2003) Radiation therapy for brain metastases from breast cancer. Breast Cancer 10:349–355
Gaspar L, Scott C, Rotman M et al (1997) Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 37:745–751
A’Hern RP (2001) Sample size tables for exact single-stage phase II designs. Stat Med 20:859–866
Shibamoto Y, Miyakawa A, Otsuka S et al (2016) Radiobiology of hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy: what are the optimal fractionation schedules? J Radiat Res 57:i76–i82
Mori Y, Kobayashi T, Shibamoto Y (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery for metastatic tumors in the pituitary gland and the cavernous sinus. J Neurosurg 105:37–42
Miyakawa A, Shibamoto Y, Takemoto S et al (2017) Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for metastatic brain tumors that recurred after gamma knife radiosurgery results in acceptable toxicity and favorable local control. Int J Clin Oncol 22:250–256
Shibamoto Y, Baba F, Oda K et al (2008) Incidence of brain atrophy and decline in mini-mental state examination score after whole-brain radiotherapy in patients with brain metastases: a prospective study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 72:1168–1173
Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW et al (2004) Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 363:1665–1672
Brown PD, Jaeckle K, Ballman KV et al (2016) Effect of radiosurgery alone vs radiosurgery with whole brain radiation therapy on cognitive function in patients with 1 to 3 brain metastases: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 316:401–409
Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D et al (2012) Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: an accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. Clin Oncol 30:419–425
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Miyakawa, A., Shibamoto, Y., Takemoto, S. et al. Low-dose Gamma Knife radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy for patients with 5 or more brain metastases with or without meningeal dissemination. Int J Clin Oncol 24, 161–167 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-018-1339-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-018-1339-7