Abstract
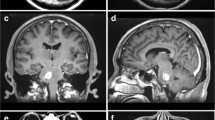
The aim of this study was to report our surgical experience on resection of the pontine cavernous malformations (CMs) via subtemporal transtentorial approach (STTA) and intradural anterior transpetrosal approach (ATPA). Clinical data were retrospectively reviewed in 61 patients with pontine CMs that were surgically treated by the STTA and the intradural ATPA. The surgical procedures, complications, and outcomes were analyzed. The study consists of 61 patients with a total of 61 pontine CMs. Other than 4 lesions located medially in the pons, all CMs were in the lateral pons with a left or right lateral epicenter (the left/right ratio was 22/35). Totally, 11 patients (18.0%) with lesions located in the upper pons were treated by the STTA, and 50 patients (82.0%) with lesions involving the lower pons were treated by the intradural ATPA. Postoperatively, the complete resection was achieved in 58 patients (95.1%) and incomplete resection in 3 patients (4.9%). Twenty-seven patients (44.3%) suffered from a new or worsened neurological deficit in the immediate postoperative period, and 8 patients (13.1%) encountered a non-neural complication, including rebleeding, cerebrospinal fluid leak, intracranial infection, and pulmonary infection, and 3 patients had contusion of temporal lobe. With a mean follow-up of 54.2 months, the patients’ neurological condition had improved in 43 cases (71.6%), not changed in 10 cases (16.7%), and worsened in 7 cases (11.7%), respectively. The Karnofsky Performance Scale (KPS) score evaluated at the last time for per patient was significantly better than their baseline status (t = 6.677, p < 0.001). However, 21 patients (35.0%) suffered from a new or worsened persistent postoperative deficit. The lateral and anterolateral pons can be exposed well by the subtemporal transtentorial and intradural anterior transpetrosal approaches. Lesions of CMs located in the lateral pons, including ventrolateral and dorsolateral pons, could be totally removed by these two lateral approaches with an acceptable surgical morbidity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abla AA, Turner JD, Mitha AP, Lekovic G, Spetzler RF (2010) Surgical approaches to brainstem cavernous malformations. Neurosurg Focus 29(3):E8
Abla AA, Lekovic GP, Turner JD, de Oliveira JG, Porter R, Spetzler RF (2011) Advances in the treatment and outcome of brainstem cavernous malformation surgery: a single-center case series of 300 surgically treated patients. Neurosurgery 68(2):403–415
Cavalcanti DD, Preul MC, Kalani MY, Spetzler RF (2016) Microsurgical anatomy of safe entry zones to the brainstem. J Neurosurg 124(5):1359–1376
Cenzato M, Stefini R, Ambrosi C, Giovanelli M (2008) Post-operative remnants of brainstem cavernomas: incidence, risk factors and management. Acta Neurochir 150(9):879–886
Faraji AH, Abhinav K, Jarbo K, Yeh FC, Shin SS, Pathak S, Hirsch BE, Schneider W, Fernandez-Miranda JC, Friedlander RM (2015) Longitudinal evaluation of corticospinal tract in patients with resected brainstem cavernous malformations using high-definition fiber tractography and diffusion connectometry analysis: preliminary experience. J Neurosurg 123(5):1133–1144
Ferroli P, Sinisi M, Franzini A, Giombini S, Solero CL, Broggi G (2005) Brainstem cavernomas: long-term results of microsurgical resection in 52 patients. Neurosurgery 56:1203–1214
Figueiredo EG, Zabramski JM, Deshmukh P, Crawford NR, Spetzler RF, Preul MC (2006) Comparative analysis of anterior petrosectomy and transcavernous approaches to retrosellar and upper clival basilar artery aneurysms. Neurosurgery 58:ONS13–ONS21
Flores BC, Whittemore AR, Samson DS, Barnett SL (2015) The utility of preoperative diffusion tensor imaging in the surgical management of brainstem cavernous malformations. J Neurosurg 122(3):653–662
Francois P, Ben Ismail M, Hamel O, Bataille B, Jan M, Velut S (2010) Anterior transpetrosal and subtemporal transtentorial approaches for pontine cavernomas. Acta Neurochir 152(8):1321–1329
Frischer JM, Gatterbauer B, Holzer S, Stavrou I, Gruber A, Novak K, Wang WT, Reinprecht A, Mert A, Trattnig S, Mallouhi A, Kitz K, Knosp E (2014) Microsurgery and radiosurgery for brainstem cavernomas: effective and complementary treatment options. World Neurosurg 81(3–4):520–528
Garcia RM, Ivan ME, Lawton MT (2015) Brainstem cavernous malformations: surgical results in 104 patients and a proposed grading system to predict neurological outcomes. Neurosurgery 76:265–278
Giliberto G, Lanzino DJ, Diehn FE, Factor D, Flemming KD, Lanzino G (2010) Brainstem cavernous malformations: anatomical, clinical, and surgical considerations. Neurosurg Focus 29(3):E9
Gross BA, Dunn IF, Du R, Al-Mefty O (2012) Petrosal approaches to brainstem cavernous malformations. Neurosurg Focus 33(2):E10
Gross BA, Batjer HH, Awad IA, Bendok BR, Du R (2013) Brainstem cavernous malformations: 1390 surgical cases from the literature. World Neurosurg 80(1–2):89–93
Guo X, Tabani H, Griswold D, Tayebi Meybodi A, Gonzalez Sanchez JJ, Lawton MT, Benet A (2017) Hearing preservation during anterior petrosectomy: the “cochlear safety line”. World Neurosurg 99:618–622
Hauck EF, Barnett SL, White JA, Samson D (2010) The presigmoid approach to ventrolateral pontine cavernomas. J Neurosurg 113(4):701–708
Horne MA, Flemming KD, Su IC, Stapf C, Jeon JP, Li D, Maxwell SS, White P, Christianson TJ, Agid R, Cho WS, Oh CW, Wu Z, Zhang JT, Kim JE, ter Brugge K, Willinsky R, Brown RD Jr, Murray GD, Salman RAS (2016) Clinical course of untreated cerebral cavernous malformations: a meta-analysis of individual patient data. Lancet Neurol 15(2):166–173
Ichimura S, Yoshida K, Kagami H, Inaba M, Orii M, Kitamura Y, Saga I, Toda M (2012) Epidural anterior petrosectomy with subdural visualization of sphenobasal vein via the anterior transpetrosal approach—technical case report. Neurosurg Rev 35(4):609–613
Ichimura S, Hori S, Hecht N, Czabanka M, Vajkoczy P (2016) Intradural anterior transpetrosal approach. Neurosurg Rev 39(4):625–631
Januszewski J, Albert L, Black K, Dehdashti AR (2016) The usefulness of diffusion tensor imaging and tractography in surgery of brainstem cavernous malformations. World Neurosurg 93:377–388
Jiang Y, Chen Y, Yao J, Tian Y, Su L, Li Y (2015) Anatomic assessment of petrous internal carotid artery, facial nerve, and cochlea through the anterior transpetrosal approach. J Craniofac Surg 26(7):2180–2183
Kashimura H, Inoue T, Ogasawara K, Ogawa A (2006) Pontine cavernous angioma resected using the subtemporal, anterior transpetrosal approach determined using three-dimensional anisotropy contrast imaging: technical case report. Neurosurgery 58(1 Suppl):ONS-E175
Kawase T, Toya S, Shiobara R, Mine T (1985) Transpetrosal approach for aneurysms of the lower basilar artery. J Neurosurg 63:857–861
Kumabe T, Suzuki M, Yoshimoto T, Suzuki J (1988) A case of cavernous angioma extended from the ventral part of the pons to the midbrain: subtemporal and trans-tentorial approach. No Shinkei Geka 16:1193–1197
Kyoshima K, Kobayashi S, Gibo H, Kuroyanagi T (1993) A study of safe entry zones via the floor of the fourth ventricle for brainstem lesions. Report of three cases. J Neurosurg 78:987–993
Li DY, Whitehead KJ (2010) Evaluating strategies for the treatment of cerebral cavernous malformations. Stroke 41:92–94
Li D, Yang Y, Hao SY, Wang L, Tang J, Xiao XR, Zhou H, Jia GJ, Wu Z, Zhang LW, Zhang JT (2013) Hemorrhage risk, surgical management, and functional outcome of brainstem cavernous malformations. J Neurosurg 119(4):996–1008
Li D, Jiao YM, Wang L, Lin FX, Wu J, Tong XZ, Wang S, Cao Y (2018) Surgical outcome of motor deficits and neurological status in brainstem cavernous malformations based on preoperative diffusion tensor imaging: a prospective randomized clinical trial. J Neurosurg 130(1):286–301
Liu KD, Chung WY, Wu HM, Shiau CY, Wang LW, Guo WY, Hung-Chi Pan D (2005) Gamma knife surgery for cavernous hemangiomas: an analysis of 125 patients. J Neurosurg 102 Suppl:81–86
Lu XY, Sun H, Xu JG, Li QY (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery of brainstem cavernous malformations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurosurg 120:982–987
MacDonald JD, Antonelli P, Day AL (1998) The anterior subtemporal, medial transpetrosal approach to the upper basilar artery and ponto-mesencephalic junction. Neurosurgery 43(1):84–89
Mare PB, Churi ON, Misra BK (2014) Anterior petrosal approach for brainstem cavernoma. Asian J Neurosurg 9(4):243
Matsushima K, Matsushima T, Kuga Y, Kodama Y, Inoue K, Ohnishi H, Rhoton AL Jr (2014) Classification of the superior petrosal veins and sinus based on drainage pattern. Neurosurgery 10(Suppl 2):357–367
Mizutani K, Toda M, Yoshida K (2016) The analysis of the petrosal vein to prevent venous complications during the anterior transpetrosal approach in the resection of petroclival meningioma. World Neurosurg 93:175–182
Ohmura T, Hirakawa K, Ohta M, Utsunomiya H, Fukushima T (2008) Cavernous malformation of the ventral midbrain successfully removed via a transsylvian-transpeduncular approach: case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 48(12):569–572
Pandey P, Westbroek EM, Gooderham PA, Steinberg GK (2013) Cavernous malformation of brainstem, thalamus, and basal ganglia: a series of 176 patients. Neurosurgery 72(4):573–589
Porter RW, Detwiler PW, Spetzler RF, Lawton MT, Baskin JJ, Derksen PT, Zabramski JM (1999) Cavernous malformations of the brainstem: experience with 100 patients. J Neurosurg 90:50–58
Reinhard M, Schuchardt F, Meckel S, Heinz J, Felbor U, Sure U, Geisen U (2016) Propranolol stops progressive multiple cerebral cavernoma in an adult patient. J Neurol Sci 367:15–17
Roszkowski M, Drabik K, Grajkowska W, Jurkiewicz E, Daszkiewicz P (2003) Direct trans-sylvian approach to the ventrolateral pons in surgical management of large cystic cavernous malformations of the brain stem in children. Neurol Neurochir Pol 37:847–860
Seo Y, Sasaki T, Nakamura H (2010) Simple landmark for preservation of the cochlea during maximum drilling of the petrous apex through the anterior transpetrosal approach. Neurol Med Chir 50(4):301–305
Shibao S, Borghei-Razavi H, Yoshida K (2016) Anterior transpetrosal approach: epidural or subdural? Neurosurg Rev 39(3):531–534
Smith ER, Chapman PH, Ogilvy CS (2003) Far posterior subtemporal approach to the dorsolateral brainstem and tentorial ring: technique and clinical experience. Neurosurgery 52:364–368
Steiger HJ, Hänggi D, Stummer W, Winkler PA (2006) Custom-tailored transdural anterior transpetrosal approach to ventral pons and retroclival regions. J Neurosurg 104(1):38–46
Steno J, Bizik I, Stenova J, Timarova G (2011) Subtemporal transtentorial resection of cavernous malformations involving the pyramidal tract in the upper pons and mesencephalon. Acta Neurochir 153(10):1955–1962
Tumturk A, Li Y, Turan Y, Cikla U, Iskandar BJ, Baskaya MK (2018) Emergency resection of brainstem cavernous malformations. J Neurosurg 128(5):1289–1296
Ulrich NH, Kockro RA, Bellut D, Amaxopoulou C, Bozinov O, Burkhardt JK, Sarnthein J, Kollias SS, Bertalanffy H (2014) Brainstem cavernoma surgery with the support of pre- and postoperative diffusion tensor imaging: initial experiences and clinical course of 23 patients. Neurosurg Rev 37(3):481–491
Wang C-C, Liu A, Zhang J-T, Sun B, Zhao Y-L (2003) Surgical management of brain-stem cavernous malformations: report of 137 cases. Surg Neurol 59(6):444–454
Xiao X, Zhang L, Wu Z, Zhang J, Jia G, Tang J, Meng G (2013) Surgical resection of large and giant petroclival meningiomas via a modified anterior transpetrous approach. Neurosurg Rev 36(4):587–593
Yang J, Ma SC, Fang T, Qi JF, Hu YS, Yu CJ (2011) Subtemporal transpetrosal apex approach: study on its use in large and giant petroclival meningiomas. Chin Med J 124(1):49–55
Zabramski JM, Kalani MY, Filippidis AS, Spetzler RF (2016) Propranolol treatment of cavernous malformations with symptomatic hemorrhage. World Neurosurg 88:631–639
Zaidi HA, Mooney MA, Levitt MR, Dru AB, Abla AA, Spetzler RF (2017) Impact of timing of intervention among 397 consecutively treated brainstem cavernous malformations. Neurosurgery:1–7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The Beijing Tiantan Hospital Research Ethics Committee approved the study. Due to the retrospective nature of the report, informed consent was not required.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, S., Xiao, XR., Li, H. et al. Surgical treatment of pontine cavernous malformations via subtemporal transtentorial and intradural anterior transpetrosal approaches. Neurosurg Rev 43, 1179–1189 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-019-01156-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-019-01156-7