Abstract
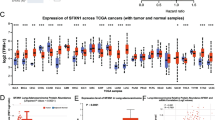
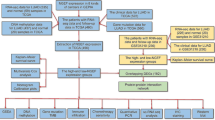
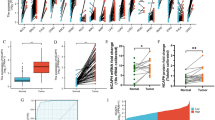
As lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer deaths globally, characterizing the tumor molecular profiles is crucial to tailoring treatments for individuals at advanced stages. Cancer cells exhibit strong dependence on iron for their proliferation, and several iron-regulatory proteins have been proposed as either oncogenes or tumor suppressive genes. This study aims to evaluate the prospective therapeutic and prognostic values of the sideroflexin (SFXN) gene family, whose functions involve mitochondrial iron metabolism, in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). Differential expression analysis using TIMER and UALCAN tools was first employed to compare SFXNs expression levels between normal and LUAD tissues. Next, SFXNs’ prognostic values, biological significance, and potential as immunotherapy candidates were examined from GEPIA, cBioPortal, MetaCore, Cytoscape, and TIMER databases. It was found that all members of SFXN family, except SFXN3, were differentially expressed in LUAD compared to normal samples and within different stages of LUAD. Survival analysis then revealed SFXN1 to be related to worse overall survival outcome in patients with LUAD. Furthermore, several correlations between expression of SFXN1 and immune infiltration cells were discovered. To conclude, our study provides evidence of SFXN family gene’s relevance to the prognosis and immunotherapeutic targets of LUAD.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acoba MG, Selen ES, Alpergin SR, Fernández-del-Río L, Ya-Wen Lu, Khalimonchuk O, Clarke CF, Pandey A, Wolfgang MJ, Claypool SM (2021) The mitochondrial carrier SFXN1 is critical for complex III integrity and cellular metabolism. Cell Rep 34(11):108869. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108869
Amorim IS, Graham LC, Carter RN, Morton NM, Hammachi F, Kunath T, Pennetta G et al (2017) Sideroflexin 3 is an α-synuclein-dependent mitochondrial protein that regulates synaptic morphology. J Cell Sci 130(2):325–331. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.194241
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Heather Butler J, Cherry M, Davis AP et al (2000) Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genet 25(1):25–29. https://doi.org/10.1038/75556
Asplund A, Edqvist P-H, Schwenk JM, Pontén F (2012) Antibodies for profiling the human proteome—the human protein atlas as a resource for cancer research. Proteomics 12(13):2067–2077. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201100504
Attwood MM, Schiöth HB (2021) Characterization of five transmembrane proteins: with focus on the tweety, sideroflexin, and YIP1 domain families. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:1950. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.708754
Azzi A, Glerum M, Koller R, Mertens W, Spycher S (1993) The mitochondrial tricarboxylate carrier. J Bioenerg Biomembr 25(5):515–524. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01108408
Barlesi F, Mazieres J, Merlio J-P, Debieuvre D, Mosser J, Lena H, Ouafik L et al (2016) Routine molecular profiling of patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: results of a 1-year nationwide programme of the French Cooperative Thoracic Intergroup (IFCT). Lancet (london, England) 387(10026):1415–1426. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00004-0
Barretina J, Caponigro G, Stransky N, Venkatesan K, Margolin AA, Kim S, Wilson CJ et al (2012) The cancer cell line encyclopedia enables predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity. Nature 483(7391):603–607. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11003
Berghmans T, Dingemans A-M, Hendriks LEL, Cadranel J (2020) Immunotherapy for nonsmall cell lung cancer: a new therapeutic algorithm. Eur Respir J 55 (2). https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.01907-2019
Brooks D, Taylor C, Dos Santos B, Linden H, Houghton A, Hecht TT, Kornfeld S, Taetle R (1995) Phase Ia trial of murine immunoglobulin A antitransferrin receptor antibody 42/6. Clin Cancer Res: Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 1(11):1259–1265
Campbell JA (1940) Effects of precipitated silica and of iron oxide on the incidence of primary lung tumours in mice. Br Med J 2(4156):275–280. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.2.4156.275
Chandel NS (2010) Mitochondrial complex III: an essential component of universal oxygen sensing machinery? Respir Physiol Neurobiol 174(3):175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resp.2010.08.004
Chandrashekar, Darshan S, Bashel B, Balasubramanya SAH, Creighton CJ, Ponce-Rodriguez I, Balabhadrapatruni VSK, Chakravarthi, Varambally S, (2017) UALCAN: a portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia (New York, N.Y.) 19(8): 649–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2017.05.002
Chen Bo, Aredo B, Ding Yi, Zhong X, Zhu Y, Zhao CX, Kumar A et al (2020) Forward genetic analysis using OCT screening identifies Sfxn3 mutations leading to progressive outer retinal degeneration in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117(23):12931–12942. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1921224117
Chen B, Xie X, Lan F, Liu W (2021) Identification of prognostic markers by weighted gene co-expression network analysis in non-small cell lung cancer. Bioengineered 12(1):4924–4935. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.1960764
Chen Q, Wang R, Zhang J, Zhou L (2019) Sideroflexin1 as a novel tumor marker independently predicts survival in lung adenocarcinoma. Transl Cancer Res 8 (4). https://doi.org/10.21037/30374
da Silva C, Milene MO, Breckwoldt FV, Correia MP, Stojanovic A, Thielmann CM, Meister M et al (2017) Iron induces anti-tumor activity in tumor-associated macrophages. Front Immunol 8:1479. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01479
Duraiyan J, Govindarajan R, Kaliyappan K, Palanisamy M (2012) Applications of immunohistochemistry. J Pharm Bioallied Sci 4(Suppl 2):S307. https://doi.org/10.4103/0975-7406.100281
Edemir B, (2020) Identification of prognostic organic cation and anion transporters in different cancer entities by in silico analysis. Int J Mol Sci 21 (12). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124491
Fleming MD, Campagna DR, Haslett JN, Trenor CC, Andrews NC (2001) A mutation in a mitochondrial transmembrane protein is responsible for the pleiotropic hematological and skeletal phenotype of flexed-tail (f/f) mice. Genes Dev 15(6):652–657. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.873001
Forciniti S, Greco L, Grizzi F, Malesci A, Laghi L (2020) Iron metabolism in cancer progression. Int J Mol Sci 21(6):2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21062257
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G, Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y et al (2013) Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the CBioPortal. Sci Signal 6(269):pl1–pl1. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2004088
Ghio AJ, Hilborn ED, Stonehuerner JG, Dailey LA, Carter JD, Richards JH, Crissman KM, Foronjy RF, Uyeminami DL, Pinkerton KE (2008) Particulate matter in cigarette smoke alters iron homeostasis to produce a biological effect. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 178(11):1130–1138. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200802-334OC
Gylfe AE, Katainen R, Kondelin J, Tanskanen T, Cajuso T, Hänninen U, Taipale J et al (2013) Eleven candidate susceptibility genes for common familial colorectal cancer. PLoS Genet 9(10):e1003876. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003876
Hildick-Smith GJ, Cooney JD, Garone C, Kremer LS, Haack TB, Thon JN, Miyata N et al (2013) Macrocytic anemia and mitochondriopathy resulting from a defect in sideroflexin 4. Am J Human Genet 93(5):906–914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.09.011
Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Miller D, Brest A, Yu M, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z, Mariotto A, Lewis DR, Chen HS, Feuer EJ, Cronin KA (eds). n.d. SEER cancer statistics review, 1975–2017, National Cancer Institute. Based on November 2019 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site, April 2020. SEER. Accessed September 25, 2021. https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2017/index.html.
Ito T, Kawai Y, Yasui Y, Iriguchi S, Minagawa A, Ishii T, Miyoshi H et al (2021) The therapeutic potential of multiclonal tumoricidal T cells derived from tumor infiltrating lymphocyte-derived IPS cells. Commun Biol 4(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-021-02195-x
Jeong J, Keum S, Kim D, You E, Ko P, Lee J, Kim J, Kim J-W, Rhee S (2018) Spindle pole body component 25 homolog expressed by ECM stiffening is required for lung cancer cell proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 500(4):937–943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.205
Kanehisa M, Goto S (2000) KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 28(1):27–30. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.27
Kory N, Wyant GA, Prakash G, de Bos JU, Bottanelli F, Pacold ME, Chan SH et al (2018) SFXN1 is a mitochondrial serine transporter required for one-carbon metabolism. Science 362(6416):eaat9528. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aat9528
Li T, Fan J, Wang B, Traugh N, Chen Q, Liu JS, Li Bo, Shirley Liu X (2017) TIMER: a web server for comprehensive analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Can Res 77(21):e108–e110. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0307
Lim SM, Hong MH, Kim HR (2020) Immunotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer: current landscape and future perspectives. Immune Netw 20 (1). https://doi.org/10.4110/in.2020.20.e10
Lockhart PJ, Holtom B, Lincoln S, Hussey J, Zimprich A, Gasser T, Wszolek ZK, Hardy J, Farrer MJ (2002) The human sideroflexin 5 (SFXN5) gene: sequence, expression analysis and exclusion as a candidate for PARK3. Gene 285(1–2):229–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-1119(02)00402-x
Lu R, Zhou Q, Linling Ju, Chen L, Wang F, Shao J (2021) Upregulation of TRIP13 promotes the malignant progression of lung cancer via the EMT pathway. Oncol Rep 46(2):172. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2021.8123
Manz DH, Blanchette NL, Paul BT, Torti FM, Torti SV (2016) Iron and cancer: recent insights. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1368(1):149–161. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.13008
Miyake S-I, Yamashita T, Taniguchi M, Tamatani M, Sato K, Tohyama M (2002) Identification and characterization of a novel mitochondrial tricarboxylate carrier. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 295(2):463–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00694-0
Mon EE, Wei F-Y, Ahmad RNR, Yamamoto T, Moroishi T, Tomizawa K (2019) Regulation of mitochondrial iron homeostasis by sideroflexin 2. J Physiol Sci 69(2):359–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12576-018-0652-2
Murase R, Abe Y, Takeuchi T, Nabeta M, Imai Y, Kamei Y, Kagawa-Miki L et al (2008) Serum autoantibody to sideroflexin 3 as a novel tumor marker for oral squamous cell carcinoma. PROTEOMICS – Clin Appl 2(4):517–27. https://doi.org/10.1002/prca.200780123
Organelle Fission Gene Ontology Term (GO:0048285). n.d. Accessed October 2, 2021. http://www.informatics.jax.org/vocab/gene_ontology/GO:0048285
Paul BT, Tesfay L, Winkler CR, Torti FM, Torti SV (2019) Sideroflexin 4 Affects Fe-S Cluster biogenesis, iron metabolism, mitochondrial respiration and heme biosynthetic enzymes. Sci Rep 9(1):19634. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-55907-z
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13(11):2498–2504. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.1239303
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A (2021) Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA: A Cancer J Clin 71(1):7–33. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21654
Sofou K, Hedberg-Oldfors C, Kollberg G, Thomsen C, Wiksell Å, Oldfors A, Tulinius M (2019) Prenatal onset of mitochondrial disease is associated with sideroflexin 4 deficiency. Mitochondrion 47(July):76–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2019.04.012
Sung H, Ferlay J, RL Siegel, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, F Bray (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J Clin 71 (3): 209–49. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Taetle R, Castagnola J, Mendelsohn J (1986) Mechanisms of growth inhibition by anti-transferrin receptor monoclonal antibodies. Can Res 46(4 Pt 1):1759–1763
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao Ge, Li C, Zhang Z (2017) GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res 45(W1):W98-102. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx247
Thielmann CM, Costa M, da Silva T, Muley MM, Herpel E, Muckenthaler MU (2019) Iron accumulation in tumor-associated macrophages marks an improved overall survival in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep 9(1):11326. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-47833-x
Tifoun N, De las Heras JM, Guillaume A, Bouleau S, Mignotte B, Le Floch N (2021) Insights into the roles of the sideroflexins/SLC56 family in iron homeostasis and iron-sulfur biogenesis. Biomedicines 9(2):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020103
Torti SV, Torti FM (2013) Iron and cancer: more ore to be mined. Nat Rev Cancer 13(5):342–355. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3495
Wu Y, Lin Y, Pan J, Xunwei Tu, Yiquan Xu, Li H, Chen Y (2021) NCAPG promotes the progression of lung adenocarcinoma via the TGF-β signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int 21(1):443. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-021-02138-w
Yoshikumi Y, Mashima H, Ueda N, Ohno H, Suzuki J, Tanaka S, Hayashi M et al (2005) Roles of CTPL/Sfxn3 and Sfxn family members in pancreatic islet. J Cell Biochem 95(6):1157–1168. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.20481
Yu Y, Gutierrez E, Kovacevic Z, Saletta F, Obeidy P, SuryoRahmanto Y, Richardson RD (2012) Iron chelators for the treatment of cancer. Curr Med Chem 19(17):2689–2702
Yu G, Wang L-G, Yan G-R, He Q-Y (2015) DOSE: an R/Bioconductor package for disease ontology semantic and enrichment analysis. Bioinformatics 31(4):608–609. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu684
Funding
This work has been supported by the Taiwan Higher Education Sprout Project by the Ministry of Education (DP2-111-21121-01-A-12)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Huy-Hoang Dang: conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft preparation. Hoang Dang Khoa Ta: conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, resources, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing. Truc T. T. Nguyen: conceptualization, visualization, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing. Gangga Anuraga: software, validation. Chih-Yang Wang: resources, data curation, supervision. Kuen-Haur Lee: resources, data curation, supervision. Nguyen Quoc Khanh Le: conceptualization, writing—review and editing, supervision, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dang, H.H., Ta, H.D.K., Nguyen, T.T.T. et al. Prospective role and immunotherapeutic targets of sideroflexin protein family in lung adenocarcinoma: evidence from bioinformatics validation. Funct Integr Genomics 22, 1057–1072 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-022-00883-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-022-00883-3