Abstract
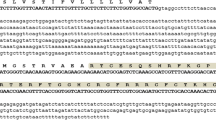
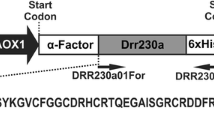
Plant defensins are small (45 to 54 amino acids) positively charged antimicrobial peptides produced by the plant species, which can inhibit the growth of a broad range of fungi at micro-molar concentrations. These basic peptides share a common characteristic three-dimensional folding pattern with one α-helix and three β-sheets that are stabilized by eight disulfide-linked cysteine residues. Instead of using two single-gene constructs, it is beneficial when two effective genes are made into a single fusion gene with one promoter and terminator. In this approach, we have linked two plant defensins namely Trigonella foenum-graecum defensin 2 (Tfgd2) and Raphanus sativus antifungal protein 2 (RsAFP2) genes by a linker peptide sequence (occurring in the seeds of Impatiens balsamina) and made into a single-fusion gene construct. We used pET-32a+ vector system to express Tfgd2-RsAFP2 fusion gene with hexahistidine tag in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) pLysS cells. Induction of these cells with 1 mM IPTG achieved expression of the fusion protein. The solubilized His6-tagged recombinant fusion protein was purified by immobilized-metal (Ni2+) affinity column chromatography. The final yield of the fusion protein was 500 ng/μL. This method produced biologically active recombinant His6-tagged fusion protein, which exhibited potent antifungal action towards the plant pathogenic fungi (Botrytis cinerea, Fusarium moniliforme, Fusarium oxysporum, Phaeoisariopsis personata and Rhizoctonia solani along with an oomycete pathogen Phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae) at lower concentrations under in vitro conditions. This strategy of combining activity of two defensin genes into a single-fusion gene will definitely be a promising utility for biotechnological applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benko-Iseppon AM, Galdino SL, Calsa T Jr, Kido EA, Tossi A, Belarmino LC, Crovella S (2010) Overview on plant antimicrobial peptides. Curr Protein Pept Sci 11:181–188
Bloch CJ, Richardson MA (1991) A new family of small (5 kDa) protein inhibitors of insect α-amylases from seeds of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) have sequence homologies with wheat γ-purothionins. FEBS Lett 279:101–104
Boman HG (1995) Peptide antibiotics and their role in innate immunity. Annu Rev Immunol 13:61–92
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Broekaert WF, Terras FR, Cammue BP, Osborn RW (1995) Plant defensins: novel antimicrobial peptides as components of the host defense system. Plant Physiol 108:1353–1358
Broekaert WF, Cammune BPA, De Bolle MFC, Thevissen K, De Samblanx GW, Osborn RW (1997) Antimicrobial peptides from plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 16:297–323
Campos MDA, Silva MS, Magalhaes CP, Ribeiro SG, Sarto RPD, Vieira EA, de Sa MFG (2008) Expression in Escherichia coli, purification, refolding and anti-fungal activity of an osmotin from Solanum nigrum. Microb Cell Factories 7:7
Carvalho AO, Gomes VM (2009) Plant defensins-prospects for the biological functions and biotechnological properties. Peptides 30:1007–1020
Chen GH, Hsu MP, Tan CH, Sung HY, Kuo CG, Fan MJ, Chen HM, Chen S, Chen CS (2005) Cloning and characterization of a plant defensin VaD1 from azuki bean. J Agric Food Chem 53:982–988
De Beer A, Vivier MA (2011) Four plant defensins from an indigenous South African Brassicaceae species display divergent activities two test pathogens despite high sequence similarity in the encoding genes. BMC Res Notes 4:459–477
Hancock REW, Lehrer R (1998) Cationic peptides: a new source of antibiotics. Trends Biotechnol 16:82–88
Hui LD, Liang JG, Tao ZY, Min AT (2007) Bacterial expression of a Trichosanthes kirilowii defensin (TDEF1) and its antifungal activity on Fusarium oxysporum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:146–151
Kirubakaran SI, Sakthivel N (2007) Cloning and overexpression of antifungal barley chitinase gene in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 52:159–166
Kovaleva V, Krynytskyy H, Gout I, Gout R (2011) Recombinant expression, affinity purification and functional characterization of Scots pine defensin1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:1093–1101
Kushmerick C, Castro MS, Cruz JS, Bloch CJ, Beiraio PSL (1998) Functional and structural features of γ-zeathionins, a new class of sodium channel blockers. FEBS Lett 440:302–306
Laemlli UK (1970) Clevage of structural proteins during the assembly of head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Landon C, Sodano P, Hetru C, Hoffmann J, Ptak M (1997) Solution structure of drosomycin, the first inducible antifungal protein from insects. Prot Sci 6:1878–1884
Lay FT, Anderson MA (2005) Defensins—components of the innate immune system in plants. Curr Protein Pept Sci 6:85–101
Li Z, Zhou M, Zhang Z, Ren L, Du L, Zhang B, Xu H, Xin Z (2011) Expression of a radish defensin in transgenic wheat confers increased resistance to Fusarium graminearum and Rhizoctonia cerealis. Funct Integr Genomics 11:63–70
Lobo DS, Pereira IB, Fragel-Madeira L, Medeiros LN, Cabral LM, Faria J, Bellio M, Campos RC, Linden R, Kurtenbach E (2007) Antifungal Pisum sativum defensin1 interacts with Neurospora crassa cyclin F related to the cell cycle. Biochemistry 46:987–996
Makrides SC (1996) Strategies for achieving high-level expression of genes in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev 60:512–538
Mello EO, Ribeiro SF, Carvalho AO, Santos IS, Da Cunha M, Santa-Catarina C, Gomes VM (2011) Antifungal activity of PvD1 defensin involves plasma membrane permeabilization, inhibition of medium acidification, and induction of ROS in fungi cells. Curr Microbiol 62:1209–1217
Melo FR, Rigden DJ, Franco OL, Mello LV, Ary MB, Grossi- De- Sa MF, Bloch C (2002) Inhibition of trypsin by cowpea thionin: characterization, molecular modeling, and docking. Proteins 48:311–319
Mendez E, Moreno A, Colilla F, Pelaez R, Limas GG, Mendez R, Soriano F, de Salinas M, Haro C (1990) Primary structure and inhibition of protein synthesis in eukaryotic cell-free system of a novel thionin, gamma-thionin, from barley endosperm. Eur J Biochem 194:533–539
Mendez E, Rocher A, Calero M, Girbes T, Citores L, Soriano F (1996) Primary structure of ω-hordothionin, a member of a novel family of thionins from barley endosperm, and its inhibition of protein synthesis in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell-free systems. Eur J Biochem 239:67–73
Mirouze M, Sels J, Richard O, Czernic P, Loubet S, Jacquier A, Franciois I, Cammue BPA, Lebrun M, Berthomieu P, Marques L (2006) A putative novel role for plant defensins: a defensin from the zinc hyper-accumulating plant, Arabidopsis halleri, confers zinc tolerance. Plant J 47:329–342
Odintsova TI, TsA E, Musolyamov AK, Odintsova MS, Pukhalsky VA, Grishin EV (2007) Seed defensins from T. kiharae and related species: genome localization of defensing encoding genes. Biochimie 89:605–612
Olli S, Kirti PB (2006) Cloning, characterization and antifungal activity of defensin Tfgd1 from Trigonella foenum-graecum L. J Biochem Mol Biol 39:278–283
Olli S, Guruprasad L, Kirti PB (2007) Characterization of defensin (Tfgd2) from Trigonella foenum-graecum. Curr Sci 93:365–369
Osborn RW, De Samblanx GW, Thevissen K, Goderis I, Torrekens S, Van Leuven F, Attenborough S, Rees SB, Broekaert WF (1995) Isolation and characterisation of plant defensins from seeds of Asteraceae, Fabaceae, Hippocastanaceae and Saxifragaceae. FEBS Lett 368:257–262
Osusky M, Zhou G, Osuska L, Hancock RE, Kay WW, Misra S (2000) Transgenic plants expressing cationic peptide chimeras exhibit broad-spectrum resistance to phytopathogens. Nat Biotechnol 18:1162–1166
Parashina EV, Serdobinskii LA, Kalle EG, Lavorova NV, Avetisov VA, Lunin VG, Naroditskii BS (2000) Genetic engineering of oilseed rape and tomato plants expressing a radish defensin gene. Russ J Plant Physiol 47:417–423
Park HC, Kang YH, Chun HJ, Koo JC, Cheong YH, Kim CY, Kim MC, Chung WS, Kim JC, Yoo JH, Koo YD, Koo SC, Lim CO, Lee SY, Cho MJ (2002) Characterization of a stamen-specific cDNA encoding a novel plant defensin in Chinese cabbage. Plant Mol Biol 50:59–69
Pelegrini PB, Lay FT, Murad AM, Anderson MA, Franco OL (2008) Novel insights on the mechanism of action of α-amylase inhibitors from the plant defensin family. Proteins 73:719–729
Punja ZK (2001) Genetic engineering of plants to enhance resistance to fungal pathogens—a review of progress and future prospects. Can J Plant Pathol 23:216–235
Singh A, Kirubakaran SI, Sakthivel N (2007) Heterologous expression of a new antifungal chitinase from wheat. Protein Expr Purif 56:100–109
Solis J, Medrano GG, Ghislain M (2007) Inhibitory effect of a defensin gene from the Andean crop maca (Lepidium meyenii) against Phytophthora infestans. J Plant Physiol 164:1071–1082
Song X, Wang J, Wu F, Li X, Teng M, Gong W (2005) cDNA cloning, functional expression and antifungal activities of a dimeric plant defensin SPE10 from Pachyrrhizus erosus seeds. Plant Mol Biol 57:13–20
Spelbrink RG, Dilmac N, Allen A, Smith TJ, Shah DM, Hockerman GH (2004) Differential antifungal and calcium channel-blocking activity among structurally related plant defensins. Plant Physiol 135:2055–2067
Stotz HU, Thomson JG, Wang Y (2009) Plant defensins: defense, development and application. Plant Signal Behav 4:1010–1012
Terras FRG, Torrekens S, Van Leuven F, Osborn RW, Vanderleyden J, Cammue BPA, Broekaert WF (1993) A new family of basic cysteine-rich plant antifungal proteins from Brassicaceae species. FEBS Lett 316:233–240
Terras FR, Eggermont K, Kovaleva V, Raikhel NV, Osborn RW, Kester A, Rees SB, Torrekens S, van Leuven F, Vanderleyden J (1995) Small cysteine-rich antifungal proteins from radish: their role in host defense. Plant Cell 7:573–588
Thevissen K, Ferket KK, Francois IE, Cammue BP (2003) Interactions of antifungal plant defensins with fungal membrane components. Peptides 24:1705–1712
Thevissen K, Warnecke DC, Francois IE, Leipelt M, Heinz E, Ott C, Zahringer U, Thomma BP, Ferket KK, Cammue BP (2004) Defensins from insects and plants interact with fungal glucosylceramides. J Biol Chem 279:3900–3905
Thomma BPHJ, Cammue BPA, Thevissen K (2002) Plant defensins. Planta 216:193–202
Van der Weerden NL, Lay FT, Anderson MA (2008) The plant defensin, NaD1, enters the cytoplasm of Fusarium oxysporum hyphae. J Biol Chem 283:14445–14452
Vijayan S, Guruprasad L, Kirti PB (2008) Prokaryotic expression of a constitutively expressed Tephrosia villosa defensin and its potent antifungal activity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 80:1023–1032
Wijaya R, Neumann GM, Condron R, Hughes AB, Poly GM (2000) Defense proteins from seed of Cassia fistula include a lipid transfer protein homologue and a protease inhibitory plant defensin. Plant Sci 159:243–255
Wilkins MR, Gasteiger E, Bairoch A, Sanchez JC, Williams KL, Appel RD, Hochstrasser DF (1999) Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol Biol 112:531–552
Wong JH, Xia L, Ng TB (2007) A review of defensins of diverse origins. Curr Protein Pept Sci 8:446–459
Xu H, Reddy ASN (1997) Cloning and expression of a PR5- like protein from Arabidopsis: inhibition of fungal growth by bacterially expressed protein. Plant Mol Biol 34:949–959
Zelicourt A, Letousey P, Thoiron S, Campion C, Simoneau P, Elmorjani K, Marion D, Simier P, Delavault P (2007) Ha-DEF1, a sunflower defensin, induces cell death in Orobanche parasitic plants. Planta 226:591–600
Zhang L, Falla TJ (2009) Host defense peptides for use as potential therapeutics. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 10:164–171
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a research grant from the Andhra Pradesh-Netherlands Biotechnology Program administered by the Institute of Public Enterprise, Osmania University Campus, Hyderabad. The authors thank the Head, Department of Plant Sciences for facilities provided by the UGC-SAP, DST-FIST, COSIST, etc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 426 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karri, V., Pulugurtha Bharadwaja, K. Tandem combination of Trigonella foenum-graecum defensin (Tfgd2) and Raphanus sativus antifungal protein (RsAFP2) generates a more potent antifungal protein. Funct Integr Genomics 13, 435–443 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-013-0334-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-013-0334-3