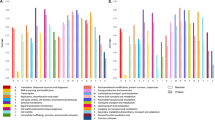
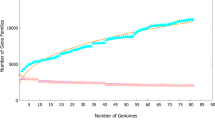
Abstract
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are among the most prevalent bacterial infections affecting people in inpatient and outpatient settings. The current study aimed to sequence the genome of uropathogenic Escherichia coli strain CUI-B1 resourced from a woman having uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis. Followed by deductive genomics towards potential drug targets using E. coli strain CUI-B1, strain O25b: H4-ST131, Proteus mirabilis strain HI4320, Klebsiella pneumoniae strain 1721, and Staphylococcus saprophyticus strain ATCC 15305 uropathogenic strains. Comparative genome analysis revealed that genes related to the survival of E. coli, P. mirabilis, K. pneumoniae, and S. saprophyticus, such as genes of metal-requiring proteins, defense-associated genes, and genes associated with general physiology, were found to be highly conserved in the genomes including strain CUI-B1. However, the genes responsible for virulence and drug resistance, mainly those that are involved in bacterial secretion, fimbriae, adherence, and colonization, were found in various genomic regions and varied from one species to another or within the same species. Based on the genome sequence, virulence, and antimicrobial-resistant gene dataset, the subtractive proteomics approach revealed 22 proteins mapped to the pathogen’s unique pathways and among them, entB, clbH, chuV, and ybtS were supposed to be potential drug targets and the single drug could be utilized for all above-mentioned strains. These results may provide the foundation for the optimal target for future discovery of drugs for E. coli-, P. mirabilis-, K. pneumoniae-, and S. saprophyticus-based infections and could be investigated further to employ in personalized drug development.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The 16s RNA sequence data was submitted to GenBank/DDBJ/ENA under accession no. OQ858381, while the Whole Genome Shotgun project has been deposited at DDBJ/ENA/GenBank under the accession JARWMK000000000. The version described in this paper is version JARWMK010000000.
References
Adamus-Bialek A, Zajac E, Parniewski P, Kaca W (2013) Comparison of antibiotic resistance patterns in collections of Escherichia coli and Proteus mirabilis uropathogenic strains. Mol Biol Rep 40:3429–3435
Alikhan NF, Petty NK, Ben Zakour NL et al (2011) BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): simple prokaryote genome comparisons. BMC Genomics 12:402
Cals JW, Ebell MH (2018) C-reactive protein: guiding antibiotic prescribing decisions at the point of care. Br J Gen Pract 668:112–113
Caza M, Kronstad JW (2013) Shared and distinct mechanisms of iron acquisition by bacterial and fungal pathogens of humans. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 19(3):80
Cepas V, Soto SM (2020) Relationship between virulence and resistance among Gram-negative bacteria. Antibiotics 9:719
Cornelis P, Dingemans J (2013) Pseudomonas aeruginosa adapts its iron uptake strategies in function of the type of infections. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 14(3):75
Daubin V, Moran NA, Ochman H (2003) Phylogenetics and the cohesion of bacterial genomes. Science 301:829–832
Ehsan N, Ahmad S, Navid A, Azam SS (2018) Identification of potential antibiotic targets in the proteome of multi-drug resistant Proteus mirabilis. Meta Gene 18:167–173
Feng A, Akter S, Leigh SA et al (2023) Genomic diversity, pathogenicity and antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli isolated from poultry in the southern United States. BMC Microbiol 23:15
Flores-Mireles A, Walker J, Caparon M et al (2015) Urinary tract infections: epidemiology, mechanisms of infection and treatment options. Nat Rev Microbiol 13:269–284
Gasteiger E et al (2005) Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In: Walker JM (ed) The proteomics protocols handbook. Springer Protocols Handbooks, Humana Press
Grant JR, Stothard P (2008) The CGView Server: a comparative genomics tool for circular genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 36:W181–W184
Hannan TJ, Totsika M, Mansfield KJ, Moore KH, Schembri MA, Hultgren SJ (2012) Host–pathogen checkpoints and population bottlenecks in persistent and intracellular uropathogenic Escherichia coli bladder infection. FEMS Microbiol Rev 3:616–648
Hatt J, Rather P (2008) Role of bacterial biofilms in urinary tract infections. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 322:163–192
Holt JG, Krieg NR, Sneath PH, Staley JT, Williams ST (1994) Bergey’s manual of determinate bacteriology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, Maryland, USA
Kahlmeter G (2003) An international survey of the antimicrobial susceptibility of pathogens from uncomplicated urinary tract infections: the ECO· SENS Project. J Antimicrob Chemother 51:69–76
Kathayat D, Lokesh D, Ranjit S, Rajashekara G (2021) Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC): an overview of virulence and pathogenesis factors, zoonotic potential, and control strategies. Pathogens 10:467
Kim J, Lee T, Kim TH (2012) An integrated approach of comparative genomics and heritability analysis of pig and human on obesity trait: evidence for candidate genes on human chromosome 2. BMC Genomics 13:711
Klein RD, Hultgren SJ (2020) Urinary tract infections: microbial pathogenesis, host–pathogen interactions and new treatment strategies. Nat Rev Microbiol 18:211–226
Knowles J, Gromo G (2003) Target selection in drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2:63–69
Kostakioti M, Hultgren SJ, Hadjifrangiskou M (2012) Molecular blueprint of uropathogenic Escherichia coli virulence provides clues toward the development of anti-virulence therapeutics. Virulence 3:592–594
Kurbasic A, Jakobsen L, Skjøt-Rasmussen L (2010) Escherichia coli isolates from broiler chicken meat, broiler chickens, pork, and pigs share phylogroups and antimicrobial resistance with community-dwelling humans and patients with urinary tract infect Kuskowski ion. Foodborne Pathog Dis 7:537–547
Meng-Ze D, Changjiang Z, Huan W, Shuo L, Wen W, Feng-Bia F (2018) The GC content as a main factor shaping the amino acid usage during bacterial evolution process. Front Microbiol 9:2948
Moriya Y, Itoh M, Okuda M, Yoshizawa AC, Kanehisa M (2007) KAAS: an automatic genome annotation and pathway reconstruction server. Nucleic Acids Res 35:182–185
Nairz M, Weiss G (2020) Iron in infection and immunity. Mol Asp Med 75:100864
Naz A, Awan FM, Obaid A, Muhammad SA, Paracha RZ, Ahmad J, Ali A (2015) Identification of putative vaccine candidates against Helicobacter pylori exploiting exoproteome and secretome: a reverse vaccinology-based approach. Infect Genet Evol 32:280–291
Ochman H, Lawrence JG, Groisman EA (2000) Lateral gene transfer and the nature of bacterial innovation. Nature 405:299–304
Paniagua-Contreras GL, Monroy-Pérez E, Díaz-Velásquez CE, Uribe-García A, Labastida A, Peñaloza-Figueroa F et al (2019) Whole-genome sequence analysis of multidrug-resistant uropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli from Mexico. Infect Drug Resist 12:2363–2377
Pelling H, Nzakizwanayo J, Milo S, Denham EL, MacFarlane WM, Bock LJ et al (2019) Bacterial biofilm formation on indwelling urethral catheters. Lett Appl Microbiol 68:277–293
Pessi G, Williams F, Hindle Z, Heurlier K, Holden MT, Cámara M, Haas D et al (2001) The global posttranscriptional regulator RsmA modulates production of virulence determinants and N-acylhomoserine lactones in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 184(335):6676–6683
Reygaert WC (2018) An overview of the antimicrobial resistance mechanisms of bacteria. AIMS Microbiol 4:482–501
Rihtar E, Žgur Bertok D, Podlesek Z (2020) The uropathogenic specific protein gene usp from Escherichia coli and Salmonella bongori is a novel member of the TyrR and H-NS regulons. Microorganisms 8:330
Sanober G, Ahmad S, Azam SS (2017) Identification of plausible drug targets by investigating the druggable genome of MDR Staphylococcus epidermidis. Gene Report 7:147–153
Saraf VS, Bhatti T, Javed S, Bokhari H (2022) Antimicrobial resistance pattern in E. coli isolated from placental tissues of pregnant women in low-socioeconomic setting of Pakistan. Curr Microbiol 79:83
Shaeriya F, Al Remawy R, Makhdoom A, Alghamdi A, Shaheen M, FA. (2021) Purple urine bag syndrome. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 32:530–531
Shah C, Baral R, Bartaula B et al (2019) Virulence factors of uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) and correlation with antimicrobial resistance. BMC Microbiol 19:204
Shruthi N, Kumar R, Kumar R (2012) Phenotypic study of virulence factors in Escherichia coli isolated from antenatal cases, catheterized patients, and faecal flora. J Clin Diagn Res 6:1699–1703
Smelov V, Naber K, Johansen TEB (2016) Improved classification of urinary tract infection: future considerations. Eur Urol Suppl 15:71–80
Solanki V, Tiwari V (2018) Subtractive proteomics to identify novel drug targets and reverse vaccinology for the development of chimeric vaccine against Acinetobacter baumannii. Sci Rep 8:9044
Srinivasan VB, Rajamohan G (2013) KpnEF, a new member of the Klebsiella pneumoniae cell envelope stress response regulon, is an SMR-type efflux pump involved in broad-spectrum antimicrobial resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 57(9):4449–4462
Stamm WE, Norrby SR (2001) Urinary tract infections: disease panorama and challenges. J Infect Dis 183:S1–S4
Stickler DJ (2008) Bacterial biofilms in patients with indwelling urinary catheters. Nat Clin Pract Urol 5:598–608
Subashchandrabose S, Hazen TH, Brumbaugh AR, Himpsl SD, Smith SN, Ernst RD, Rasko DA et al (2014) Host-specific induction of Escherichia coli fitness genes during human urinary tract infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111:18327–18332
Tabasi M, Asadi Karam MR, Habibi M, Yekaninejad MS, Bouzari S (2015) Phenotypic assays to determine virulence factors of uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolates and their correlation with antibiotic resistance pattern. Osong Public Health Res Perspect 6:261–268
Uddin R, Saeed K, Khan W, Azam SS, Wadood A (2015) Metabolic pathway analysis approach: identification of novel therapeutic target against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Gene 556:213–226
Yu NY, Wagner JR, Laird MR, Melli G et al (2010) PSORTb 3.0: improved protein subcellular localization prediction with refined localization subcategories and predictive capabilities for all prokaryotes. Bioinformatics 26:1608–1615
Funding
This research was funded by the Researchers Supporting Project number (RSP2023R332), King Saud University, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AA, RN, and AI collected samples, performed basics analysis, and wrote 1st relevant 1st draft. AH, WBA, AH, and IF performed and guided bioinformatics analysis. ZMZR wrote the “Discussion” section and proof reading. MI supervised whole work and drafted the manuscript for final submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Amin, A., Noureen, R., Iftikhar, A. et al. Uropathogenic bacteria and deductive genomics towards antimicrobial resistance, virulence, and potential drug targets. Int Microbiol 27, 325–335 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-023-00416-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-023-00416-3