Abstract
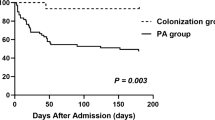
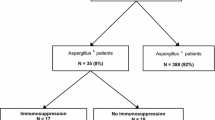
Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis (CPA) is associated with mortality in patients with Mycobacterium avium complex lung disease (MAC-LD). An Aspergillus-positive respiratory specimen often reflects colonization, and thus the clinical significance of Aspergillus isolation in MAC-LD patients is not well understood. The objective of this study was to investigate the clinical characteristics and outcomes of MAC-LD patients in whom Aspergillus was isolated from respiratory specimens. We performed a retrospective review of the medical records of 329 MAC-LD patients. We compared the characteristics and mortality rates between patients with Aspergillus isolation and those without. All Aspergillus species detected from respiratory specimens within the follow-up period were reviewed. Aspergillus was detected in 40 (12.2%) of the 329 patients. There were no significant differences in the clinical characteristics and mortality rates between patients with and without Aspergillus isolation. Among the 40 patients with Aspergillus isolation, 9 (22.5%) developed CPA. CPA was most often caused by A. fumigatus. In the 40 Aspergillus-positive patients, patients with A. fumigatus isolation had a significantly higher mortality rate than those without (P < 0.001). The multivariate Cox proportional hazards model showed older age (P = 0.050), presence of respiratory comorbidities (P = 0.008), hypoalbuminemia (P < 0.001), and isolation of A. fumigatus (P = 0.005) to be prognostic factors for mortality in MAC-LD patients. There was no significant difference in the mortality rates between patients with Aspergillus isolation and those without. However, isolation of A. fumigatus may be associated with poor prognosis in MAC-LD patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adjemian J, Olivier KN, Seitz AE, Holland SM, Prevots DR (2012) Prevalence of nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease in US Medicare beneficiaries. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 185:881–886
Prevots DR, Shaw PA, Strickland D, Jackson LA, Reabel MA, Blosky MA, Montes de Oca R, Shea YR, Seitz AE, Holland SM, Olivier KN (2010) Nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease prevalence at four integrated health care delivery systems. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 182:970–976
Wickremasinghe M, Ozerovitch LJ, Davies G, Wodehouse T, Chadwick MV, Abdallah S, Shah P, Wilson R (2005) Non-tuberculous mycobacteria in patients with bronchiectasis. Thorax 60:1045–1051
Angrill J, Agusti C, de Celis R, Rano A, Gonzalez J, Sole T, Xaubet A, Rodriguez-Roisin R, Torres A (2002) Bacterial colonisation in patients with bronchiectasis: microbiological pattern and risk factors. Thorax 57:15–19
Martinez-Garcia MA, Soler-Cataluna JJ, Perpina-Tordera M, Roman-Sanchez P, Soriano J (2007) Factors associated with lung function decline in adult patients with stable non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis. Chest 132:1565–1572
Park SJ, Mehrad B (2009) Innate immunity to Aspergillus species. Clin Microbiol Rev 22:535–551
Godet C, Philippe B, Laurent F, Cadranel J (2014) Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis: an update on diagnosis and treatment. Respiration 88:162–174
Smith NL, Denning DW (2011) Underlying conditions in chronic pulmonary aspergillosis including simple aspergilloma. Eur Respir J 37:865–872
Kobashi Y, Fukuda M, Yoshida K, Miyashita N, Niki Y, Oka M (2006) Chronic necrotizing pulmonary aspergillosis as a complication of pulmonary Mycobacterium avium complex disease. Respirology 11:809–813
Zoumot Z, Boutou AK, Gill S, van Zeller M, Hansell DM, Wells AU, Wilson R, Loebinger MR (2014) Mycobacterium avium complex infection in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis. Respirology 19:714–722
Takeda K, Imamura Y, Takazono T, Yoshida M, Ide S, Hirano K, Tashiro M, Saijo T, Kosai K, Morinaga Y, Nakamura S, Kurihara S, Tsukamoto M, Miyazaki T, Tashiro T, Kohno S, Yanagihara K, Izumikawa K (2016) The risk factors for developing of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis in nontuberculous mycobacteria patients and clinical characteristics and outcomes in chronic pulmonary aspergillosis patients coinfected with nontuberculous mycobacteria. Med Mycol 54:120–127
Khasawneh F, Mohamad T, Moughrabieh MK, Lai Z, Ager J, Soubani AO (2006) Isolation of Aspergillus in critically ill patients: a potential marker of poor outcome. J Crit Care 21:322–327
Shi Y, Liu HZ, Wang XT, Liu Y, Rui X, Tang B, Chai WZ, Zhao H (2009) The clinical significance of Aspergillus isolation from airway samples in critically ill patients. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi 32:444–449
Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, Catanzaro A, Daley C, Gordin F, Holland SM, Horsburgh R, Huitt G, Iademarco MF, Iseman M, Olivier K, Ruoss S, von Reyn CF, Wallace RJ Jr, Winthrop K, ATS Mycobacterial Diseases Subcommittee; American Thoracic Society; Infectious Disease Society of America (2007) An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 175:367–416
Hayashi M, Takayanagi N, Kanauchi T, Miyahara Y, Yanagisawa T, Sugita Y (2012) Prognostic factors of 634 HIV-negative patients with Mycobacterium avium complex lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 185:575–583
Furuuchi K, Ito A, Hashimoto T, Kumagai S, Ishida T (2017) Clinical significance of the radiological severity score in Mycobacterium avium complex lung disease patients. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 21:452–457
Denning DW, Cadranel J, Beigelman-Aubry C, Ader F, Chakrabarti A, Blot S, Ullmann AJ, Dimopoulos G, Lange C, European Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases and European Respiratory Society (2016) Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis: rationale and clinical guidelines for diagnosis and management. Eur Respir J 47:45–68
Kumagai S, Ito A, Hashimoto T, Marumo S, Tokumasu H, Kotani A, Yamaki H, Shirata M, Furuuchi K, Fukui M, Ishida T (2017) Development and validation of a prognostic scoring model for Mycobacterium avium complex lung disease: an observational cohort study. BMC Infect Dis 17:436
Kunst H, Wickremasinghe M, Wells A, Wilson R (2006) Nontuberculous mycobacterial disease and Aspergillus-related lung disease in bronchiectasis. Eur Respir J 28:352–357
Lowes D, Al-Shair K, Newton PJ, Morris J, Harris C, Rautemaa-Richardson R, Denning DW (2017) Predictors of mortality in chronic pulmonary aspergillosis. Eur Respir J 49:1601062
Soubani AO, Khanchandani G, Ahmed HP (2004) Clinical significance of lower respiratory tract Aspergillus culture in elderly hospitalized patients. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 23:491–494
Latgé JP (1999) Aspergillus fumigatus and aspergillosis. Clin Microbiol Rev 12:310–350
Dagenais TR, Keller NP (2009) Pathogenesis of Aspergillus fumigatus in invasive aspergillosis. Clin Microbiol Rev 22:447–465
Wasylnka JA, Moore MM (2000) Adhesion of Aspergillus species to extracellular matrix proteins: evidence for involvement of negatively charged carbohydrates on the conidial surface. Infect Immun 68:3377–3384
Tashiro T, Izumikawa K, Tashiro M, Takazono T, Morinaga Y, Yamamoto K, Imamura Y, Miyazaki T, Seki M, Kakeya H, Yamamoto Y, Yanagihara K, Yasuoka A, Kohno S (2011) Diagnostic significance of Aspergillus species isolated from respiratory samples in an adult pneumology ward. Med Mycol 49:581–587
Hector A, Kirn T, Ralhan A, Graepler-Mainka U, Berenbrinker S, Riethmueller J, Hogardt M, Wagner M, Pfleger A, Autenrieth I, Kappler M, Griese M, Eber E, Martus P, Hartl D (2016) Microbial colonization and lung function in adolescents with cystic fibrosis. J Cyst Fibros 15:340–349
Smith K, Rajendran R, Kerr S, Lappin DF, Mackay WG, Williams C, Ramage G (2015) Aspergillus fumigatus enhances elastase production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa co-cultures. Med Mycol 53:645–655
Funding
No financial support was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Tadashi Ishida has received honoraria from Pfizer Japan Inc. The other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furuuchi, K., Ito, A., Hashimoto, T. et al. Clinical significance of Aspergillus species isolated from respiratory specimens in patients with Mycobacterium avium complex lung disease. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 37, 91–98 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-017-3105-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-017-3105-6