Abstract
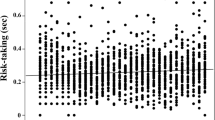
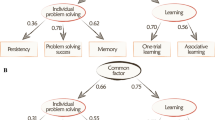
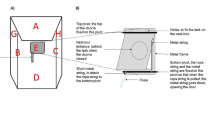
Innovation — the ability to solve problems in a novel way — is not only associated with cognitive abilities and relative brain size, but also by noncognitive traits, such as personality and motivation. We used a novel foraging task with three access options to determine how neophobia, exploration, and persistence influence innovation in 12 habituated bat-eared foxes (Otocyon megalotis) in the Kalahari Desert. Bat-eared foxes offer a unique system to understand cognition as they have the smallest relative brain size of measured canids and a specialized, termite-based diet, yet have displayed foraging innovations. Interestingly, most of our individuals solved the task at least once and six individuals solved the task in every trial. Neophobia did not influence success on the first trial, but both exploration and persistence influenced success across all trials. Those individuals that solved the puzzle over multiple trials became faster over time, suggesting that they learned how to open the box more efficiently. We found some variation in the method to open the puzzle box with six individuals solving the puzzle using two methods and one individual using all three methods. This is the first study to show innovation in a novel foraging task in wild bat-eared foxes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amici F, Widdig A, Lehmann J, Majolo B (2019) A meta-analysis of interindividual differences in innovation. Anim Behav 155:257–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2019.07.008
Benson-Amram S, Dantzer B, Stricker G et al (2016) Brain size predicts problem-solving ability in mammalian carnivores. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:2532. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1505913113
Benson-Amram S, Holekamp KE (2012) Innovative problem solving by wild spotted hyenas. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2012.1450
Benson-Amram S, Weldele ML, Holekamp KE (2013) A comparison of innovative problem-solving abilities between wild and captive spotted hyaenas, Crocuta crocuta. Anim Behav 85:349–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2012.11.003
Biondi LM, Bó MS, Vassallo AI (2010) Inter-individual and age differences in exploration, neophobia and problem-solving ability in a Neotropical raptor (Milvago chimango). Anim Cogn 13:701–710. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-010-0319-8
Boddy AM, McGowen MR, Sherwood CC et al (2012) Comparative analysis of encephalization in mammals reveals relaxed constraints on anthropoid primate and cetacean brain scaling. J Evol Biol 25:981–994. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1420-9101.2012.02491.x
Borrego N (2020) Socially tolerant lions (Panthera leo) solve a novel cooperative problem. Anim Cogn 23:327–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-019-01336-4
Borrego N, Gaines M (2016) Social carnivores outperform asocial carnivores on an innovative problem. Anim Behav 114:21–26
Chow PKY, Lea SEG, Leaver LA (2016) How practice makes perfect: the role of persistence, flexibility and learning in problem-solving efficiency. Anim Behav 112:273–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2015.11.014
Day RL, Coe RL, Kendal JR, Laland KN (2003) Neophilia, innovation and social learning: a study of intergeneric differences in callitrichid monkeys. Anim Behav 65:559–571. https://doi.org/10.1006/anbe.2003.2074
Ducatez S, Clavel J, Lefebvre L (2015) Ecological generalism and behavioural innovation in birds: technical intelligence or the simple incorporation of new foods? J Anim Ecol 84:79–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2656.12255
Ensminger AL, Westneat DF (2012) Individual and sex differences in habituation and neophobia in house sparrows (Passer domesticus). Ethology 118:1085–1095. https://doi.org/10.1111/eth.12009
Forss SIF, Motes-Rodrigo A, Dongre P et al (2022) Captivity and habituation to humans raise curiosity in vervet monkeys. Anim Cogn 25:671–682. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-021-01589-y
Fristoe TS, Iwaniuk AN, Botero CA (2017) Big brains stabilize populations and facilitate colonization of variable habitats in birds. Nat Ecol Evol 1:1706–1715
Greenberg RS (2003) The role of neophobia and neophilia in the development of innovative behaviour of birds. Animal innovation. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 175–196
Greggor AL, Thornton A, Clayton NS (2015) Neophobia is not only avoidance: improving neophobia tests by combining cognition and ecology. Curr Opin Behav Sci 6:82–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cobeha.2015.10.007
Griffin AS, Diquelou M, Perea M (2014) Innovative problem solving in birds: a key role of motor diversity. Anim Behav 92:221–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2014.04.009
Griffin AS, Guez D (2014) Innovation and problem solving: a review of common mechanisms. Behav Processes 109 Part B:121–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beproc.2014.08.027
Halekoh U, Højsgaard S, Yan J (2006) The R package geepack for generalized estimating equations. J Stat Softw 15:1–11
Huebner F, Fichtel C (2015) Innovation and behavioral flexibility in wild redfronted lemurs (Eulemur rufifrons). Anim Cogn 18:777–787. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-015-0844-6
Jacobs PJ, le Roux A (2016) First report of a myrmecophagous bat-eared fox (Otocyon megalotis) hunting a hare (Lepus sp.). Afr J Ecol 54:128–130. https://doi.org/10.1111/aje.12259
Jacobson SL, Puitiza A, Snyder RJ et al (2021) Persistence is key: investigating innovative problem solving by Asian elephants using a novel multi-access box. Anim Cogn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-021-01576-3
Johnson-Ulrich L, Johnson-Ulrich Z, Holekamp K (2018) Proactive behavior, but not inhibitory control, predicts repeated innovation by spotted hyenas tested with a multi-access box. Anim Cogn 21:379–392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-018-1174-2
Johnson-Ulrich L, Yirga G, Strong RL, Holekamp KE (2021) The effect of urbanization on innovation in spotted hyenas. Anim Cogn 24:1027–1038. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-021-01494-4
Jumbam KR, Périquet S, Dalerum F, le Roux A (2019) Spatial and temporal variation in the use of supplementary food in an obligate termite specialist, the bat-eared fox. Afr Zool 54:63–71. https://doi.org/10.1080/15627020.2019.1596754
Lamprecht J (1979) Field observations on the behaviour and social system of the bat-eared fox Otocyon megalotis Desmarest. Ethology 49:260–284
Lefebvre L, Gaxiola A, Dawson S et al (1998) Feeding innovations and forebrain size in Australasian birds. Behaviour 135:1077–1097. https://doi.org/10.1163/156853998792913492
Lefebvre L, Reader SM, Sol D (2004) Brains, innovations and evolution in birds and primates. Brain Behav Evol 63:233–246
Lefebvre L, Whittle P, Lascaris E, Finkelstein A (1997) Feeding innovations and forebrain size in birds. Anim Behav 53:549–560
Lermite F, Peneaux C, Griffin AS (2017) Personality and problem-solving in common mynas (Acridotheres tristis). Behav Processes 134:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beproc.2016.09.013
Maas B, Macdonald DW (2004) Bat-eared foxes. Biology and conservation of wild canids. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 227–242
MacLean EL, Hare B, Nunn CL et al (2014) The evolution of self-control. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:E2140. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1323533111
Manrique HM, Völter CJ, Call J (2013) Repeated innovation in great apes. Anim Behav 85:195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2012.10.026
Morand-Ferron J, Cole EF, Rawles JEC, Quinn JL (2011) Who are the innovators? A field experiment with 2 passerine species. Behav Ecol 22:1241–1248. https://doi.org/10.1093/beheco/arr120
Morand-Ferron J, Quinn JL (2011) Larger groups of passerines are more efficient problem solvers in the wild. Proc Natl Acad Sc 108:15898–15903
O’Connor VL, Thomas P, Chodorow M, Borrego N (2022) Exploring innovative problem-solving in African lions (Panthera leo) and snow leopards (Panthera uncia). Behav Processes 199:104648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beproc.2022.104648
Overington SE, Griffin AS, Sol D, Lefebvre L (2011) Are innovative species ecological generalists? A test in North American birds. Behav Ecol 22:1286–1293
Overington SE, Morand-Ferron J, Boogert NJ, Lefebvre L (2009) Technical innovations drive the relationship between innovativeness and residual brain size in birds. Anim Behav 78:1001–1010
Pekár S, Brabec M (2018) Generalized estimating equations: a pragmatic and flexible approach to the marginal GLM modelling of correlated data in the behavioural sciences. Ethology 124:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1111/eth.12713
Perry SE, Barrett BJ, Godoy I (2017) Older, sociable capuchins (Cebus capucinus) invent more social behaviors, but younger monkeys innovate more in other contexts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:7806. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1620739114
Prasher S, Evans JC, Thompson MJ, Morand-Ferron J (2019) Characterizing innovators: ecological and individual predictors of problem-solving performance. PLoS ONE 14:e0217464. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0217464
Quinn JL, Cole EF, Reed TE, Morand-Ferron J (2016) Environmental and genetic determinants of innovativeness in a natural population of birds. Phil Trans R Soc B 371:20150184
Ramsey G, Bastian ML, van Schaik C (2007) On the concept of animal innovation and the challenge of studying innovation in the wild. Behav Brain Sci 30:425–432. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0140525X07002567
Reader SM, Laland KN (2002) Social intelligence, innovation, and enhanced brain size in primates. PNAS 99:4436–4441. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.062041299
Reader SM, Morand-Ferron J, Flynn E (2016) Animal and human innovation: novel problems and novel solutions. Phil Trans R Soc B 371:20150182
Réale D, Reader SM, Sol D et al (2007) Integrating animal temperament within ecology and evolution. Bioll Rev 82:291–318
Rössler T, Mioduszewska B, O’Hara M et al (2020) Using an innovation arena to compare wild-caught and laboratory Goffin’s cockatoos. Sci Rep 10:8681. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-65223-6
Sol D, Griffin AS, Bartomeus I (2012) Consumer and motor innovation in the common myna: the role of motivation and emotional responses. Anim Behav 83:179–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2011.10.024
Thornton A, Samson J (2012) Innovative problem solving in wild meerkats. Anim Behav 83:1459–1468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2012.03.018
Timmermans S, Lefebvre L, Boire D, Basu P (2000) Relative size of the hyperstriatum ventrale is the best predictor of feeding innovation rate in birds. BBE 56:196–203. https://doi.org/10.1159/000047204
van Horik JO, Madden JR (2016) A problem with problem solving: motivational traits, but not cognition, predict success on novel operant foraging tasks. Anim Behav 114:189–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2016.02.006
Webster SJ, Lefebvre L (2001) Problem solving and neophobia in a columbiform–passeriform assemblage in Barbados. Anim Behav 62:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1006/anbe.2000.1725
Welch RJ, le Roux A, Petelle MB, Périquet S (2018) The influence of environmental and social factors on high- and low-cost vigilance in bat-eared foxes. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 72:29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00265-017-2433-y
Williams DM, Wu C, Blumstein DT (2021) Social position indirectly influences the traits yellow-bellied marmots use to solve problems. Anim Cogn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-020-01464-2
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank two anonymous reviewers and Dr. Pizza Chow for their constructive feedback on previous versions of this manuscript. This article is funded by National Research Foundation (Grant no. TTK1206041007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Petelle, M.B., Jacobs, P.J. & le Roux, A. Innovative problem-solving in a small, wild canid. Anim Cogn 26, 405–413 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-022-01678-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-022-01678-6