Abstract
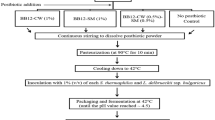
Rice cake, songpyeon, is a commonly consumed snack food in Korea. Currently, the recommended shelf life of rice cakes is only 1 day at room temperature because of concerns over quality deterioration and microbial safety. In this study, retort sterilization for 15 to 19 min was used to produce microbiologically safe songpyeon, and quality characteristics were analyzed. Sterilization of songpyeon at 121°C for 15 min resulted in complete eradication of Bacillus cereus and B. subtilis. Total plate count, yeast, fungi, and coliform counts were below detection. With increasing sterilization time, the average L* and a* values of songpyeon decreased from 28.86 to 23.07 and −1.63 to −6.73, respectively, whereas the b* value tended to increase from 4.91 to 9.82 on average, showing low lightness and high yellowness. Texture analysis showed increased gumminess (1240.6 to 2469.63 g) and decreased chewiness (2283.94 to 1366.26 g) and hardness (2933.94 to 1616.26 g) in songpyeon with increasing sterilization time. According to sensory evaluation, songpyeon sterilized at 121°C for 17 min was preferred by sensory panels based on average appearance (7.65), color (7.15), taste (7.45), and overall acceptance (7.4) scores. Therefore, sterilization at 121°C for 17 min is suggested to be optimal for producing microbiologically safe songpyeon with the best quality characteristics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cha HM, Han G, Chung HJ. A study on the trend analysis regarding the rice consumption of Korean adults using Korean national health and nutrition examination survey data from 1988, 2001 and 2005. Nutr. Res. Pract. 6: 254–262 (2012)
Lee H, Byun SM, Kim HS. Studies on the dietary fiber of brown rice and milled rice. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 20: 576–571 (1988)
Um MY, Ahh J, Jung CH, Ha TY. Cholesterol-lowering effect of rice protein by enhancing fecal excretion of lipids in rats. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 18: 210–213 (2013)
Kim GY, Kang JY, Lee IS, Lee HY. Quality characteristics of cookies with various levels of functional rice flour. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 34: 642–646 (2002)
Kim SJ, Ma SJ, Kim HJ, Kim SJ. Preparation and quality characteristics of rice breads. J. Korean Soc. Food Cult. 20: 433–437 (2005)
Yong Y, Tao WY, Liu YJ, Zhu F. Inhibition of Bacillus cereus by lactic acid bacteria starter cultures in rice fermentation. Food Control 19: 159–161 (2008)
Choi SY, Jeong SH, Jeong MS, Park KH, Jeong YG, Cho JI, Lee SH, Hwang IG, Bahk GJ, Oh DH, Chung HS, Ha SD. A monitoring for the management of microbiological hazard in rice-cake by climate change. J. Food Hyg. Safety 27: 301–305 (2012)
Koh BK. Development of the method to extend shelf life of Backsulgie with enzyme treatment. Korean J. Soc. Food Sci. 15: 533–538 (1999)
Oh MH, Shin HC, Park JD, Lee HY, Kim KS, Kum JS. Effect of added trehalose and enzyme on the qualities of Backsulgie. J. Korea Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 39: 992–998 (2010)
Yim KY, Kim SH. A survey on the utilization of Korean rice-cakes and the evaluation about their commercial products by housewives. J. Korean Soc. Food Cult. 3: 163–175 (1988)
Lee SY, Chung HJ, Shin JH, Dougherty RH, Kang DH. Survival and growth of food borne pathogens during cooking and storage of oriental-style rice cakes. J. Food Protect. 69: 3037–3042 (2006)
Jaquette CB, Beuchat LR. Combined effects of pH, nisin and temperature on growth and survival of psychrotrophic Bacillus cereus. J. Food Protect. 61: 563–570 (1998)
Granum PE, Lund, T. Bacillus cereus and its food poisoning toxins. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 157: 223–228 (1997)
Kim SH, Kim JS, Choi JP, Park JH. Prevalence and frequency of foodborne pathogens on unprocessed agricultural and marine products. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 38: 594–598 (2006)
Hyang IG, Lee SH, Cho JI, Choi SY, Jeong SH. Microbiological contamination levels in the processing of Korea rice cakes. J. Food Hyg. Safety 27: 161–168 (2012)
Woo KJ, Jung EJ. Quality characteristics of Chalduk according to the soaking time of glutinous rice in water. J. East Asian Soc. Diet. Life. 16: 677–683 (2006)
Yoon SJ. Quality characteristics of retort Tteok (Korean Rice Cake) prepared with various dextrinization time. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 39: 260–265 (2007)
Byun Y, Bae HJ, Cooksey K, Whiteside S. Comparison of the quality and storage stability of salmon packaged in various retort pouches. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 43: 551–555 (2009)
Bindu J, Ravishankar CN, Srinivasa Gopal TK. Shelf life evaluation of a ready-toeat black clam (Villorita cyprinoides) product in indigenous retort pouches. J. Food Eng. 78: 995–1000 (2007)
Srinivasa Gopal T K, Vijayan P K, Balachandran K K, Madhavan P, Lyer TSG. Traditional Kerala style fish curry in indigenous retort pouch. Food Control 12: 523–527 (2001)
Chandrasekar V, Rai RD, Gopal TKS, Verma RN. Preparation and storage of mushroom curry in retort pouches. Mushroom Res. 10: 103–107 (2001)
Food and Drug Administration. Microbiological Method & Bacteriological Analytical Manual. Available from http://www.fda.gov. Accessed Dec. 15, 2015.
AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC Intl. 18th ed. Method 934.01. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Gaithersburg, MD, USA (2005)
Meilgaard M, Varr BT, Civille GB. Sensory evaluation techniques. CRC Press Inc., Boca Raton, FL, USA. pp. 39–112 (1987)
Ha DS, Kim DH, Jo BC, Jeong YG, Ha JH, Jeong SH. Estimation of shelf-life of commercially sterilized fried rice containing meat. J. Food Hyg. Safety 26: 209–213 (2011)
Lee HS, Jang MS. Microbiological hazard evaluation of the product flow of Korean rice cakes. Korean J. Food Cook Sci. 22: 747–755 (2006)
Jeon JH, Park JH. Toxin Gene Analysis of Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis isolated from Cooked Rice. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 42: 361–367 (2010)
Lee SY, Gwon SY, Kim SJ, Moon BK. Inhibitory effect of commercial green tea and rosemary leaf powders on the growth of foodborne pathogens in laboratory media and oriental-style rice cakes. J. Food Protect. 72: 1107–1111 (2009)
Ji Y, Zhu KX, Qian HF, Zhou HM. Microbiological characteristics of cake prepared from rice flour and sticky rice flour. Food Control 18: 1507–1511 (2007)
Oh MH, Kim KJ. Effect of process rice flour on the sensory and mechanical characteristic of Backsulgi by storage time and temperature. Korean J. Food Cook Sci. 19: 34–45 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JH., Chung, HJ., Choi, S.H. et al. Effect of retort sterilization on microbial safety and quality characteristics of a rice cake, songpyeon . Food Sci Biotechnol 25, 1047–1052 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-016-0169-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-016-0169-5