Abstract
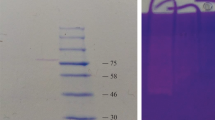
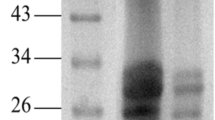
Skatole, a substance with an unpleasant flavor, is released from the cecum and colon of entire male pigs. In this study, a novel skatole-degrading protease from the fermentation broth of Lactobacillus brevis 1.12 was extracted and purified through (NH4)2SO4 precipitation and chromatography with DEAE-Sephadex A-25 and Sephadex G-75. The purified protease was found to be homogeneous in terms of SDS-PAGE and had a molecular mass estimate of 57.5 kDa. This skatole-degrading protease had an optimal pH of 5.0 and optimal temperature of 35°C. The enzyme was only inhibited greatly at a 10 mmol 1/L concentration of K+. The results suggest that the novel skatole-degrading protease was purified. The biochemical characteristics of this protease can provide useful information for its potential use in industrial applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Font Furnols M, Gispert M, Guerrero L, Velarde A, Tibau J, Soler J, Hortós M, García-Regueiro JA, Pérez J, Suárez P, Oliver MA. Consumers’ sensory acceptability of pork from immunocastrated male pigs. Meat Sci. 80: 1013–1018 (2008)
Pauly C, Spring-Staehli P, O’Doherty JV, Kragten SA, Dubois S, Messadène J, Bee G. The effects of method of castration, rearing condition and diet on sensory quality of pork assessed by a trained panel. Meat Sci. 86: 498–504 (2010)
Xue JL, Dial GD, Pettigrew JE. Performance, carcass, and meat quality advantages of boars over barrows: A literature review. J. Swine Health Prod. 5: 21–28 (1997)
Jensen MT, Cox RP, Jensen BB. 3-Methylindole (skatole) and indole production by mixed populations of pig fecal bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61: 3180–3184 (1995)
Yokoyama MT, Carlson JR. Microbial metabolites of tryptophan in the intestinal tract with special reference to skatole. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 32: 173–178 (1979)
Hansen MJ, Kjeldsen N. Introduction to Danish research on boar taint. pp. 13–20. In: Skatole and Boar Taint. Jensen WK (ed). Roskilde, Denmark (1998)
Udesen F. Financial consequences of production of entire male pigs. pp. 195–202. In: Skatole and Boar Taint. Jensen WK (ed). Roskilde, Denmark (1998)
Lunde K, Skuterud E, Hersleth M, Egelandsdal B. Norwegian consumers’ acceptability of boar tainted meat with different levels of androstenone or skatole as related to their androstenone sensitivity. Meat Sci. 86: 706–711 (2010)
von Borell E, Baumgartner J, Giersing M, Jäggin N, Prunier A, Tuyttens FA, Edwards SA. Animal welfare implications of surgical castration and its alternatives in pigs. Animal 3:1488–1496 (2009)
Robic A, Larzul C, Bonneau M. Genetic and metabolic aspects of androstenone and skatole deposition in pig adipose tissue: A review. EDP Sci. 40: 129–143 (2008)
Bonneau M, Dufour R, Chouvet C, Roulet C, Meadus W, Squires EJ. The effects of immunization against luteinizing hormonereleasing hormone on performance, sexual development, and levels of boar taint-related compounds in intact male pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 72: 14–20 (1994)
Jaros P, Bqrgi E, Stärk KDC, Claus R, Hennessy D, Thuna R. Effect of active immunization against GnRH on androstenone concentration, growth performance and carcass quality in intact male pigs. Livest. Prod. Sci. 9: 231–238 (2005)
Lunde K, Egelandsdal B, Choinski J, Mielnik M, Flåtten A, Kubberød E. Marinating as a technology to shift sensory thresholds in ready-to-eat entire male pork meat. Meat Sci. 80: 1264–1272 (2008)
Stolzenbach S, Lindahl G, Lundström K, Chen G, Byrne DV. Perceptual masking of boar taint in Swedish fermented sausages. Meat Sci. 81: 580–588 (2009)
Hansen LL, Mejer H, Thamsborg SM, Byrne DV, Roepstorff A, Karlsson AH, Hansen-Møller J, Jensen MT, Tuomola M. Inuence of chicory roots (Cichorium intybus L) on boar taint in entire male and female pigs. Anim. Sci. 82: 359–368 (2006)
Li P. Molecular biology of organic pollutants anaerobic bioremoval in swine wastewater. PhD thesis, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, China (2009)
Yin B, Huang L, Gu JD. Bioremoval of 1-methylindole and 3-methylindole by mangrove sediment enrichment incubations and a pure incubation of an isolated pseudomonas aeruginosa Gs. Water Air Soil Poll. 176: 185–199 (2006)
Gu J, Fan Y, Shi H. Relationship between structures of substituted indolic compounds and their removal by marine an anaerobic microorganisms. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 45: 379–384 (2002)
Xu CJ, Li CYT, Kong ANT. Induction of phase I, II and III drug metabolism/transport by xenobiotics. Arch. Pharm. Res. 28: 249–268 (2005)
Zamaratskaia G, Squires EJ. Biochemical, nutritional and genetic effects on boar taint in entire male pigs. Animal 3:1508–1521 (2009)
Matal J, Matuskova Z, Tunkova A, Anzenbacherova E, Anzenbacher P. Porcine CYP2A19, CYP2E1 and CYP1A2 forms are responsible for skatole biotransformation in the reconstituted system. Neuroendocrinol. Lett. 30: 36–40 (2009)
Diaz GJ, Squires EJ. Metabolism of 3-methylindole by procine liver microsomes: responsible cytochrome P450 enzymes. Toxicol. Sci. 55: 284–292 (2000)
Squires EJ, Lundström K. Relationship between cytochrome P4502E1 in liver and levels of skatole and its metabolites in intact male pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 75: 2506–2511 (1997)
Chen G, Zamaratskaia G, Andersson HK, Lundstrström K. Effects of raw potato starch and live weight on fat and plasma skatole, indole and androstenone levels measured by different methods in entire male pigs. Food Chem. 101: 439–448 (2007)
Rasmussena MK, Bruniusb C, Zamaratskaiab G, Ekstrand B. Feeding dried chicory root to pigs decrease androstenone accumulation in fat by increasing hepatic 3-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase expression. J. Steroid Biochem. 130: 90–95 (2012)
Park JP, Oh TK, Yun JW. Purication and characterization of a novel transfructosylating enzyme from Bacillus macerans EG-6. Process Biochem. 37: 471–476 (2001)
Ju XY, Cao XY, Sun Y, Wang Z, Cao CL, Liu JJ, Jiang JH. Purication and characterization of a brinolytic enzyme from Streptomyces sp. XZNUM 00004. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 28: 2479–2486 (2012)
Yegin S, Goksungur Y, Fernandez-Lahore M. Purication, structural characterization, and technological properties of an aspartyl proteinase from submerged cultures of Mucor mucedo DSM 809. Food Chem. 133: 1312–1319 (2012)
Sarath G, De La Motte RS, Wagner FW. Proteolytic enzymes: Apractical approach. Vol. 1, pp. 25–55. In: Peptidase Assay Methods. Beynon RJ, Bond JS (eds). Oxford University Press, New York, NY, USA (1989)
Lee SK, Hwang JY, Choi SH, Kim SM. Purification and characterization of Aspergillus oryzae LK-101 salt-tolerant acid protease isolated from soybean paste. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 19: 327–334 (2010)
Wu YY, Wang P, Li LH, Yang XQ, Diao SH. Purification and characteristics of serine protease from the head of Pacific white shrimp. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 21: 1129–1134 (2012)
Bradford MM. Rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–253 (1976)
Abidi F, Chobertb JM, Haertléb T, Marzouki MN. Purication and biochemical characterization of stable alkaline protease Prot-2 from Botrytis cinerea. Process Biochem. 46: 2301–2310 (2011)
Ogbonna AC, Okolo BN. Purication and some properties of a metalloprotease from sorghum malt variety KSV8-1. World J. Microb. Biot. 21: 1051–1056 (2005)
Sadana R, Mittal A, Khurana S, Singh H, Kamboj RC. Purification and characterization L-like proteinase from goat brain. India J. Biochem. Bio. 40: 315–323 (2003)
Sun LM, Zhu BW, Wu HT, Yu L, Zhou DY, Dong XP, Yang JF, Li DM, Ye WX, Murata Y. Purification and Characterization of Cathepsin B from the Gut of the Sea Cucumber (Stichopus japonicas). Food Sci. Biotechnol. 20: 919–925 (2011)
Kim MS, Park MJ, Jeong YH. Purification and Characterization of Lysozyme from Filipino venus, Ruditapes philippinarum. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 21: 1463–1468 (2012)
Li CH, Ni DJ, Song LH, Zhao JM, Zhang H, Li L. Molecular cloning and characterization of a catalase gene from Zhikong scallop Chlamys farreri. Fish Shellsh Immunol. 24: 26–34 (2008)
Rao SB, Mizutani O, Hirano T, Masaki K, Iefuji H. Purification and characterization of a novel aspartic protease from basidiomycetous yeast Cryptococcus sp. S-2. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 112: 441–446 (2011)
Kim JS, Kim JE, Choi BS, Park SE, SApkota K, Kim S, Lee HH, Kim CS, Park Y, Kim MK, Kim YS, Kim SJ. Purication and characterization of brinolytic metalloprotease from Perenniporia fraxinea mycelia. Mycol. Res. 112: 990–998 (2008)
Fu XY, Xue CH, Miao BC, Li ZJ, Gao X, Yang WG. Characterization of proteases from the digestive tract of sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicus): High alkaline protease activity. Aquaculture 246: 321–329 (2005)
Li Y, Liang S, Zhi DJ, Chen P, Sua F, Li HY. Purication and characterization of Bacillus subtilis milk-clotting enzyme from Tibet Plateau and its potential use in yak dairy industry. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 234: 733–741 (2012)
Li GY, Cai YJ, Liao XR, Yin J. A novel nonionic surfactant- and solvent-stable alkaline serine protease from Serratia sp. SYBC H with duckweed as nitrogen source: production, purification, characteristics and application. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 38: 845–853 (2011)
Choudhury R, Bhaumik SK, De T, Chakraborti T. Identication, purication, and characterization of a secretory serine protease in an Indian strain of Leishmania donovani. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 320: 1–14 (2009)
Chung DM, Choi NS, Maeng PJ, Chun HK, Kim SH. Purification and characterization of a novel fibrinolytic enzyme from chive (Allium tuberosum). Food Sci. Biotechnol. 19: 697–702 (2011)
Manikandan M, Pasic L, Kannan V. Purication and biological characterization of a halophilic thermostable protease from Haloferax lucentensis VKMM 007. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 25: 2247–2256 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, X., He, Z.F. & Li, H.J. Purification and characterization of a novel skatole-degrading protease from Lactobacillus brevis 1.12. Food Sci Biotechnol 22, 1–7 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-013-0224-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-013-0224-4