Abstract
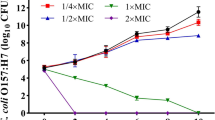
Flavonoids have biofunctional effects as antioxidant and antimicrobial agents. The objective of this study was to evaluate the bactericidal activity and antilipopolysaccharide (LPS) effects of flavonoids on Escherichia coli O157:H7. The effects of flavonoids on the growth of E. coli O157:H7 were bacteriostatic rather than bactericidal at concentrations below 200 μM, and there was no significant difference among the flavonoids tested (p<0.05). LPS production in E. coli O157:H7 treated with 200 μM quercetin and naringenin decreased by 34.06±1.03 and 19.90±1.51%, respectively, relative to the control (no flavonoid). Luteolin, genkwanin, hesperetin, and apigenin caused decreases in LPS production of 69.85±1.03, 61.18±1.15, 60.74±1.10, and 58.93±0.98%, respectively, relative to the control. Based on these results, luteolin had the greater inhibitory effect on LPS production by E. coli O157:H7 than other flavonoids tested in this study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calderwood SB, Acheson DWK, Keusch GT, Barrett TJ, Griffin PM, Stockbine NA, Swaminathan B, Kaper JB, Levine MM, Kaplan BS, Karch H, O’Brien AD, Obrig TG, Takeda Y, Tarr PI, Wachsmuth IK. Proposed new nomenclature for SLT (VT) family. ASM News 62: 118–119 (1996)
Swain P, Nayak SK, Nanda PK, Dash S. Biological effects of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin) in fish: A review. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 25: 191–201 (2008)
Terplan VG, Zaadhof KJ, Buchholz-Berchtold S. Detection of endotoxins of Gram-negative microorganisms in milk by the Limulus test. Arch. Lebensmittelhyg. 26: 217–221 (1975)
Sullivan JD, Ellis JPC, Lee RG, Combs WS, Watson SW. Comparison of the Limulus amoebocytes lysate test with plate counts and chemical analyses for assessment of the quality of the lean fish. Appl. Environ. Microb. 42: 720–722 (1983)
Jay JM. Rapid estimation of microbial numbers in fresh ground beef by use of the Limulus test. J. Food Protect. 44: 275–278 (1981)
Waehtel RE, Tsuji K. Comparison of Limulus amebocyte lysates and correlation with the United States pharmacopeial pyrogen test. Appl. Environ. Microb. 33: 1265–1269 (1977)
Becker RAB, Martinellia AHS, Mitidierib S, Federa V, Wassermanna GE, Santia L, Vainsteina MH, Oliveirad JTA, Fiuzae LM, Pasqualia G, Carlinia CR. Antifungal activity of plant and bacterial ureases. Toxicon 50: 971–983 (2007)
Fariba S, Gholamreza DN, Mansour M. Major flavonoids with antioxidant activity from Teucrium polium L. Food Chem. 112: 885–888 (2009)
Giulia DC, Nicola M, Angelo AI, Francesco C. Flavonoids: Old and new aspects of a class of natural therapeutic drugs. Life Sci. 65: 337–353 (1999)
Shina SY, Bajpaia VK, Kim HR, Kang SC. Antibacterial activity of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) against food borne and food spoilage microorganisms. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 40: 1515–1519 (2007)
Teresita G, Alejandra ER, Américo OJ, Lilian EP. Antiinflammatory properties of plant flavonoids: Effects of rutin, quercetin, and hesperidin on adjuvant arthritis in rat. Farmaco 56: 683–687 (2001)
Ying S, Ning F, David DYC, Kingsley KD. Determination of potentially anti-carcinogenic flavonoids in wines by micellar electrokinetic chromatography. Food Chem. 106: 415–420 (2008)
Song JH, Kim SK, Chang KW, Han SK, Yi HK, Jeon JG. In vitro inhibitory effects of Polygonum cuspidatum on bacterial viability and virulence factors of Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sobrinus. Arch. Oral Biol. 51: 1131–1140 (2006)
Zdzislawa N. A review of anti-infective and anti-inflammatory chalcones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 42: 125–137 (2007)
Ríos JL, Recio MC. Medicinal plants and antimicrobial activity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 100: 80–84 (2005)
Maria J, Rodriguez V, Maria R, Manca N. Influence of phenolic compounds from wines on the growth of Listeria monocytogenes. Food Control 18: 587–593 (2007)
Tim CTP, Lamb AJ. Antimicrobial activity of flavonoids. Int. J. Antimicrob. Ag. 26: 343–356 (2005)
Yun NR, Jeong IY, Lee YN, Lim YJ. Antibacterial activity of chitosan acetate on bacteria associated with food-borne disease. J. Chitin Chitosan 13: 30–35 (2008)
Bang W, Hanson DJ, Drake MA. Effect of salt and sodium nitrite on growth and enterotoxin production of Staphylococcus aureus during the production of air-dried fresh pork sausage. J. Food Protect. 71: 191–195 (2008)
Obata T, Nomura M, Kase Y, Sasaki H, Shirasawa Y. Early detection of the Limulus amebocyte lysate reaction evoked by endotoxins. Anal. Biochem. 373: 281–286 (2008)
Conti M, Mastromarino P, Sorgro R, Desideri N. Anti-picornavirus activity of synthetic flavon-3-yl esters. J. Antiviral Chem. Chemother. 9: 511–515 (1998)
Stojanovic G, Radulovic N, Hashimoto T, Palic R. Antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activity of four known and one new triterpenoid from Combretum imberbe (Combretaceae). J. Ethnopharmacol. 101: 185–190 (2005)
Jirawan OA, Suzukib T, Gasaluck P, Eumkeb GS. Antimicrobial properties and action of galangal (Alpinia galanga Linn.) on Staphylococcus aureus. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 39: 1214–1220 (2006)
Kim KT, Moon SH, Yeo EJ, Han YS, Nah SY, Paik H-D. Inhibitory effect of 7-O-butyl naringenin on growth of Helicobacter pylori ATCC 26695. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 15: 466–468 (2006)
Osman U, Berrin O, Yakut A, Ufuk A, Erdem Y. Flavonoids with anti-Helicobacter pylori activity from Cistus laurifolius leaves. J. Ethnopharmacol. 108: 457–461 (2006)
Nahum YS, Sharon E, Ilan R. Mammary pathogenic Escherichia coli. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 11: 60–65 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, KA., Moon, S.H., Kim, KT. et al. Antimicrobial effects of various flavonoids on Escherichia coli O157:H7 cell growth and lipopolysaccharide production. Food Sci Biotechnol 19, 257–261 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-010-0037-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-010-0037-7