Abstract
Objectives
This study was conducted to investigate the prevalence of vertebral fracture (VF) and its risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) as compared to healthy individuals, and to explore the underlying risk factors.
Methods
The electronic databases of PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library were applied to search for the relevant literatures, which reported the prevalence of VF in both RA patients and healthy controls (up to Mar 31, 2021). The non-weighted prevalence of VF, pooled estimates of odds ratio (OR), and its 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated with the use of random-effects model; between-study heterogeneity was evaluated by Cochrane Q statistic, then was quantified with I2. Publication bias was evaluated using Egger’s linear regression test.
Results
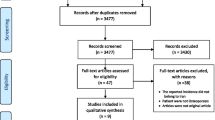
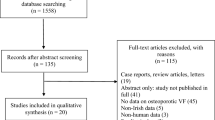
A number of 867 literatures were identified after searching for online databases, based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 11 eligible studies, which comprising 3805 RA patients and 59,517 healthy participants, were finally incorporated in meta-analysis. The results showed that RA patients had an increased prevalence of VF (20.29 vs 8.63%), and an elevated risk for VF (OR = 3.04, 95% CI 1.97–4.71) as compared to healthy population. Additional subgroup analysis suggested that age, body mass index (BMI), disease activity, and drug therapy might be associated with risk of VF in RA.
Conclusions
Overall, our study demonstrated an increased risk of VF in patients with RA, suggesting that age, race, BMI, disease activity, and drug therapy may be represented as risk factors contributing to the occurrence of VF in RA.
Key Points • RA patients had the increased prevalence and risk of vertebral fracture (VF) as compared to healthy population. • Age, race, BMI, disease activity, and drug therapy might be associated with VF in RA. • Our findings would be helpful for the early evaluation of RA patients with high VF risk. |




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Singh JA, Saag KG, Bridges SL Jr et al (2016) 2015 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 68(1):1–26. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.39480
Kroot EJ, Nieuwenhuizen MG, de Waal Malefijt MC et al (2001) Change in bone mineral density in patients with rheumatoid arthritis during the first decade of the disease. Arthritis Rheum 44(6):1254–1260. https://doi.org/10.1002/1529-0131(200106)44:6%3c1254::AID-ART216%3e3.0.CO;2-G
Rudan I, Sidhu S, Papana A et al (2015) Prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review and analysis. J Glob Health 5(1):010409. https://doi.org/10.7189/jogh.05.010409
Usenbo A, Kramer V, Young T et al (2015) Prevalence of arthritis in Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 10(8):e0133858. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0133858
Kochi Y (2010) Genetic background of tolerance breakdown in rheumatoid arthritis. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi 33(2):48–56. https://doi.org/10.2177/jsci.33.48
Alpizar-Rodriguez D, Finckh A (2017) Environmental factors and hormones in the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Immunopathol 39(4):461–468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-017-0624-2
Deodhar AA, Woolf AD (1996) Bone mass measurement and bone metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis: a review. Br J Rheumatol 35(4):309–322. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/35.4.309
Xue AL, Wu SY, Jiang L et al (2017) Bone fracture risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 96(36):e6983. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000006983
Roux C (2011) Osteoporosis in inflammatory joint diseases. Osteoporos Int 22(2):421–433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-010-1319-x
Vosse D, de Vlam K (2009) Osteoporosis in rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 27(4 Suppl 55):S62–S67
Ghazi M, Kolta S, Briot K et al (2012) Prevalence of vertebral fractures in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: revisiting the role of glucocorticoids. Osteoporos Int 23(2):581–587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-011-1584-3
van Staa TP, Geusens P, Bijlsma JW et al (2006) Clinical assessment of the long-term risk of fracture in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 54(10):3104–3112. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.22117
Tong JJ, Xu SQ, Zong HX et al (2020) Prevalence and risk factors associated with vertebral osteoporotic fractures in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 39(2):357–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04787-9
Arai K, Hanyu T, Sugitani H et al (2006) Risk factors for vertebral fracture in menopausal or postmenopausal Japanese women with rheumatoid arthritis: a cross-sectional and longitudinal study. J Bone Miner Metab 24(2):118–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-005-0657-9
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J et al (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. J Clin Epidemiol 62(10):1006–1012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2009.06.005
Robert K, Pages C, Ledru A et al (2005) Regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase by homocysteine in hippocampus. Neuroscience 133(4):925–935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.03.034
Higgins JP, Thompson SG (2002) Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21(11):1539–1558. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.1186
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ et al (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327:557–560
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M et al (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315(7109):629–634
Guañabens N, Olmos JM, Hernandez JL et al (2021) Vertebral fractures are increased in rheumatoid arthritis despite recent therapeutic advances: a case-control study. Osteoporos Int 32(7):1333–1342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-021-05824-7
Chen YF, Zong HX, Xu SQ et al (2021) Synergistic effect of sarcopenia and poor balance on osteoporotic vertebral fracture in Chinese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-021-05703-w
Pierini FS, Brom M, Scolnik M et al (2021) Osteoporotic fractures in rheumatoid arthritis patients in Argentina: a matched retrospective cohort study. Adv Rheumatol 61(1):21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42358-021-00179-3
Kim HA, Lee HY, Jung JY et al (2020) Trabecular bone score is a useful parameter for the prediction of vertebral fractures in patients with polymyalgia rheumatica. J Clin Densitom 23(3):373–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocd.2019.05.006
Fauny M, Albuisson E, Bauer E et al (2019) Study of vertebral fracture and Scanographic Bone Attenuation Coefficient in rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis vs. controls. Sci Rep 9(1):13323. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-49712-x
Okano T, Inui K, Tada M et al (2017) High frequency of vertebral fracture and low bone quality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-Results from TOMORROW study. Mod Rheumatol 27(3):398–404. https://doi.org/10.1080/14397595.2016.1213943
Liu W, Xu S, Ma X et al (2014) Exploration of risk factors on the occurrence of osteoporotic vertebral fracture in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 53(11):852–857
Brennan SL, Toomey L, Kotowicz MA et al (2014) Rheumatoid arthritis and incident fracture in women: a case-control study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 15:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2474-15-13
Palma S, Delgado-Rodriguez M (2005) Assessment of publication bias in meta-analyses of cardiovascular diseases. J Epidemiol Community Health 59(10):864–9. 59/10/864 [pii] https://doi.org/10.1136/jech.2005.033027
Goldring SR (2015) Inflammatory signaling induced bone loss. Bone 80:143–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2015.05.024
Heinlen L, Humphrey MB (2017) Skeletal complications of rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoporos Int 28(10):2801–2812. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-017-4170-5
Jin S, Hsieh E, Peng L et al (2018) Incidence of fractures among patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int 29(6):1263–1275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-018-4473-1
Ursum J, Britsemmer K, van Schaardenburg D et al (2009) High prevalence of vertebral deformities in elderly patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 68(9):1512–1513. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2008.105957
O’Brien CA, Jia D, Plotkin LI et al (2004) Glucocorticoids act directly on osteoblasts and osteocytes to induce their apoptosis and reduce bone formation and strength. Endocrinology 145(4):1835–1841. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2003-0990
Sparks JA (2019) Rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med 170(1):ITC1–ITC16. https://doi.org/10.7326/AITC201901010
di Munno O, Mazzantini M, Sinigaglia L et al (2004) Effect of low dose methotrexate on bone density in women with rheumatoid arthritis: results from a multicenter cross-sectional study. J Rheumatol 31(7):1305–1309
Buckley LM, Leib ES, Cartularo KS et al (1997) Effects of low dose methotrexate on the bone mineral density of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 24(8):1489–1494
Bologna C, Edno L, Anaya JM et al (1994) Methotrexate concentrations in synovial membrane and trabecular and cortical bone in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum 37(12):1770–1773. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780371210
May KP, West SG, McDermott MT et al (1994) The effect of low-dose methotrexate on bone metabolism and histomorphometry in rats. Arthritis Rheum 37(2):201–206. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780370208
Westhovens R, Dequeker J (2000) Rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis. Z Rheumatol 59(Suppl 1):33–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003930070036
Kwon OC, Oh JS, Hong S et al (2019) Conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and bone mineral density in rheumatoid arthritis patients with osteoporosis: possible beneficial effect of leflunomide. Clin Exp Rheumatol 37(5):813–819
Vis M, Wolbink GJ, Lodder MC et al (2003) Early changes in bone metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with infliximab. Arthritis Rheum 48(10):2996–2997. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.11292
Zerbini CAF, Clark P, Mendez-Sanchez L et al (2017) Biologic therapies and bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoporos Int 28(2):429–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-016-3769-2
Ozen G, Pedro S, Wolfe F et al (2019) Medications associated with fracture risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 78(8):1041–1047. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215328
Coulson KA, Reed G, Gilliam BE et al (2009) Factors influencing fracture risk, T score, and management of osteoporosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in the Consortium of Rheumatology Researchers of North America (CORRONA) registry. J Clin Rheumatol 15(4):155–160. https://doi.org/10.1097/RHU.0b013e3181a5679d
Malysheva K, de Rooij K, Lowik CW et al (2016) Interleukin 6/Wnt interactions in rheumatoid arthritis: interleukin 6 inhibits Wnt signaling in synovial fibroblasts and osteoblasts. Croat Med J 57(2):89–98. https://doi.org/10.3325/cmj.2016.57.89
Briot K, Rouanet S, Schaeverbeke T et al (2015) The effect of tocilizumab on bone mineral density, serum levels of Dickkopf-1 and bone remodeling markers in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine 82(2):109–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2014.10.015
Abu-Shakra M, Zisman D, Balbir-Gurman A et al (2018) Effect of tocilizumab on fatigue and bone mineral density in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Isr Med Assoc J 20(4):239–244
Chen YM, Chen HH, Huang WN et al (2017) Tocilizumab potentially prevents bone loss in patients with anticitrullinated protein antibody-positive rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 12(11):e0188454. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188454
Murakami K, Kobayashi Y, Uehara S et al (2017) A Jak1/2 inhibitor, baricitinib, inhibits osteoclastogenesis by suppressing RANKL expression in osteoblasts in vitro. PLoS ONE 12(7):e0181126. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181126
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K. Y. conceived of the presented idea. Y. L. developed the theory and performed the computations. J. J verified the analytical methods. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was not necessary because all data contained and analyzed in this study are publicly available.
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Jiang, J., Mo, M. et al. Incidence and risk factors for vertebral fracture in rheumatoid arthritis: an update meta-analysis. Clin Rheumatol 41, 1313–1322 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-021-06046-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-021-06046-2