Abstract
Objective
Hypertrophic pachymeningitis (HP) related to anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) is the most frequently seen immune-mediated HP. We investigated cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers related to the pathogenesis of ANCA-related HP (ANCA-HP).
Methods
The levels of B cell activation factor of the tumor necrosis factor family (BAFF), a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL), and transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1) in the CSF were compared between patients with ANCA-HP (n = 12), other types of immune-mediated HP (other HP; n = 12), multiple sclerosis (MS; n = 14), and non-inflammatory neurological disorders (NIND; n = 10). In addition, we evaluated whether ANCA would be detected in CSF.
Results
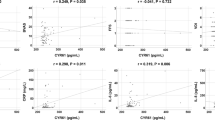
CSF levels of BAFF, APRIL, and TGF-β1 were significantly increased in ANCA-HP and other HP. In particular, BAFF and APRIL levels were significantly correlated with the IgG index in ANCA-HP. In other HP, BAFF and APRIL levels were significantly correlated with cell counts and protein levels in CSF. Of 12 patients with ANCA-HP, the CSF of 7 patients (58%) tested positive for myeloperoxidase (MPO)- or proteinase 3 (PR3)-ANCA, while none of the CSF samples from other HP, MS, or NIND patients tested positive.
Conclusion
The levels of BAFF, APRIL, and TGF-β1 may serve as useful CSF biomarkers for assessing the disease activity of immune-mediated HP. Moreover, BAFF and APRIL in the CSF may be implicated in the pathogenesis of ANCA-HP via promoting autoreactive B cells, while detecting MPO- or PR3-ANCA in the CSF may be found in some patients with ANCA-HP.
Key Points • CSF BAFF, APRIL, and TGF-β1 levels increase significantly in immune-mediated HP. • CSF BAFF and APRIL levels are significantly correlated with IgG index in ANCA-HP. • Detection of MPO- or PR3-ANCA in the CSF is found in some patients with ANCA-HP. • BAFF, APRIL, and ANCA in the CSF may be implicated in the pathogenesis of ANCA-HP. |


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yonekawa T, Murai H, Utsuki S, Matsushita T, Masaki K, Isobe N, Yamasaki R, Yoshida M, Kusunoki S, Sakata K, Fujii K, Kira J (2014) A nationwide survey of hypertrophic pachymeningitis in Japan. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 85:732–739
Shimojima Y, Kishida D, Sekijima Y (2017) Increased BAFF and APRIL levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-related hypertrophic pachymeningitis. Cytokine 99:305–309
Yokoseki A, Saji E, Arakawa M, Kosaka T, Hokari M, Toyoshima Y, Okamoto K, Takeda S, Sanpei K, Kikuchi H, Hirohata S, Akazawa K, Kakita A, Takahashi H, Nishizawa M, Kawachi I (2014) Hypertrophic pachymeningitis: significance of myeloperoxidase anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody. Brain 137:520–536
Shimojima Y, Kishida D, Hineno A, Yazaki M, Sekijima Y, Ikeda SI (2017) Hypertrophic pachymeningitis is a characteristic manifestation of granulomatosis with polyangiitis: a retrospective study of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Int J Rheum Dis 20:489–496
Riku S, Kato S (2003) Idiopathic hypertrophic pachymeningitis. Neuropathology 23:335–344
Wallace ZS, Carruthers MN, Khosroshahi A, Carruthers R, Shinagare S, Stemmer-Rachamimov A, Deshpande V, Stone JH (2013) IgG4-related disease and hypertrophic pachymeningitis. Medicine (Baltimore) 92:206–216
Zhang X, Fujii T, Ogata H, Yamasaki R, Masaki K, Cui Y, Matsushita T, Isobe N, Kira JI (2019) Cerebrospinal fluid cytokine/chemokine/growth factor profiles in idiopathic hypertrophic pachymeningitis. J Neuroimmunol 330:38–43
Hamzaoui K, Houman H, Hentati F, Hamzaoui A (2008) BAFF is up-regulated in central nervous system of neuro-Behcet’s disease. J Neuroimmunol 200:111–114
Sumita Y, Murakawa Y, Sugiura T, Wada Y, Nagai A, Yamaguchi S (2012) Elevated BAFF levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with neuro-Behcet’s disease: BAFF is correlated with progressive dementia and psychosis. Scand J Immunol 75:633–640
George-Chandy A, Trysberg E, Eriksson K (2008) Raised intrathecal levels of APRIL and BAFF in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: relationship to neuropsychiatric symptoms. Arthritis Res Ther 10:R97
Wang H, Wang K, Zhong X, Qiu W, Dai Y, Wu A, Hu X (2012) Cerebrospinal fluid BAFF and APRIL levels in neuromyelitis optica and multiple sclerosis patients during relapse. J Clin Immunol 32:1007–1011
De Virgilio A, de Vincentiis M, Inghilleri M, Fabrini G, Conte M, Gallo A, Rizzo MI, Greco A (2017) Idiopathic hypertrophic pachymeningitis: an autoimmune IgG4-related disease. Immunol Res 65:386–394
Shimojima Y (2019) Hypertrophic pachymeningitis related to ANCA associated vasculitis. Neurology (in Japanese) 91:352–360
Ushiyama S, Kinoshita T, Shimojima Y, Ohashi N, Kishida D, Miyazaki D, Nakamura K, Sekijima Y, Ikeda SI (2016) Hypertrophic pachymeningitis as an early manifestation of relapsing polychondritis: case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Neurol 8:211–217
Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA, Basu N, Cid MC, Ferrario F, Flores-Suarez LF, Gross WL, Guillevin L, Hagen EC, Hoffman GS, Jayne DR, Kallenberg CG, Lamprecht P, Langford CA, Luqmani RA, Mahr AD, Matteson EL, Merkel PA, Ozen S, Pusey CD, Rasmussen N, Rees AJ, Scott DG, Specks U, Stone JH, Takahashi K, Watts RA (2013) 2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum 65:1–11
Watts R, Lane S, Hanslik T, Hauser T, Hellmich B, Koldingsnes W, Mahr A, Segelmark M, Cohen-Tervaert JW, Scott D (2007) Development and validation of a consensus methodology for the classification of the ANCA-associated vasculitides and polyarteritis nodosa for epidemiological studies. Ann Rheum Dis 66:222–227
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Nakamura T, Satoh-Nakamura T, Nakajima A, Kawano M, Mimori T, Chiba T (2017) Current approach to the diagnosis of IgG4-related disease—combination of comprehensive diagnostic and organ-specific criteria. Mod Rheumatol 27:381–391
Baughman RP, Lower EE, du Bois RM (2003) Sarcoidosis. Lancet 361:1111–1118
Mukhtyar C, Lee R, Brown D, Carruthers D, Dasgupta B, Dubey S, Flossmann O, Hall C, Hollywood J, Jayne D, Jones R, Lanyon P, Muir A, Scott D, Young L, Luqmani RA (2009) Modification and validation of the Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score (version 3). Ann Rheum Dis 68:1827–1832
Hu HH, Chen DQ, Wang YN, Feng YL, Cao G, Vaziri ND, Zhao YY (2018) New insights into TGF-beta/Smad signaling in tissue fibrosis. Chem Biol Interact 292:76–83
Hahn LD, Fulbright R, Baehring JM (2016) Hypertrophic pachymeningitis. J Neurol Sci 367:278–283
Ransohoff RM, Engelhardt B (2012) The anatomical and cellular basis of immune surveillance in the central nervous system. Nat Rev Immunol 12:623–635
Wraith DC, Nicholson LB (2012) The adaptive immune system in diseases of the central nervous system. J Clin Invest 122:1172–1179
Pardali E, Sanchez-Duffhues G, Gomez-Puerto MC, Ten Dijke P (2017) TGF-beta-induced endothelial-mesenchymal transition in fibrotic diseases. Int J Mol Sci 18:2157
Biernacka A, Dobaczewski M, Frangogiannis NG (2011) TGF-beta signaling in fibrosis. Growth Factors 29:196–202
Miyazawa K, Miyazono K (2017) Regulation of TGF-beta family signaling by inhibitory Smads. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 9:a022095
Guo X, Wang XF (2009) Signaling cross-talk between TGF-beta/BMP and other pathways. Cell Res 19:71–88
Kim HA, Jeon SH, Seo GY, Park JB, Kim PH (2008) TGF-beta1 and IFN-gamma stimulate mouse macrophages to express BAFF via different signaling pathways. J Leukoc Biol 83:1431–1439
Jang YS, Kim JH, Seo GY, Kim PH (2011) TGF-beta1 stimulates mouse macrophages to express APRIL through Smad and p38MAPK/CREB pathways. Mol Cell 32:251–255
Reiber H, Peter JB (2001) Cerebrospinal fluid analysis: disease-related data patterns and evaluation programs. J Neurol Sci 184:101–122
Fitzner B, Hecker M, Zettl UK (2015) Molecular biomarkers in cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis patients. Autoimmun Rev 14:903–913
Tangye SG, Bryant VL, Cuss AK, Good KL (2006) BAFF, APRIL and human B cell disorders. Semin Immunol 18:305–317
Mackay F, Ambrose C (2003) The TNF family members BAFF and APRIL: the growing complexity. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 14:311–324
Rickert RC, Jellusova J, Miletic AV (2011) Signaling by the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily in B-cell biology and disease. Immunol Rev 244:115–133
Jennette JC, Falk RJ (2014) Pathogenesis of antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-mediated disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol 10:463–473
Krumbholz M, Specks U, Wick M, Kalled SL, Jenne D, Meinl E (2005) BAFF is elevated in serum of patients with Wegener’s granulomatosis. J Autoimmun 25:298–302
Bader L, Koldingsnes W, Nossent J (2010) B-lymphocyte activating factor levels are increased in patients with Wegener’s granulomatosis and inversely correlated with ANCA titer. Clin Rheumatol 29:1031–1035
Nagai M, Hirayama K, Ebihara I, Shimohata H, Kobayashi M, Koyama A (2011) Serum levels of BAFF and APRIL in myeloperoxidase anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated renal vasculitis: association with disease activity. Nephron Clin Pract 118:c339–c345
Lenert A, Lenert P (2015) Current and emerging treatment options for ANCA-associated vasculitis: potential role of belimumab and other BAFF/APRIL targeting agents. Drug Des Devel Ther 9:333–347
Zhao Y, Odell E, Choong LM, Barone F, Fields P, Wilkins B, Tungekar FM, Patel P, Sanderson JD, Sangle S, D'Cruz D, Spencer J (2012) Granulomatosis with polyangiitis involves sustained mucosal inflammation that is rich in B-cell survival factors and autoantigen. Rheumatology (Oxford) 51:1580–1586
Spranger M, Schwab S, Meinck HM, Tischendorf M, Sis J, Breitbart A, Andrassy K (1997) Meningeal involvement in Wegener’s granulomatosis confirmed and monitored by positive circulating antineutrophil cytoplasm in cerebrospinal fluid. Neurology 48:263–265
Faust J, Visbeck A, Fitzek S, Fitzek C, Orth T, Wandel E, Mayet WJ (2000) Vasculitic wallenberg syndrome with detection of anti-proteinase 3 antibodies in the cerebrospinal fluid of a patient with severe Wegener’s granulomatosis and only mild kidney involvement. Nephrol Dial Transplant 15:893–896
Vincent FB, Saulep-Easton D, Figgett WA, Fairfax KA, Mackay F (2013) The BAFF/APRIL system: emerging functions beyond B cell biology and autoimmunity. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 24:203–215
Stein JV, Lopez-Fraga M, Elustondo FA, Carvalho-Pinto CE, Rodriguez D, Gomez-Caro R, De Jong J, Martinez AC, Medema JP, Hahne M (2002) APRIL modulates B and T cell immunity. J Clin Invest 109:1587–1598
Hellmich B, Flossmann O, Gross WL, Bacon P, Cohen-Tervaert JW, Guillevin L, Jayne D, Mahr A, Merkel PA, Raspe H, Scott DG, Witter J, Yazici H, Luqmani RA (2007) EULAR recommendations for conducting clinical studies and/or clinical trials in systemic vasculitis: focus on anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis 66:605–617
Yates M, Watts RA, Bajema IM, Cid MC, Crestani B, Hauser T, Hellmich B, Holle JU, Laudien M, Little MA, Luqmani RA, Mahr A, Merkel PA, Mills J, Mooney J, Segelmark M, Tesar V, Westman K, Vaglio A, Yalcindag N, Jayne DR, Mukhtyar C (2016) EULAR/ERA-EDTA recommendations for the management of ANCA-associated vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis 75:1583–1594
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank the members of the Department of Medicine (Neurology and Rheumatology) for their efforts providing medical care, Dr. Mitsutoshi Sugano (Department of Laboratory Medicine, Shinshu University Hospital) for their cooperation with the laboratory analysis, and Dr. Masayoshi Koinuma (Center for Clinical Research, Shinshu University Hospital) for his statistical advice.
Funding
This study was supported by a Health and Labour Sciences Research Grant on Rare and Intractable Diseases (Evidence-based Early Diagnosis and Treatment Strategies for Neuroimmunological Diseases) from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The present study was approved by the Local Ethics Committee of Shinshu University. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikeda, J., Shimojima, Y., Usami, Y. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers implicated in the pathogenesis of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-related hypertrophic pachymeningitis. Clin Rheumatol 39, 1803–1811 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-04971-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-04971-2