Abstract
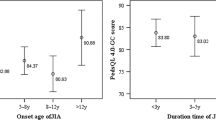
The aim of our study is to investigate the factors influencing the quality of life, assessed by the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory 4.0 (PedsQL4) Generic Score Scales, in Moroccan patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. This is a cross-sectional study conducted between January and June 2012, covering children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) seen at the consultations of El Ayachi Hospital and Children’s Hospital of the University Hospital of Rabat. Quality of life is assessed by the PedsQL4 which is a questionnaire composed of 23 items, completed by the child and the parent; the response to each item ranges from 0 to 100, so that higher scores indicate a better quality of life. The functional impact is assessed by the Childhood Health Assessment Questionnaire (CHAQ), and the disease activity by the number of tender and swollen joints, visual analogue scale (VAS) activity, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and C-reactive protein. Forty-seven patients are included; the average age of the patients is 11 ± 3.35 years, and 40.4 % are females, with a median disease duration of 4 (2; 6) years. The oligoarticular form presents 26.7 %, the systemic form 24.4 %, and the enthesic form 22.2 %. The median of PedsQL4 is 80.43 (63.19; 92.93), and the median of the CHAQ is 0 (0; 1). Our study shows that some clinical and biological characteristics have significant effects on PedsQL by both parent and child reports. This study suggests that the achievement of the quality of life of our patients with JIA depends on the disease activity measured by swollen joints, the number of awakenings, parent VAS, physician VAS, patient VAS, and the ESR.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seid M, Opipari L, Huang B, Brunner HI, Lovell DJ (2009) Disease control and health-related quality of life in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 61:393–399
Ravelli A, Martini A (2007) Juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Lancet 369:767
Moorthy LN, Peterson MG, Hassett AL, Lehman TJ (2010) Burden of childhood-onset arthritis. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J 8:20
Gutiérrez-Suárez R, Pistorio A, Cespedes Cruz A, Norambuena X, Flato B, Rumba I et al (2007) Health-related quality of life of patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis coming from 3 different geographic areas. The PRINTO multinational quality of life cohort study. Rheumatol (Oxford) 46(2):314–320
Brunner HI, Giannini EH (2003) Health-related quality of life in children with rheumatic diseases. Curr Opin Rheumatol 15:602–612
Group WHOQOL (1993) The development of the World Health Organization quality of life assessment instrument (the WHOQOL). Qual Life Res 2(2):153–159
Baars R, Atherton C, Koopman H, Bullinger M, Power M, group D (2005) The European DISABKIDS project: development of seven condition-specific modules to measure health related quality of life in children and adolescents. Health Qual Life Outcomes 3:70
Oliveira S, Ravelli A, Pistorio A, Castell E, Malattia C, Prieur AM et al (2007) Proxy-reported health-related quality of life of patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. The Pediatric Rheumatology International Trials Organization multinational quality of life cohort study. Arthritis Rheum 57:35–43
Arkela-Kautiainen M, Haapasaari J, Kautiainen H, Vilkkumaa I, Malkia E, Leirisalo-Repo M (2005) Favourable social functioning and health-related quality of life of patients with JIA in early adulthood. Ann Rheum Dis 64:875–880
Petty RE, Southwood TR, Manners P et al (2004) International League of Associations for Rheumatology classification of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: second revision, Edmonton, 2001. J Rheumatol 31:390–392
Varni J, Seid M, Kurtin P (2001) PedsQL 4.0: reliability and validity of the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory version 4.0 generic core scales in healthy and patient populations. Med Care 39(8):800–812
Varni JW, Seid M, Smith Knight T, Burwinkle T, Brown J, Szer IS (2002) The PedsQL in pediatric rheumatology: reliability, validity, and responsiveness of the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory generic core scales and rheumatology module. Arthritis Rheum 46:714–725
Cronbach LJ (1951) Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika 16:297–334
Rostom S, Amine B, Bensabbah R, Chkirat B, Abouqal R, Hajjaj-Hassouni N (2010) Psychometric properties evaluation of the childhood health assessment questionnaire (CHAQ) in Moroccan juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Rheumatol Int 30:879–885
Singh G, Athreya B, Fries J, Goldsmith D (1994) Measurement of health status in children with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 37(12):1761–1769
Dempster H, Porepa M, Young N, Feldman BM (2001) The clinical meaning of functional outcome scores in children with juvenile arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 44(8):1768–1774
Amine B, Rostom S, Benbouazza K, Abouqal R, Hajjaj-Hassouni N (2009) Health related quality of life survey about children and adolescents with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Rheumatol Int 29:275–279
Lundberg V, Lindh V, Eriksson C, Petersen S, Eurenius E (2012) Health-related quality of life in girls and boys with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: self- and parental reports in a cross-sectional study. Pediatr Rheumatol 10:33
April KT, Feldman DE, Platt RW, Duffy CM (2006) Comparison between children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) and their parents concerning perceived quality of life. Qual Life Res 15(4):655–661
Sawyer MG, Whitham JN, Roberton DM, Taplin JE, Varni JW, Baghurst PA (2004) The relationship between health-related quality of life, pain and coping strategies in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43(3):325–330
Shaw K, Southwood T, McDonagh J (2006) Growing up and moving on in rheumatology: parents as proxies of adolescents with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 55(2):189–198
Upton P, Lawford J, Eiser C (2008) Parent–child agreement across child health-related quality of life instruments: a review of the literature. Qual Life Res 17(6):895–913
Norrby U, Nordholm L, Fasth A (2003) Reliability and validity of the Swedish version of child health questionnaire. Scand J Rheumatol 32(2):101–107
April KT, Cavallo S, Feldman DE, Ni A (2012) The associations among economic hardship, caregiver psychological distress, disease activity, and health-related quality of life in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Qual Life Res 21:1185–1191
Disclosures
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ezzahri, M., Amine, B., Rostom, S. et al. Factors influencing the quality of life of Moroccan patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 33, 1621–1626 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2489-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2489-2