Abstract
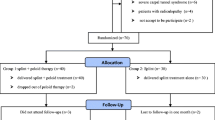
This study aimed to compare the short-term efficacy of splinting (S) and splinting plus low-level laser therapy (SLLLT) in mild or moderate idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) with a prospective, randomized controlled study. The patients with unilateral, mild, or moderate idiopathic CTS who experienced symptoms over 3 months were included in the study. The SLLLT group received ten sessions of laser therapy and splinting while S group was given only splints. The patients were evaluated at the baseline and after 3 months of the treatment. Follow-up parameters were nerve conduction study (NCS), Boston Questionnaire (BQ), grip strength, and clinical response criteria. Forty-five patients with CTS completed the study. Twenty-four patients were in S and 21 patients were in SLLLT group. In the third-month control, SLLLT group had significant improvements on both clinical and NCS parameters (median motor nerve distal latency, median sensory nerve conduction velocities, BQ symptom severity scale, and BQ functional capacity scale) while S group had only symptomatic healing (BQ symptom severity scale). The grip strength of splinting group was decreased significantly. According to clinical response criteria, in SLLLT group, five (23.8%) patients had full and 12 (57.1%) had partial recovery; four (19%) patients had no change or worsened. In S group, one patient (4.2%) had full and 17 (70.8%) partial recovery; six (25%) patients had no change or worsened. Additionally, applied laser therapy provided better outcomes on NCS but not in clinical parameters in patients with CTS.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gerritsen AA, de Vet HC, Scholten RJ, Bertelsmann FW, de Krom MC, Bouter LM (2002) Splinting vs surgery in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 288(10):1245–1251
Demirci S, Kutluhan S, Koyuncuoglu HR, Kerman M, Heybeli N, Akkuş S, Akhan G (2002) Comparison of open carpal tunnel release and local steroid treatment outcomes in idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome. Rheumatol Int 22(1):33–37
Ucan H, Yagci I, Yilmaz L, Yagmurlu F, Keskin D, Bodur H (2006) Comparison of splinting, splinting plus local steroid injection and open carpal tunnel release outcomes in idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome. Rheumatol Int 27(1):45–51
Botte MJ, von Schroeder HP, Abrams RA, Gellman H (1996) Recurrent carpal tunnel syndrome. Hand Clin 12(4):731–743
Stolp-Smith KA, Pascoe MK, Ogburn PL Jr (1998) Carpal tunnel syndrome in pregnancy: frequency, severity, and prognosis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 79(10):1285–1287
Manente G, Torrieri F, Di Balassio F, Staniscia T, Romano F, Uncini A (2001) An innovative hand brace for carpal tunnel syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Muscle Nerve 24:1020–1025
Ayhan-Ardic FF, Erdem HR (2000) Long-term clinical and electrophysiological results of local steroid injection in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. Funct Neurol 15(3):157–165
Giannini F, Passero S, Cioni R, Paradiso C, Battistini N, Giordano N, Vaccai D, Marcolongo R (1991) Electrophysiologic evaluation of local steroid injection in carpal tunnel syndrome. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 72(10):738–742
Dammers JW, Veering MM, Vermeulen M (1999) Injection with methylprednisolone proximal to the carpal tunnel: randomised double blind trial. BMJ 319(7214):884–886
Ozdogan H, Yazici H (1984) The efficacy of local steroid injections in idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome: a double-blind study. Br J Rheumatol 23(4):272–275
O'Gradaigh D, Merry P (2000) Corticosteroid injection for the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 59(11):918–919
Ebenbichler GR, Resch KL, Nicolakis P, Wiesinger GF, Uhl F, Ghanem AH, Fialka V (1998) Ultrasound treatment for treating the carpal tunnel syndrome: randomised "sham" controlled trial. BMJ 316(7133):731–735
Padua L, Padua R, Aprile I, Tonali P (1998) Noninvasive laser neurolysis in carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve 21(9):1232–1233
Weintraub MI (1997) Noninvasive laser neurolysis in carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve 20(8):1029–1031
Naeser MA, Hahn KA, Lieberman BE, Branco KF (2002) Carpal tunnel syndrome pain treated with low-level laser and microamperes transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation: a controlled study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 83(7):978–988
Bakhtiary AH, Rashidy-Pour A (2004) Ultrasound and laser therapy in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. Aust J Physiother 50(3):147–151
Evcik D, Kavuncu V, Cakir T, Subasi V, Yaman M (2007) Laser therapy in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Photomed Laser Surg 25(1):34–39
Shooshtari SM, Badiee V, Taghizadeh SH, Nematollahi AH, Amanollahi AH, Grami MT (2008) The effects of low level laser in clinical outcome and neurophysiological results of carpal tunnel syndrome. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol 48(5):229–231
Chang WD, Wu JH, Jiang JA, Yeh CY, Tsai CT (2008) Carpal tunnel syndrome treated with a diode laser: a controlled treatment of the transverse carpal ligament. Photomed Laser Surg 26:551–557
Dincer U, Cakar E, Kiralp MZ, Kilac H, Dursun H (2009) The effectiveness of conservative treatments of carpal tunnel syndrome: splinting, ultrasound, and low-level laser therapies. Photomed Laser Surg 27:119–125
Stevens JC (1997) AAEM mimimonograph # 26: the electrodiagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve 20(12):1477–1486
Levine DW, Simmons BP, Koris MJ, Daltroy LH, Hohl GG, Fossel AH, Katz JN (1993) A self-administered questionnaire for the assessment of severity of symptoms and functional status in carpal tunnel syndrome. J Bone and Joint Surg 75(11):1585–1592
Heybeli N, Özerdemoğlu RA, Aksoy OG, Mumcu EF (2001) Karpal Tünel Sendromu: Cerrahi tedavi izleminde fonksiyonel ve semptomatik skorlama. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 35:147–151
Heybeli N, Kutluhan S, Demirci S, Kerman M, Mumcu EF (2002) Assessment of outcome of carpal tunnel syndrome: a comparison of electrophysiological findings and a self-administered Boston questionnaire. J Hand Surg [Br] 27(3):259–264
Mondelli M, Reale F, Sicurelli F, Padua L (2000) Relationship between the self-administered Boston questionnaire and electrophysiological findings in follow-up of surgically-treated carpal tunnel syndrome. J Hand Surg [Br] 25(2):128–134
Schuind FA, Mouraux D, Robert C, Brassinne E, Rémy P, Salvia P, Meyer A, Moulart F, Burny F (2003) Functional and outcome evaluation of the hand and wrist. Hand Clin 19(3):361–369
Akkus S, Kutluhan S, Akhan G, Tunc E, Ozturk M, Koyuncuoglu HR (2002) Does fibromyalgia affect the outcomes of local steroid treatment in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome? Rheumatol Int 22(3):112–115
Irvine J, Chong SL, Amirjani N, Chan KM (2004) Double-blind randomized controlled trial of low-level laser therapy in carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve 30(2):182–187
Disclosures
Each author certifies that he or she has no commercial associations that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yagci, I., Elmas, O., Akcan, E. et al. Comparison of splinting and splinting plus low-level laser therapy in idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome. Clin Rheumatol 28, 1059–1065 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-009-1213-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-009-1213-0