Abstract
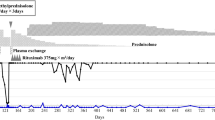
We report a 29-year-old Japanese woman with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) and adult onset Still’s disease (AOSD). Her disease was refractory to high-dose glucocorticoids, two courses of steroid pulse therapy, and addition of cyclosporine (3.5 mg/kg/day). The serum interleukin-6 level was markedly elevated. Therefore, we administered an anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody (tocilizumab, 8 mg/kg fortnightly), which dramatically improved her symptoms and the levels of acute-phase proteins. In addition, rapid tapering of the glucocorticoid dose was possible. Four months later, she was maintained on tocilizumab infusion once a month with low-dose steroid therapy. Cyclosporine is one of the first-line immunosuppressants for AOSD, especially when associated with DIC, hepatic failure, or hemophagocytic syndrome. In patients with cyclosporine-resistant AOSD, tocilizumab may be another useful option.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Efthimiou P, Georgy S (2006) Pathogenesis and management of adult-onset Still’s disease. Semin Arthritis Rheum 36:144–152
Fitzgerald AA, Leclercq SA, Yan A et al (2005) Rapid responses to anakinra in patients with refractory adult-onset Still’s disease. Arthritis Rheum 52:1794–1803
Kötter I, Wacker A, Koch S et al (2007) Anakinra in patients with treatment-resistant adult-onset Still’s disease: four case reports with serial cytokine measurements and a review of the literature. Semin Arthritis Rheum 37:189–197
Fujii T, Nojima T, Yasuoka H et al (2001) Cytokine and immunogenetic profiles in Japanese patients with adult Still’s disease. Association with chronic articular disease. Rheumatology (Oxford) 40:1398–1404
Scheinberg MA, Chapira E, Fernandes ML et al (1996) Interleukin 6: a possible marker of disease activity in adult onset Still’s disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol 14:653–655
Hoshino T, Ohta A, Yang D et al (1998) Elevated serum interleukin 6, interferon-gamma, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels in patients with adult Still’s disease. J Rheumatol 25:396–398
Fautrel B, Sibilia J, Mariette X et al (2005) Tumour necrosis factor alpha blocking agents in refractory adult Still’s disease: an observational study of 20 cases. Ann Rheum Dis 64:262–266
Kalliolias GD, Georgiou PE, Antonopoulos IA et al (2007) Anakinra treatment in patients with adult-onset Still’s disease is fast, effective, safe and steroid sparing: experience from an uncontrolled trial. Ann Rheum Dis 66:842–843
Iwamoto M, Nara H, Hirata D et al (2002) Humanized monoclonal anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody for treatment of intractable adult-onset Still’s disease. Arthritis Rheum 46:3388–3389
Marchesoni A, Ceravolo GP, Battafarano N et al (1997) Cyclosporin A in the treatment of adult onset Still’s disease. J Rheumatol 24:1582–1587
Shojania K, Chalmers A, Rangno K (1995) Cyclosporin A in the treatment of adult Still’s disease. J Rheumatol 22:1391–1392
Park JH, Bae JH, Choi YS et al (2004) Adult-onset Still’s disease with disseminated intravascular coagulation and multiple organ dysfunctions dramatically treated with cyclosporine A. J Korean Med Sci 19:137–141
Nishida T, Suzuki K, Kuwada N et al (2001) Hemophagocytic syndrome and adult Still’s disease associated with meningoencephalitis and unconsciousness. Intern Med 40:1037–1040
Nagashima T, Aoki Y, Onishi S et al (2008) Steroid-refractory severe hepatic failure in adult onset Still’s disease responding to cyclosporine. Clin Rheumatol 27:1451–1453
Yokota S, Imagawa T, Miyamae T et al (2004) Long-term therapeutic experience of humanized anti-IL-6 receptor monoclonal antibody (aIL-6R Mab) in systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis (So-JIA). Arthritis Rheum 50:S438
Disclosures
Dr. Iwamoto and Minota have received royalties from Chugai Pharmaceutical Company, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan (less than $10,000). The other authors have disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsumoto, K., Nagashima, T., Takatori, S. et al. Glucocorticoid and cyclosporine refractory adult onset Still’s disease successfully treated with tocilizumab. Clin Rheumatol 28, 485–487 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-009-1097-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-009-1097-z