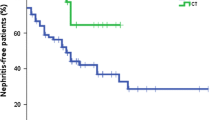
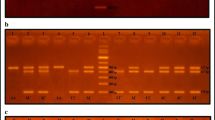
Abstract
The clinical course of Henoch–Schönlein Purpura (HSP) in children is variable, with some patients having a much more rapidly progressing course than others. We investigated whether polymorphisms of the renin–angiotensin system (RAS) genes are involved in HSP. Three RAS genotypes were examined in 114 children with HSP and in 164 healthy children: the angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) insertion/deletion polymorphism, the M235T mutation in the angiotensinogen gene (Agt), and the A1166C in the angiotensin II type I receptor (AT1R) gene. Significant differences were observed between HSP patients and control group in the frequency of ACE and Agt genotypes (p=0.004 and p=0.003, respectively). The TT genotype of Agt gene was associated with a 3.5-fold increased risk for Henoch–Schönlein nephritis (HSN) compared with the MM/MT genotype (odds ratio, 3.5; 95% confidence interval, 1.2–10.4). There was a trend to a higher prevalence of the TT genotype of the Agt gene among patients with nephrotic range proteinuria when compared to the patients with mild proteinuria, although the difference did not reach a statistical significance. The results of this study suggest that polymorphisms of ACE gene and Agt gene likely influence the risk of developing HSP. However, among the three genes of the RAS studies, only Agt gene was associated with the susceptibility to HSN. RAS gene polymorphisms studied are not associated with the presence of nephrotic range proteinuria. Additional studies are warranted to verify the correlation between RAS gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to HSP.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levy M (2001) Familial cases of Berger’s disease and anaphylactoid purpura. Kidney Int 60:1611–1612
McLean RH, Wyatt RJ, Julian BA (1984) Complement phenotypes in glomerulonephritis: increased frequency of homozygous null C4 phenotypes in IgA nephropathy and Henoch–Schönlein purpura. Kidney Int 26:855–860
Jin DK, KohsakaT, Koo JW, Ha IS, Cheong HI, Choi Y (1996) Complement 4 locus gene deletion and DQA1*0301 gene: genetic risk factors for IgA nephropathy and Henoch–Schönlein nephritis. Nephron 73:390–395
Anderson PW, Do YS, Hsueh WA (1993) Angiotensin II causes mesangial cell hypertrophy. Hypertension 21:29–35
Rigat B, Hubert C, Alhenc-Gelas F, Cambien F, Corvol P, Soubrier F (1993) An I/D polymorphism in the ACE gene accounting for half the variance of serum enzyme levels. J Clin Invest 86:1343–1346
Cambien F, Poirier O, Lecerf L, Evans A, Cambou JP, Arveiler D, Luc G, Bard JM, Bara L, Ricard S, Tiret L, Amouyei P, Alhenc-Gelas F, Soubrier F (1992) Deletion polymorphism in the gene for angiotensin-converting enzyme is a potent risk factor for myocardial infarction. Nature 359:641–644
Yoshida H, Kuriyama S, Atsumi Y, Tomonari H, Mitarai T, Hamaguchi A, Kubo H, Kawaguchi Y, Kon V, Matsuoka K, Ichikawa I, Sakai O (1996) Angiotensin I converting enzyme gene polymorphism in non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int 50:657–664
Hunley TE, Julian BA, Phillips JA, Summer ML, Yoshida H, Horn RG, Brown NJ, Fogo A, Ichikawa I, Kon V (1996) Angiotensin converting enzyme gene polymorphism: potential silencer motif and impact on progression in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int 49:571–577
Yoshida H, Mitarai T, Kawamura T, Kitajima T, Miyazaki Y, Nagasawa R, Kubo H, Ichikawa I, Sakai O (1995) Role of deletion polymorphism of the ACE gene in the progress and therapeutic responsiveness of IgA nephropathy. J Clin Invest 96:2162–2169
Yoshioka T, Xu Y, Yoshida H, Shiraga H, Muraki T, Ito K (1998) Deletion polymorphism of the angiotensin converting enzyme gene predicts persistent proteinuria in Henoch–Schönlein purpura nephritis. Arch Dis Child 79:394–399
Stratta P, Canavese C, Ciccone G, Barolo S, Dall’Omo AM, Fasano ME, Mazzola G, Berutti S, Fop F, Curtoni ES, Piccoli G (1999) Angiotensin I-converting enzyme genotype significantly affects progression of IgA glomerulonephritis in an Italian population. Am J Kid Dis 33:1071–1079
Frishberg Y, Becker-Cohen R, Halle D, Feigin E, Eisenstein B, Halevy R, Lotan D, Juabej I, Ish-Shalom N, Magen D, Shvil Y, Sinai-treiman L, Drukker A (1998) Genetic polymorphism of the renin–angiotensin system and the outcome of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in children. Kidney Int 54:1843–1849
Tiret L, Bonnardeaux A, Poirier O, Ricard S, Marques-Vidal P, Evans A, Arveiler D, Luc G, Kee F, Ducimetiere P, Soubrier F, Cambien F (1994) Synergistic effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme and angiotensin-II type 1 receptor gene polymorphisms on risk of myocardial infarction. Lancet 344:910–913
Bonnardeaux A, Davies E, Jeunmaitre X, Fery I, Charru A, Clauser E, Tiret L, Cambien F, Corvol P, Soubrict F (1999) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene polymorphisms in human essential hypertension. Hypertension 24:63–69
Jeunemaitre X, Soubrier F, Kotelevtsev YV, Lifton RP, Williams CS, Charru A, Hunt SC, Hopkins PN, Williams RR, LaLouel JM (1992) Molecular basis of human hypertension: role of angiotensinogen. Cell 71:169–180
Lalouel J, Rohrwasser A, Terreros D, Morgan T, Ward K (2001) Angiotensinogen in essential hypertension: from genetics to nephrology. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:606–615
Mills JA, Michel BA, Block D (1990) The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of Henoch–Schönlein purpura. Arthritis Rheum 33:1114–1121
Lindpaintner K, Pfeffer MA, Kreutz R et al (1995) A prospective evaluation of an angiotensin-converting-enzyme gene polymorphism and the risk of ischemic heart disease. N Engl J Med 16:706–711
Siragy HM, Carey RM (1990) The subtype-2(AT2) angiotensin mediates renal production of nitric oxide in conscious rats. J Clin Invest 100:264–269
Sechi LA, Grady EF, Griffin CA, Kalinyak JE, Schambelan M (1992) Distribution of angiotensin II receptor subtypes in rat and human kidney. Am J Physiol 262:F236–F240
Wolf G, Neilson EG (1993) Angiotensin II as a renal growth factor. Am Soc Nephrol 3:1531–1540
Buikema H, Pinto YM, Rooks G, Grandjean JG, Schunkert H, van Gilst WH (1996) The deletion polymorphism of the angiotensin-converting enzyme gene is related to phenotypic differences in human arteries. Eur Heart J 17:787–794
Kainulainen K, Perola M, Terwilliger J, Kaprio J, Kaskenvuo M, Syvanen AC, Vartiainen E, Peltonen L, Kontula K (1999) Evidence for involvement of the type 1 angiotensin II receptor locus in essential hypertension. Hypertension 33:844–849
Marre M, Jeunemaitre X, Gallois Y, Roidier M, Chatellier G, Sert C, Dusselier L, Kahal Z, Chaillous L, Halimi S, Muller A, Sackmann H, Bauduceau B, Bled F, Passa P, Gelas FA (1997) Contribution of genetic polymorphism in the renin–angiotensin system to the development of renal complications in insulin-dependent diabetes. J Clin Invest 99:1585–1595
Pei Y, Scholey J, Thai K, Suzuki M, Cattran D (1997) Association of angiotensinogen gene T235 variant with progression of IgA nephropathy in Caucasian patients. J Clin Invest 15:814–820
Perna A, Ruggenenti P, Testa A, Spoto B, Benini R, Misefari V, Remuzzi G, Zoccali C (2000) ACE genotype and ACE inhibitors induced renoprotection in chronic proteinuric nephropathies. Kidney Int 57:274–281
Pullmann R, Lukác J, Skerenová M, Rovensky J, Hybenová J, Melus V, Velec S, Pulmann R, Hyrdel R (1999) Association between lupus erythematosus and insertion/deletion polymorphism of the angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) gene. Clin Exp Rheum 17:593–596
Schmidt S, Stier E, Hartung R, Stein G, Bahnisch J, Woodroffe AJ, Clarkson AR, Ponticelli C, Campise M, Mayer G, Ganten D, Ritz E (1995) No associations of converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism with immunoglobulin A glomerulonephritis. Am J Kidney Dis 26:727–731
Frimat L, Philippe C, Maghakian M, Jonveaux P, Ligny BH, Guillemin F, Kessler M (2000) Polymorphism of angiotensin converting enzyme, angiotensinogen, and angiotensin II type 1 receptor genes and end stage renal failure in IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 11:2062–2067
Perticone F, Ceravolo R, Maio R, Ventura G, Zingone A, Perrotti N, Mattioli PL (1998) Angiotensin-converting enzyme gene polymorphism is associated with endothelium-dependent vasodilation in never treated hypertensive patients. Hypertension 31:900–905
Dudley J, Afifi E, Gardner A, Tizard EJ, McGraw ME (2000) Polymorphism of the ACE gene in Henoch–Schönlein purpura nephritis. Pediatr Nephrol 14:218–220
Amoroso A, Danek G, Vatta S, Crovella S, Berrino M, Guarrera S, Fasono M, Mazzola G, Amore A, Gianoglia B, Peruzzi L, Coppo R (1998) Polymorphisms in angiotensin-converting enzyme gene and severity of renal disease in Henoch–Schoenlein patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 13:3184–3188
Maruyama K, Yoshida M, Nishio H, Shirakawa T, Kawamura T, Tanaka R, Nakamura H, Iijima K, Yoshikawa N (2001) Polymorphisms of the renin–angiotensin system genes in childhood IgA nephropathy. Pediatr Nephrol 16:350–355
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özkaya, O., Söylemezoğlu, O., Gönen, S. et al. Renin–angiotensin system gene polymorphisms: association with susceptibility to Henoch–Schonlein purpura and renal involvement. Clin Rheumatol 25, 861–865 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-006-0207-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-006-0207-4