Abstract
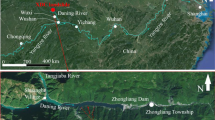
Landslide-induced waves often result in severe casualties, economic losses, and even catastrophic consequences, which are far more destructive than the landslide itself. In this paper, accurate geomorphological and geological characteristics of the Wangjiashan landslide in Baihetan Reservoir, southwest China, were obtained through field investigations, and a three-dimensional model was built for numerical calculation. Through the time series curve of cumulative deformation, the water level variation of the reservoir was found to be the major factor causing the landslide deformation and eventual failure. The generation and propagation progress of water waves induced by the Wangjiashan landslide was simulated by coupling the granular flow model and renormalization group turbulence model in FLOW3D. The results show that a large sliding mass silts up the channel, forming a landslide dam with a maximum height of 21.5 m. Nevertheless, it does not block the channel and will not affect standard navigation on account of the wide channel in this area. The maximum run-up wave height of waves spreading to the Xiangbiling resettlement area on the opposite bank is 3.7 m. As the resettlement area is only 1.3 km away from the landslide, and its elevation is only 2.5 m higher than the normal water level of the reservoir, landslide-induced waves should be considered a potential threat. The most vulnerable area affected by landslide-induced waves is about 8 km long along the river, where wave run-up heights are more than 1 m. The results in this paper have important reference values for the early warning and prevention of potential disasters caused by landslides and landslide-induced waves.













Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ataie-Ashtiani B, Nik-Khah A (2008) Impulsive waves caused by subaerial landslides. Environ Fluid Mech 8:263–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10652-008-9074-7
Ataie-Ashtiani B, Yavari-Ramshe S (2011) Numerical simulation of wave generated by landslide incidents in dam reservoirs. Landslides 8:417–432. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-011-0258-8
Bagnold RA (1954) Experiments on gravity-free dispersion of large solid spheres in a Newtonian fluid under shear. Proceedings of the Royal Society A 225:49–63. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1954.0186
Biscarini C (2010) Computational fluid dynamics modelling of landslide generated water waves. Landslides 7:117–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-009-0194-z
Boon CW, Houlsby GT, Utili S (2014) New insights into the 1963 Vajont slide using 2D and 3D distinct-element method analyses. Geotechnique 64:800–816. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.14.P.041
Bosa S, Petti M (2011) Shallow water numerical model of the wave generated by the Vajont landslide. Environ Model Softw 26:406–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2010.10.001
Evers FM, Fuchs H, Hager WH (2018) Tsunamis generated by fast granular landslides: 3D experiments and empirical predictors. J Hydraul Res 56:581–582. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221686.2017.1399939
Flow Science (2016) FLOW-3D V11.2 User’s Manual
Franco A, Moernaut J, Schneider-Muntau B, Strasser M, Gems B (2021) Triggers and consequences of landslide-induced impulse waves-3D dynamic reconstruction of the Taan Fiord 2015 tsunami event. Eng Geol 294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106384.
Fritz H, Hager W, Minor H (2004) Near field characteristics of landslide generated impulse waves. J Waterw Port Coast Ocean Eng 130:287–302. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-950X(2004)130:6(287)
Fritz HM, Hager WH, Minor HE (2001) Lituya Bay case: rockslide impact and wave run-up. Sci Tsunami Haz 19:3–19
Fritz HM, Mohammed F, Yoo J (2009) Lituya Bay landslide impact generated mega-tsunami 50(th) anniversary. Pure Appl Geophys 166:153–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-008-0435-4
He KQ, Wang SQ, Du W, Wang SJ (2010) Dynamic features and effects of rainfall on landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir region, China: using the Xintan landslide and the large Huangya landslide as the examples. Environmental Earth Sciences 59:1267–1274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0114-5
Heinrich P (1992) Nonlinear water waves generated by submarine and aerial landslides. J Waterway Port Coastal Ocean Eng 118. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-950X(1992)118:3(249).
Heller V, Spinneken J (2015) On the effect of the water body geometry on landslide-tsunamis: physical insight from laboratory tests and 2D to 3D wave parameter transformation. Coast Eng 104:113–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coastaleng.2015.06.006
Hirt CW (2010) A Continuum Model for High Concentration Granular Media: Illustrated by Application to Sand Core Blowing. In: Flow Science Report 10-TN88
Hirt CW (2013) A FLOW-3D® continuum model for granular media. Flow Science Report, 02–13
Hu YX, Yu ZY, Zhou JW (2020) Numerical simulation of landslide-generated waves during the 11 October 2018 Baige landslide at the Jinsha River. Landslides 17:2317–2328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01382-x
Huang BL, Wang SC, Zhao YB (2017) Impulse waves in reservoirs generated by landslides into shallow water. Coast Eng 123:52–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coastaleng.2017.03.003
Mao J, Zhao L, Di Y, Liu X, Xu W (2020a) A resolved CFD-DEM approach for the simulation of landslides and impulse waves. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma2019.112750
Mao J, Zhao L, Liu X, Di Y (2020b) A resolved CFDEM algorithm based on the immersed boundary for the simulation of fluid-solid interaction. Powder Technol 374:290–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.07.028
Mih WC (1999) High concentration granular sheer flow. J Hydraul Res 37:229–248. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221689909498308
Noda E (1970) Water waves generated by landslides. Jourbal of Waterway, Harbors and Coastal Engineering Division 96:835–855
Pablo Ibanez J, Hatzor YH (2018) Rapid sliding and friction degradation: lessons from the catastrophic Vajont landslide. Eng Geol 244:96–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.07.029
Panizzo A, De Girolamo P, Di Risio M, Maistri A, Petaccia A (2005a) Great landslide events in Italian artificial reservoirs. Nat Hazard 5:733–740. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-5-733-2005
Panizzo A, De Girolamo P, Petaccia A (2005b) Forecasting impulse waves generated by subaerial landslides. J Geophys Res Oceans 110. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004JC002778
Robbe-Saule M, Morize C, Henaff R, Bertho Y, Sauret A, Gondret P (2021) Experimental investigation of tsunami waves generated by granular collapse into water. J Fluid Mech 907. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2020.807.
Scheidegger A (1973) On the Prediction of the Reach and Velocity of Catastrophic Landslides. Rock Mech Rock Eng 5:231–236. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01301796
Shokina N, Aizinger V (2015) On numerical modelling of impulse water waves generated by submarine landslides. Environmental Earth Sciences 74:7387–7405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4746-3
Walder JS, Watts P, Sorensen OE, Janssen K (2003) Tsunamis generated by subaerial mass flows. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 108. https://doi.org/10.1029/2001JB000707
Wang JJ, Xiao LL, Ward SN (2021a) Tsunami Squares modeling of landslide tsunami generation considering the ‘Push Ahead’ effects in slide/water interactions: Theory, experimental validation, and sensitivity analyses. Eng Geol 288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106141
Wang JJ, Xiao LL, Ward SN, Du J (2021b) Tsunami Squares modeling of the 2007 Dayantang landslide generated waves considering the effects in slide/water interactions. Eng Geol 284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106032.
Ward SN (2001) Landslide tsunami. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 106:11201–11215. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000jb900450
Weiss R, Fritz H, Wünnemann K (2009) Hybrid modeling of the mega-tsunami runup in Lituya Bay after half a century. Geophys Res Lett 36. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009GL037814
Wiegel RL, Noda EK, Kuba EM, Gee DM, Tornberg GF (1970) Water waves generated by landslides in reservoirs. Journal of Waterway, Harbors and Coastal Engineering Division 96:307–333. https://doi.org/10.1061/AWHCAR.0000020
Wu S, Hu X, Zheng W, Zhang G, Liu C, Xu C, Zhang H, Liu Z (2022) Displacement behaviour and potential impulse waves of the Gapa landslide subjected to the Jinping Reservoir fluctuations in Southwest China. Geomorphology 397:108013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2021.108013
Xiao L, Wang J, Ward SN, Chen L (2018) Numerical modeling of the June 24, 2015, Hongyanzi landslide generated impulse waves in Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides 15:2385–2398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-1057-2
Xu WJ, Zhou Q, Dong XY (2021a) SPH-DEM coupling method based on GPU and its application to the landslide tsunami. Part II: Reproduction of the Vajont Landslide Tsunami Acta Geotechnica. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-021-01387-3
Xu WJ, Wang YJ, Dong XY (2021b) Influence of reservoir water level variations on slope stability and evaluation of landslide tsunami. Bull Eng Geol Env 80:4891–4907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02218-1
Yavari-Ramshe S, Ataie-Ashtiani B (2016) Numerical modeling of subaerial and submarine landslide-generated tsunami waves-recent advances and future challenges. Landslides 13:1325–1368. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-016-0734-2
Yeylaghi S, Moa B, Buckham B, Oshkai P, Vasquez J, Crawford C (2017) ISPH modelling of landslide generated waves for rigid and deformable slides in Newtonian and Non-Newtonian reservoir fluids. Adv Water Resour 107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2017.06.013
Yin YP, Huang BL, Chen XT, Liu GN, Wang SC (2015) Numerical analysis on wave generated by the Qianjiangping landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides 12:355–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0564-7
Zhou JW, Xu FG, Yang XG, Yang YC, Lu PY (2016) Comprehensive analyses of the initiation and landslide-generated wave processes of the 24 June 2015 Hongyanzi landslide at the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides 13:589–601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-016-0704-8
Zhou Q, Xu WJ, Dong X (2021) SPH-DEM coupling method based on GPU and its application to the landslide tsunami. Part I: Method and Validation ACTA Geotechnica. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-021-01388-2
Acknowledgements
PowerChina Huadong Engineering Corporation Limited is gratefully acknowledged for providing the study site and geological data.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 51939004 and 52109122).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Shi, A., Xu, W. et al. Numerical investigation of landslide-induced waves: a case study of Wangjiashan landslide in Baihetan Reservoir, China. Bull Eng Geol Environ 82, 110 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03148-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03148-w