Abstract
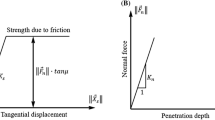
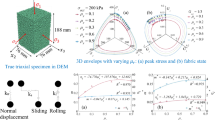
A quasi-static homogeneous drained triaxial compression test on cohesionless sand under constant lateral pressure was simulated using a three-dimensional DEM model. Grain roughness was modelled by means of symmetric clusters composed of rigid spheres imitating irregular particle shapes. The effect of grain roughness on shear strength, dilatancy, kinetic, elastic and dissipated energies was numerically analyzed. Some numerical results were compared with available experimental results.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
References
Alonso-Marroquin F., Vardoulakis I., Herrmann H., Weatherley D., Mora P.: Effect of rolling on dissipation in fault gouges. Phys. Rev. E 74, 031306 (2006)
Alonso-Marroquin F., Mühlhaus H.B., Herrmann H.: Micromechanical investigation of granular ratcheting using a discrete model of polygonal particles. Particuology 6, 390–403 (2008)
Alonso-Marroquin F., Wang Y.: An efficient algorithm for granular dynamics simulations with complex-shaped objects. Granul. Matter 11(5), 317–329 (2009)
Bardet J.P.: Introduction to computational granular mechanics. In: Cambou, B. (ed) Behaviour of Granular Materials, CISM 385, pp. 99–171. Springer, Udine (1998)
Belheine N., Plassiard J.P., Donze F.V., Darve F., Seridi A.: Numerical simulations of drained triaxial test using 3D discrete element modeling. Comput. Geotech. 36(1–2), 320–331 (2009)
Bi Z., Sun Q., Jin F., Zhang M.: Numerical study on energy transformation in granular matter under biaxial compression. Granul. Matter 13, 503–510 (2011)
Brinkgreve, R.: Geomaterial models and numerical analysis of softening. Dissertation, Delft University, pp. 1–153. (1994)
Collins I.F.: The concept of stored plastic work or frozen elastic energy in soil mechanics. Geotechnique 55, 373–382 (2005)
Collins I.F., Houlsby G.T.: Application of thermomechanical principles to the modelling of geotechnical materials. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 453, 1975–2001 (1997)
Cundall P.A., Strack O.D.L.: The distinct numerical model for granular assemblies. Geotechnique 29, 47–65 (1979)
Cundall P.A., Hart R.: Numerical modeling of discontinua. J. Eng. Comput. 9, 101–113 (1992)
Ferellec J.F., McDowell G.R.: A method to model realistic particle shape and inertia in DEM. Granul. Matter 12, 459–467 (2010)
Gudehus G., Nübel K.: Evolution of shear bands in sand. Geotechnique 54(3), 187–201 (2004)
Herrmann H.J., Luding S.: Modeling granular media on the computer. Continuum Mech. Thermodyn. 10(4), 189–231 (1998)
Hertz H.: On the contact of elastic solids. J. Reine Angew. Math. 92, 156–171 (1882)
Iwashita K., Oda M.: Rolling resistance at contacts in simulation of shear band development by DEM. ASCE J. Eng. Mech. 124(3), 285–292 (1998)
Jerier J.F., Richefeu V., Imbault D., Donze F.V.: Packing spherical discrete elements for large scale simulations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 199, 1668–1676 (2010)
Jiang M.J., Yu H.S., Harris D.: A novel discrete model for granular material incorporating rolling resistance. Comput. Geotech. 32, 340–357 (2005)
Ketterhagen W.R., Amende M.T., Hancock B.C.: Process modeling in the pharmaceutical industry using the discrete element method. Pharm. Res. Dev. 98, 442–470 (2009)
Kolymbas D., Wu W.: Recent results of triaxial tests with granular materials. Powder Technol. 60(2), 99–119 (1990)
Kozicki J., Donze F.V.: A new open-source software developed for numerical simulations using discrete modelling methods. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 197, 4429–4443 (2008)
Kozicki J., Donze F.V.: Yade-open DEM: an open-source software using a discrete element merhod to simulate granular material. Eng. Comput. 26(7), 786–805 (2009)
Kruyt N.P., Rothenburg L.: Shear strength, dilatancy, energy and dissipation in quasi-static deformation of granular materials. J. Stat. Mech. P07021, 1–10 (2006)
Luding S.: Cohesive, frictional powders: contact models for tension. Granul. Matter. 10(4), 235–246 (2008)
Maeda K., Sakai H., Kondo A., Yamaguchi T., Fukuma M., Nukudani E.: Stress-chain based micromechanics of sand with grain shape effect. Granul. Matter 12, 499–505 (2010)
Matsushima T., Chang C.S.: Quantitative evolution of the effect of irregularly shaped particles in sheared granular assemblies. Granul. Matter 13, 269–276 (2011)
Mindlin R.D., Deresiewicz H.: Elastic spheres in contact under varying oblique forces. J. Appl. Mech. Trans. ASME 75, 327–344 (1953)
Mohamed A., Gutierrez M.: Comprehensive study of the effects of rolling resistance on the stress-strain and strain localization behavior of granular materials. Granul. Matter 12(5), 527–541 (2010)
Ng T.T.: Particle shape effect on macro- and micro-behaviors of monodisperse ellipsoids. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 33, 511–552 (2009)
Oda M., Kazama H.: Micro-structure of shear band and its relation to the mechanism of dilatancy and failure of granular soils. Geotechnique 48(4), 465–481 (1998)
Ord A., Hibbs B., Regenauer-Lieb K.: Shear band emergence in granular materials—a numerical study. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 31, 373–393 (2007)
Pena A.A., Lizcano A., Alonso-Mattoquin F., Herrmann H.J.: Biaxial test simulations using a packing of polygonal particles. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 32, 143–160 (2008)
Rojek J.: Discrete element modelling of rock cutting. Comput. Methods Mater. Sci. 7(2), 224–230 (2007)
Rothenburg L., Bathurst R.J.: Micromechanical features of granular materials with planar elliptical particles. Geotechnique 42, 79–7995 (1992)
Salot C., Gotteland P., Villard P.: Influence of relative density on granular materials behaviour: DEM simulations of triaxial tests. Granul. Matter 11(4), 221–236 (2009)
Šmilauer, V., Chareyre, B.: Yade DEM Formulation. Manual (2011)
Tillemans H.J., Herrmann H.J.: Simulating deformations of granular solids under shear. Phys. A 217(3–4), 261–288 (1995)
Tejchman J., Wu W.: Numerical study on shear band patterning in a Cosserat continuum. Acta Mech. 99, 61–74 (1993)
Tejchman J.: Influence of a characteristic length on shear zone formation in hypoplasticity with different enhancements. Comput. Geotech. 31(8), 595–611 (2004)
Tejchman J.: FE modeling of shear localization in granular bodies with micro-polar hypoplasticity. In: Wu, W., Borja, R.I. (eds) Springer Series in Geomechanics and Geoengineering, Springer, Berlin (2008)
Tejchman J., Gorski J.: Computations of size effects in granular bodies within micro-polar hypoplasticity during plane strain compression. Int. J. Solids Struct. 45(6), 1546–1569 (2008)
Thornton C., Yin K.K., Adams M.J.: Numerical simulation of the impact fracture and fragmentation of agglomerates. J. Phys. D 29, 424–435 (1996)
Widulinski L., Kozicki J., Tejchman J.: Numerical simulation of a triaxial test with sand using DEM. Arch. Hydro Eng. Environ. Mech. 56(3–4), 3–26 (2009)
Widulinski L., Tejchman J., Kozicki J., Leśniewska D.: Discrete simulations of shear zone patterning in sand in earth pressure problems of a retaining wall. Int. J. Solids Struct. 48(7–8), 1191–1209 (2011)
Wu, W.: Hypoplastizität als Mathematisches Modell zum Mechanischen Verhalten granularer Stoffe. Heft 129, Institute for Soil- and Rock-Mechanics, University of Karlsruhe (1992)
Zhao, Z., Liu, C.S.: Energy dissipation and dispersion effects in granular media. Phys. Rev. E 78(031307), (2008)
Zhu H.P., Zhou Z.Y., Yang R.Y., Yu A.B.: Discrete particle simulation of particulate systems: theoretical developments. Chem. Eng. Sci. 62, 3378–3396 (2007)
Yan Y., Ji S.: Discrete element modelling of direct shear tests for a granular material. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 34, 978–990 (2010)
Acknowledgments
Scientific work has been carried out by the first two authors as a part of the Project: “Innovative resources and effective methods of safety improvement and durability of buildings and transport infrastructure in the sustainable development” financed by the European Union (POIG.01.01.02-10-106/09-01).
Open Access
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Kozicki, J., Tejchman, J. & Mróz, Z. Effect of grain roughness on strength, volume changes, elastic and dissipated energies during quasi-static homogeneous triaxial compression using DEM. Granular Matter 14, 457–468 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-012-0352-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-012-0352-1