Abstract
Purpose
A growing proportion of inguinal hernia patients are at least 65 years old. Assessing operational benefits versus risks in this group of elderly patients merits research.
Methods
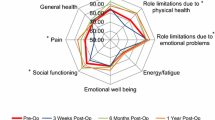
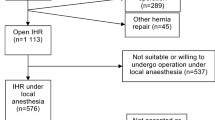
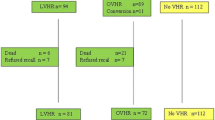
Patients in two prospective trials (1:n = 134, 89 elderly; 2:n = 398, 70 elderly) completed RAND-36 questionnaires preoperatively (response rate 100 and 98.5 %, respectively) and at 3 (98.5 %) or 12 months (89.6 %) after open inguinal hernia repair. In both groups, preoperative and postoperative quality of life data were statistically compared within age categories. Quality of life change was compared between age categories. Immediate complications were recorded.
Results
The dimensions physical functioning and pain improved significantly in the elderly and under 65-year-olds. Role functioning/physical and social functioning showed improvement as well, but less constantly. No statistical difference in complication rates was found across age groups.
Conclusion
Inguinal hernia surgery improves physical and social dimensions of quality of life among elderly and under 65-year-olds similarly.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nordin P (2011) Swedish Hernia Register. [Svenskt Bråckregister - Verksamhetsberättelse och resultatrapport 2010]
Rautiainen H, Rasilainen J (2011) [Toimenpiteelliset hoitojaksot 2010 – Vårdperioder med åtgärder 2010.] Procedural admissions 2010. 41/2011
Ruhl CE, Everhart JE (2007) Risk factors for inguinal hernia among adults in the US population. Am J Epidemiol. doi:10.1093/aje/kwm011
Scott N, Go Peter MNYH, Graham P, McCormack K, Ross Sue J, Grant A (2001) Open mesh versus non-mesh for groin hernia repair
Sanjay P, Jones P, Woodward A (2006) Inguinal hernia repair: are ASA grades 3 and 4 patients suitable for day case hernia repair? Hernia. doi:10.1007/s10029-005-0048-0
Nienhuijs SW, Remijn EE, Rosman C (2005) Hernia repair in elderly patients under unmonitored local anaesthesia is feasible. Hernia 9:218–222
Rogers FB, Guzman EA (2011) Inguinal hernia repair in a community setting: implications for the elderly. Hernia. doi:10.1007/s10029-010-0733-5
Bay-Nielsen M, Perkins FM, Kehlet H, Danish Hernia Database (2001) Pain and functional impairment 1 year after inguinal herniorrhaphy: a nationwide questionnaire study. Ann Surg 233:1–7
Nienhuijs S, Staal E, Strobbe L, Rosman C, Groenewoud H, Bleichrodt R (2007) Chronic pain after mesh repair of inguinal hernia: a systematic review. Am J Surg 194:394–400
Bay-Nielsen M, Kehlet H (2008) Anaesthesia and post-operative morbidity after elective groin hernia repair: a nation-wide study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. doi:10.1111/j.1399-6576.2007.01514.x
Gianom D, Schubiger C, Decurtins M (2002) [Trusses in the current management of hernia]. Chirurg
Primatesta P, Goldacre MJ (1996) Inguinal hernia repair: incidence of elective and emergency surgery, readmission and mortality. Int J Epidemiol 25:835–839
Kulah B, Kulacoglu IH, Oruc MT, Duzgun AP, Moran M, Ozmen MM, Coskun F (2001) Presentation and outcome of incarcerated external hernias in adults. Am J Surg
Kulah B, Polat Duzgun A, Moran M, Kulacoglu IH, Mahir Ozmen M, Coskun MSF (2001) Emergency hernia repairs in elderly patients. Am J Surg 182:455–459
Simons MP, Aufenacker T, Bay-Nielsen M, Bouillot JL, Campanelli G, Conze J, de Lange D, Fortelny R, Heikkinen T, Kingsnorth A, Kukleta J, Morales-Conde S, Nordin P, Schumpelick V, Smedberg S, Smietanski M, Weber G, Miserez M (2009) European Hernia Society guidelines on the treatment of inguinal hernia in adult patients. Hernia 13:343–403
INCA Trialists Collaboration (2011) Operation compared with watchful waiting in elderly male inguinal hernia patients: a review and data analysis. J Am Coll Surg. doi:10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2010.09.030
Mizrahi H, Parker MC (2012) Management of asymptomatic inguinal hernia: a systematic review of the evidence. Arch Surg. doi:10.1001/archsurg.2011.914;10.1001/archsurg.2011.914
Mattila K, Vironen J, Eklund A, Kontinen VK, Hynynen M (2011) Randomized clinical trial comparing ambulatory and inpatient care after inguinal hernia repair in patients aged 65 years or older. Am J Surg. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2010.04.024
Pierides G, Scheinin T, Remes V, Hermunen K, Vironen J (2012) Randomized comparison of self-fixating and sutured mesh in open inguinal hernia repair. Br J Surg. doi:10.1002/bjs.8705;10.1002/bjs.8705
Hays RD, Sherbourne CD, Mazel RM (1993) The RAND 36-Item Health Survey 1.0. Health Econ
Aalto A, Aro AR, Teperi J (1999) RAND-36 as a measure of Health-Related Quality of Life. Reliability, construct validity and reference values in the Finnish general population. Dissertation or Thesis, STAKES (National Institute of Health and Welfare): Research Reports 101
Walters SJ (2004) Sample size and power estimation for studies with health related quality of life outcomes: a comparison of four methods using the SF-36. Health Qual Life Outcomes. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-2-26
Zieren J, Zieren HU, Wenger F, Muller JM (2000) Repair of inguinal hernia in the elderly. Results of the plug-and-patch repair with special reference to quality of life. Chirurg 71:564–567
Fei L, Filippone G, Trapani V, Cecchi M, Cuttitta D (2005) New devices for inguinal hernia repair in elderly patients. Acta Biomed
Lawrence K, McWhinnie D, Jenkinson C, Coulter A (1997) Quality of life in patients undergoing inguinal hernia repair. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 79:40–45
Bitzer EM, Lorenz C, Nickel S, Dorning H, Trojan A (2008) Patient-reported outcomes in hernia repair. Hernia 12:407–414
Nikkolo C, Lepner U, Murruste M, Vaasna T, Seepter H, Tikk T (2010) Randomised clinical trial comparing lightweight mesh with heavyweight mesh for inguinal hernioplasty. Hernia. doi:10.1007/s10029-010-0630-y
Mathur S, Bartlett AS, Gilkison W, Krishna G (2006) Quality of life assessment in patients with inguinal hernia. ANZ J Surg 76:491–493
Oudhoff JP, Timmermans DR, Knol DL, Bijnen AB, van der Wal G (2007) Waiting for elective general surgery: impact on health related quality of life and psychosocial consequences. BMC Public Health 7:164
Poobalan AS, Bruce J, King PM, Chambers WA, Krukowski ZH, Smith WC (2001) Chronic pain and quality of life following open inguinal hernia repair. Br J Surg 88:1122–1126
Conflict of interest
GP declares no conflict of interest. KM declares no conflict of interest. JV declares no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pierides, G., Mattila, K. & Vironen, J. Quality of life change in elderly patients undergoing open inguinal hernia repair. Hernia 17, 729–736 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-013-1171-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-013-1171-y