Abstract
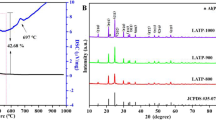
For advanced all-solid-state lithium batteries, the solid electrolyte is one of the most critical components that significantly affect battery performance. Herein, solid electrolytes 75Li2S·(25-x)P2S5·xP2O5 (mol%) are successfully prepared via wet chemistry method. Their XRD patterns show that only the crystalline phase β-Li3PS4 is detected for x = 0, 1, 2, 3, 5 mol% and the highest room-temperature ionic conductivity of 2.53 × 10−4 S cm−1 is obtained when x = 2. Next, effects of heat treatment on the structure and electrochemical performance of 75Li2S·23P2S5·2P2O5 are systematically studied. The thermal stability, morphology, structure, and crystal phase of the 75Li2S·23P2S5·2P2O5 electrolyte heated at different temperatures are characterized by thermogravimetric analysis and differential scanning calorimetry (TGA-DSC), SEM, N2 adsorption/desorption, Raman, and XRD. The 75Li2S·23P2S5·2P2O5 electrolyte heat-treated at 320 °C exhibits the highest ionic conductivity of 2.72 × 10−4 S cm−1, the lowest electronic conductivity of 4.8 × 10−9 S cm−1, and excellent electrochemical stability against the metallic lithium electrode. When the heat treatment temperature further increases from 320 to 500 °C, the electrolyte partially decomposes into Li4P2S6 and Li2S. Our results underscore the importance of heat treatment for the synthesis and performance optimization of solid electrolytes for the application of high-energy solid-state batteries.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Available upon request.
References
Goodenough JB, Kim Y (2010) Challenges for rechargeable Li batteries. Chem Mater 22(3):587–603
Scrosati B, Garche J (2010) Lithium batteries: status, prospects and future. J Power Sources 195(9):2419–2430
Cheng F, Liang J, Tao Z, Chen J (2011) Functional materials for rechargeable batteries. Adv Mater 23(15):1695–1715
Sakuda A, Hayashi A, Tatsumisago M (2013) Sulfide solid electrolyte with favorable mechanical property for all-solid-state lithium battery. Sci Rep 3(1):2261
Cao C, Li ZB, Wang XL, Zhao XB, Han WQ (2014) Recent advances in inorganic solid electrolytes for lithium batteries. Front Energy Res 2:1–10
Jung YS, Oh DY, Nam YJ, Park KH (2015) Issues and challenges for bulk-type all-solid-state rechargeable lithium batteries using sulfide solid electrolytes. Isr J Chem 55(5):472–485
Dietrich C, Weber DA, Sedlmaier SJ, Indris S, Culver SP, Walter D, Janek J, Zeier WG (2017) Lithium ion conductivity in Li2S-P2S5 glasses-building units and local structure evolution during the crystallization of superionic conductors Li3PS4, Li7P3S11 and Li4P2S7. J Mater Chem A 5(34):18111–18119
Lin Z, Liu Z, Fu W, Dudney NJ, Liang C (2013) Lithium polysulfidophosphates: a family of lithium-conducting sulfur-rich compounds for lithium-sulfur batteries. Angew Chem Int Ed 52(29):7460–7463
Liu Z, Fu W, Payzant EA, Yu X, Wu Z, Dudney NJ, Kiggans J, Hong K, Rondinone AJ, Liang C (2013) Anomalous high ionic conductivity of nanoporous β-Li3PS4. J Am Chem Soc 135(3):975–978
Muramatsu H, Hayashi A, Ohtomo T, Hama S, Tatsumisago M (2011) Structural change of Li2S-P2S5 sulfide solid electrolytes in the atmosphere. Solid State Ionics 182(1):116–119
Homma K, Yonemura M, Kobayashi T, Nagao M, Hirayama M, Kanno R (2011) Crystal structure and phase transitions of the lithium ionic conductor Li3PS4. Solid State Ionics 182(1):53–58
Miura A, Rosero-Navarro NC, Sakuda A, Tadanaga K, Phuc NHH, Matsuda A, Machida N, Hayashi A, Tatsumisago M (2019) Liquid-phase syntheses of sulfide electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium battery. Nat Rev Chem 3(3):189–198
Xu RC, Xia XH, Yao ZJ, Wang XL, Gu CD, Tu JP (2016) Preparation of Li7P3S11 glass-ceramic electrolyte by dissolution-evaporation method for all-solid-state lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 219:235–240
Wang H, Hood ZD, Xia Y, Liang C (2016) Fabrication of ultrathin solid electrolyte membranes of β-Li3PS4 nanoflakes by evaporation-induced self-assembly for all-solid-state batteries. J Mater Chem A 4(21):8091–8096
Ito S, Nakakita M, Aihara Y, Uehara T, Machida N (2014) A synthesis of crystalline Li7P3S11 solid electrolyte from 1,2-dimethoxyethane solvent. J Power Sources 271:342–345
Phuc NHH, Totani M, Morikawa K, Muto H, Matsuda A (2016) Preparation of Li3PS4 solid electrolyte using ethyl acetate as synthetic medium. Solid State Ionics 288:240–243
Yamamoto T, Phuc NHH, Muto H, Matsuda A (2019) Preparation of Li7P2S8I solid electrolyte and its application in all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries with graphite anode. Electron Mater Lett 15(4):409–414
Yubuchi S, Tsukasaki H, Sakuda A, Mori S, Hayashi A, Tatsumisago M (2019) Quantitative analysis of crystallinity in an argyrodite sulfide-based solid electrolyte synthesized via solution processing. RSC Adv 9(25):14465–14471
Gobet M, Greenbaum S, Sahu G, Liang C (2014) Structural evolution and Li dynamics in nanophase Li3PS4 by solid-state and pulsed-field gradient NMR. Chem Mater 26(11):3558–3564
Tao Y, Chen S, Liu D, Peng G, Yao X, Xu X (2015) Lithium superionic conducting oxysulfide solid electrolyte with excellent stability against lithium metal for all-solid-state cells. J Electrochem Soc 163(2):A96–A101
Tachez M, Malugani J-P, Mercier R, Robert G (1984) Ionic conductivity of and phase transition in lithium thiophosphate Li3PS4. Solid State Ionics 14(3):181–185
Brockner UPW, Cyvin BNCSJ (1986) Darstellung, Schwingungsspektrum und Normalkoordinatenanalyse des Gold-ortho-Thiophosphates, AuPS4. J Raman Spectrosc 17:257–261
Sourisseau C, Cavagnat R, Fouassier M, Brec R, Elder SH (1995) Infrared, Raman, resonance Raman spectra and lattice dynamics calculations of the solid potassium(I) nickel(II) thiophosphate compound, KNiPS4. Chem Phys 195(1-3):351–369
Sang L, Haasch RT, Gewirth AA, Nuzzo RG (2017) Evolution at the solid electrolyte/gold electrode interface during lithium deposition and stripping. Chem Mater 29(7):3029–3037
Xie D, Chen S, Zhang Z, Ren J, Yao L, Wu L, Yao X, Xu X (2018) High ion conductive Sb2O5-doped β-Li3PS4 with excellent stability against Li for all-solid-state lithium batteries. J Power Sources 389:140–147
Mizuno F, Hayashi A, Tadanaga K, Tatsumisago M (2006) High lithium ion conducting glass-ceramics in the system Li2S-P2S5. Solid State Ionics 177(26–32):2721–2725
Wang X, Xiao R, Li H, Chen L (2016) Oxygen-driven transition from two-dimensional to three-dimensional transport behaviour in β-Li3PS4 electrolyte. Phys Chem Chem Phys 18(31):21269–21277
Hayashi A, Muramatsu H, Ohtomo T, Hama S, Tatsumisago M (2014) Improved chemical stability and cyclability in Li2S-P2S5-P2O5-ZnO composite electrolytes for all-solid-state rechargeable lithium batteries. J Alloys Compd 591:247–250
Xiao R, Li H, Chen L (2015) High-throughput design and optimization of fast lithium ion conductors by the combination of bond-valence method and density functional theory. Sci Rep 5(1):14227
de Klerk NJJ, van der Maas E, Wagemaker M (2018) Analysis of diffusion in solid-state electrolytes through MD simulations, improvement of the Li-ion conductivity in β-Li3PS4 as an example. ACS Appl Energy Mater 1(7):3230–3242
Dietrich C, Sadowski M, Sicolo S, Weber DA, Sedlmaier SJ, Weldert KS, Indris S, Albe K, Janek J, Zeier WG (2016) Local structural investigations, defect formation, and ionic conductivity of the lithium ionic conductor Li4P2S6. Chem Mater 28(23):8764–8773
Han F, Yue J, Fan X, Gao T, Luo C, Ma Z, Suo L, Wang C (2016) High-performance all-solid-state lithium-sulfur battery enabled by a mixed-conductive Li2S nanocomposite. Nano Lett 16(7):4521–4527
Chen Y, Cai L, Liu Z, dela Cruz CR, Liang C, An K (2015) Correlation of anisotropy and directional conduction in β-Li3PS4 fast Li+ conductor. Appl Phys Lett 107(1):013904
C. Yu J, Xu A, Zhang L, Song R, Wu L (2004) Synthesis and characterization of porous magnesium hydroxide and oxide nanoplates. J Phys Chem B 108(1):64–70
Kamaya N, Homma K, Yamakawa Y, Hirayama M, Kanno R, Yonemura M, Ta K, Kato Y, Hama S, Kawamoto K, Mitsui A (2011) A lithium superionic conductor. Nat Mater 10(9):682–686
Han F, Westover AS, Yue J, Fan X, Wang F, Chi M, Leonard DN, Dudney NJ, Wang H, Wang C (2019) High electronic conductivity as the origin of lithium dendrite formation within solid electrolytes. Nat Energy 4(3):187–196
Yu K, Gu R, Wu L, Sun H, Ma R, Jin L, Xu Y, Xu Z, Wei X (2018) Ionic and electronic conductivity of solid electrolyte Li0.5La0.5TiO3 doped with LiO2-SiO2-B2O3 glass. J Alloys Compd 739:892–896
Maier J (2004) Ionic transport in nano-sized systems. Solid State Ionics 175(1–4):7–12
Puina W, Rodewaldb S, Ramlaub R, Heitjansa P, Maierb J (2000) Local and overall ionic conductivity in nanocrystalline CaF2. Solid State Ionics 131(1):159–164
Teragawa S, Aso K, Tadanaga K, Hayashi A, Tatsumisago M (2014) Liquid-phase synthesis of a Li3PS4 solid electrolyte using N-methylformamide for all-solid-state lithium batteries. J Mater Chem A 2(14):5095–5099
Phuc NHH, Morikawa K, Mitsuhiro T, Muto H, Matsuda A (2017) Synthesis of plate-like Li3PS4 solid electrolyte via liquid-phase shaking for all-solid-state lithium batteries. Ionics 23(8):2061–2067
Bach P, Stratmann M, Valencia-Jaime I, Romero AH, Renner FU (2015) Lithiation and delithiation mechanisms of gold thin film model anodes for lithium ion batteries: electrochemical characterization. Electrochim Acta 164:81–89
Bach P, Valencia-Jaime I, Rütt U, Gutowski O, Romero AH, Renner FU (2016) Electrochemical lithiation cycles of gold anodes observed by in situ high-energy X-ray diffraction. Chem Mater 28(9):2941–2948
Hood ZD, Kates C, Kirkham M, Adhikari S, Liang C, Holzwarth NAW (2016) Structural and electrolyte properties of Li4P2S6. Solid State Ionics 284:61–70
Funding
The work was supported by funding from Youth Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21603204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Jiuyong Li, Weiming Liu, Xiaofeng Zhang, and Yibo Ma. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Jiuyong Li and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Liu, W., Zhang, X. et al. Heat treatment effects in oxygen-doped β-Li3PS4 solid electrolyte prepared by wet chemistry method. J Solid State Electrochem 25, 1259–1269 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-021-04904-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-021-04904-2