Abstract
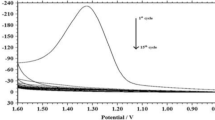
A novel and simple biosensor based on poly(indoleacetic acid) film-modified electrode (PIAA/CPE) was fabricated by electrochemical polymerization of indoleacetic acid on a carbon paste electrode (CPE) through cyclic voltammetry. The resulting electrode was characterized by scanning electron microscopy, and the electrochemical behaviors of dopamine (DA) and epinephrine (EP) at the electrode were studied. It was illustrated that PIAA/CPE had excellent electrochemical catalytic activities toward DA and EP. The anodic peak currents (I pa) were dramatically enhanced by about seven-fold for DA and ten times for EP at PIAA/CPE. Thus, the determinations of DA and EP were carried out using PIAA/CPE successfully. The linear responses were obtained in the range of 3.0 × 10−7∼7.0 × 10−4 and 1.0 × 10−6 ∼8.0 × 10−4 mol L−1 with the detection limits (3σ) of 1 × 10−7 and 4 × 10−7 mol L−1 corresponding with DA and EP, respectively. Moreover, the cathodic peaks of DA and EP were well-separated with a potential difference about 325 mV in pH 5.3 phosphate-buffered saline, so simultaneous determination of DA and EP was carried out in this paper. Additionally, the interference studies showed that the PIAA/CPE exhibited excellent selectivity in the presence of ascorbic acid (AA). With good selectivity and sensitivity, the present method has been successfully applied to the determination of DA and EP in pharmaceutical samples.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jaber M, Robinson SW, Missale C, Caron MG (1996) Neuropharmacol 35:1503–1519
Sec Kin Z, Volkan M (2005) Anal Chim Acta 547:104–108
Wang HY, Sun Y, Tang B (2002) Talanta 57:899–907
Fotopoulou MA, Ioannou PC (2002) Anal Chim Acta 462:179–185
Carrera V, Sabater E, Vilanova E, Sogorb MA (2007) J Chromatogr B 847:88–94
Muzzi C, Bertocci E, Terzuoli L, Porcelli B, Ciari I, Pagani R, Guerranti R (2008) Biomed Pharmacother 62:253–258
Vuorensola K, Sirén H, Karjalainen U (2003) J Chromatogr B 778:277–289
Manjunatha R, Suresh GS, Melo JS, D’Souza SF, Venkatesha TC (2010) Sens Actuat B 145:643–650
Chen PY, Vittal R, Nien PC, Ho KC (2009) Biosens Bioelectron 24:3504–3509
Jia Z, Liu J, Shen YB (2007) Electrochem Commun 9:2739–2743
Huang JS, Liu Y, Hou HQ, You TY (2008) Biosens Bioelectron 24:632–637
Zhu SY, Li HJ, Niu WX, Xu G (2009) Biosens Bioelectron 25:940–943
Wang Y, Chen ZZ (2009) Colloids Surf B 74:322–327
Zhou YZ, Zhang LJ, Chen SL (2009) Chinese Chem Lett 20:217–220
Zhang YZ, Cai YJ, Su S (2006) Anal Biochem 350:285–291
Wang HS, Li TH, Jia WL, Xu HY (2006) Biosens Bioelectron 22:664–669
Maciejewskaa J, Pisareka K, Bartosiewicza I, Krysinski P, Jackowska K, Biegunski AT (2011) Electrochim Acta. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2011.01.043
Waltman RJ, Diaz AF, Bargon J (1984) J Phys Chem 88:4343–4346
Pandey PC, Chauhan DS, Singh V (2009) Electrochim Acta 54:2266–2270
Laviron E (1979) J Electroanal Chem 101:19–28
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Shaanxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation for Young Scientist (No. 2009JQ2011), the Shaanxi Provincial Education Department Foundation (No. 08JK322), the Basic Research Foundation (No. JC1014), and Youth Scientist Foundation (No. RC0942) of Xi’an University of Architecture & Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., He, M., Huang, C. et al. A novel and simple biosensor based on poly(indoleacetic acid) film and its application for simultaneous electrochemical determination of dopamine and epinephrine in the presence of ascorbic acid. J Solid State Electrochem 16, 2203–2210 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-012-1646-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-012-1646-2