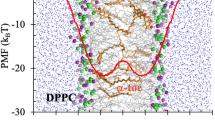
Abstract
Heroin, or diamorphine (C21H23NO5), is an opium product used for various pharmaceutical and euphoric purposes. In this work, the molecular dynamics simulation study of the heroin inside the two lipid bilayers, dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DMPC) and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC) are presented. The whole study was conducted at three different temperatures. The location of the heroin drug, the nature of the diffusion, rotational correlation function and structural variation inside both lipid bilayers is studied. Moreover, the free energy of the solvation of the drug inside both lipid bilayers is calculated. It is found that during the whole molecular dynamics study, the drug locates at the center of both lipid membranes. The effect of the temperature is not seen at the drug location. The nature of the diffusion of the heroin drug is anomalous. The radius of gyration is calculated to study the structural variations of the heroin molecule inside both lipid bilayers. It is found that the heroin molecule does not change its structure at three temperatures. From the rotational correlation function, it is seen that the drug is more hindered for rotation inside the DPPC lipid bilayer as compared to the DMPC lipid bilayer. It is applicable for all three temperatures. The rotational correlation time of the drug is decreased while the temperature of the system is increased. In the case of DMPC, there is an abrupt change in rotational correlation time while the phase is changed.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kennedy AP, Epstein DH, Jobes ML, Agage D, Tyburski M, Phillips KA, Ali AA, Bari R, Hossain SM, Hovsepian K, Rahman MM, Ertin E, Kumar S, Preston KL (2015) Continuous in-the-field measurement of heart rate Correlates of drug use, craving, stress, and mood in polydrug users. Drug Alcohol Depend. 151:159–166
Darke S, Duflou J (2016) The toxicology of heroin-related death: estimating survival times. Addiction 111(9):1607–1613
Strang J, Groshkova T, Uchtenhagen A, van den Brink W, Haasen C, Schechter MT, Lintzeris N, Bell J, Pirona A, Oviedo-Joekes E et al (2015) And heroin on trial: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials of diamorphine-prescribing as treatment for refractory heroin addiction. Br J Psychiatr 207 (1):5–14
Sharma A, Govindan P, Toukatly M, Healy J, Henry C, Senter S, Najafian B, Kestenbaum B (2018) Heroin use is associated with aa-type kidney amyloidosis in the pacific northwest. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 13:CJN–13641217
Piepenbrink MS, Samuel M, Zheng B, Carter B, Fucile C, Bunce C, Kiebala M, Khan AA, Thakar J, Maggirwar SB, Morse D, Rosenberg AF, Haughey NJ, Valenti W, Keefer MC, Kobie JJ (2016) Humoral dysregulation associated with increased systemic inflammation among injection heroin users. PLOS ONE 11:1–21, 07
Safarinejad MR, Asgari SA, Farshi A, Ghaedi G, Kolahi AA, Iravani S, Khoshdel AR (2013) The effects of opiate consumption on serum reproductive hormone levels, sperm parameters, seminal plasma antioxidant capacity and sperm DNA integrity. Reprod Toxicol 36:18–23
Pattison LP, McIntosh S, Budygin EA, Hemby SE (2012) Differential regulation of accumbal dopamine transmission in rats following cocaine, heroin and speedball self-administration. J Neurochem 122(1):138–146
Solis E, Cameron-Burr KT, Shaham Y, Kiyatkin EA (2017) Intravenous heroin induces rapid brain hypoxia and hyperglycemia that precede brain metabolic response. eNeuro
Bond C, LaForge KS, Tian M, Melia D, Zhang S, Borg L, Gong J, Schluger J, Strong JA, Leal SM, Tischfield JA, Kreek MJ, Yu L (1998) Single-nucleotide polymorphism in the human mu opioid receptor gene alters β-endorphin binding and activity. Possible implications for opiate addiction. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95(16):9608–9613
Veilleux JC, Colvin PJ, Anderson J, York C, Heinz AJ (2010) A review of opioid dependence treatment. Pharmacological and psychosocial interventions to treat opioid addiction. Clin Psychol Rev 30(2):155–166
Kumar S, Yadav DK, Choi E, Kim M (2018) Insight from molecular dynamic simulation of reactive oxygen species in oxidized skin membrane. Sci Rep 8(1):13271
Yadav DK, Kumar S, Choi E, Sharma P, Misra S, Kim M (2018) Insight into the molecular dynamic simulation studies of reactive oxygen species in native skin membrane. Front Pharmacol., 9
Johnson SJ, Bayerl TM, McDermott DC, Adam GW, Rennie AR, Thomas RK, Sackmann E Structure of an adsorbed dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer measured with specular reflection of neutrons
Kargar F, Emadi S, Fazli H (2017) The molecular behavior of a single β-amyloid inside a dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer at three different temperatures: an atomistic simulation study: Aβ interaction with DPPC: atomistic simulation. Proteins: Struct Funct Bioinf 85(7):1298–1310
Yadav DK, Kumar S, Misra S, Yadav L, Teli M, Sharma P, Chaudhary S, Kumar N , Choi EH, Kim HS, Kim MH (2018) Molecular insights into the interaction of rons and thieno [3, 2-c] pyran analogs with SIRT6/COX-2: a molecular dynamics study. Sci Rep 8(1):4777
Van Der Spoel D, Lindahl E, Hess B, Groenhof G, Mark AE, Berendsen HJ, David VDS, Erik L, Berk H, Gerrit G, Alan ME, Herman BJC (2005) Gromacs: fast, flexible, and free. J Comput Chem 26(16):1701–1718
Hess B, Kutzner C, Spoel DVD, Lindahl E (2008) Gromacs 4: Algorithms for highly efficient load-balanced and scalable molecular simulation. J Chem Theory Comput 4(3):435– 447
Oostenbrink C, Villa A, Mark AE, Gunsteren WFV (2004) A biomolecular force field based on the free enthalpy of hydration and solvation: the GROMOS force-field parameter sets 53a5 and 53a6. J Comput Chem 25 (13):1656–1676
Poger D, Gunsteren V, Wilfred F, Mark AE (2010) A new force field for simulating phosphatidylcholine bilayers. J Comput Chem 31(6):1117–1125
Malde AK, Zuo L, Breeze M, Stroet M, Poger D, Nair PC, Oostenbrink C, Mark AE (2011) An automated force field topology builder (ATB) and repository: version 1.0. J Chem Theory Comput 7 (12):4026–4037
Berendsen HJ, van der Spoel D, van Drunen R (1995) GROMACS: a message-passing parallel molecular dynamics implementation. Comput Phys Commun 91(1-3):43–56
Lindahl E, Hess B, Spoel DVD (2001) Gromacs 3.0: a package for molecular simulation and trajectory analysis. J Mol Model 7(8):306–317
Páll S., Hess B (2013) A flexible algorithm for calculating pair interactions on {SIMD} architectures. Comput Phys Commun 184(12):2641–2650
Wennberg CL, Murtola T, Hess B, Lindahl E (2013) Lennard–Jones lattice summation in bilayer simulations has critical effects on surface tension and lipid properties. J Chem Theory Comput 9(8):3527–3537
Wennberg CL, Murtola T, Páll S., Abraham MJ, Hess B, Lindahl E (2015) Direct-space corrections enable fast and accurate Lorentz–Berthelot combination rule Lennard–Jones lattice summation. J Chem Theory Comput 11(12):5737–5746
Essmann U, Perera L, Berkowitz ML, Darden T, Lee H, Pedersen LG (1995) A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J Chem Phys 103:8577–8593
Darden T, York D, Pedersen L (1993) Particle mesh Ewald: an n log (n) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J Chem Phys 98(12):10089–10092
Berger O, Edholm O, Jahnig F (2002) Molecular dynamics simulations of a fluid bilayer of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine at full hydration, constant pressure, and constant temperature. Biophys J 72(5):1997
Evans DJ, Holian BL (1985) The Nose-Hoover thermostat. J Chem Phys 83(8):4069–4074
Parrinello M, Rahman A (1981) Polymorphic transitions in single crystals: a new molecular dynamics method. J Appl Phys 52(12):7182–7190
Hess B, Bekker H, Berendsen H, Fraaije JGEM, et al (1997) Lincs: a linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J Comput Chem 18(12):1463–1472
Jorge M, Garrido NM, Queimada AJ, Economou IG, Macedo EA (2010) Effect of the integration method on the accuracy and computational efficiency of free energy calculations using thermodynamic integration. J Chem Theory Comput 6(4):1018–1027
Javanainen M, Hammaren H, Monticelli L, Jeon J, Miettinen MS, Martinez-Seara H, Metzler R, Vattulainen I (2013) Anomalous and normal diffusion of proteins and lipids in crowded lipid membranes. Faraday Discuss 161:397–417
Zhang R, Duan X, Ding M, Shi T (2018) Molecular dynamics simulation of salt diffusion in polyelectrolyte assemblies. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 122:6656–6665
Feng S, Voth GA (2010) Molecular dynamics simulations of imidazolium-based ionic liquid/water mixtures. Alkyl side chain length and anion effects. Fluid Phase Equilib 294(1):148–156
(2011) Gromacs 4.5.4 Manual: http://www.gromacs.org/Documentation/Manual
Williams T, Kelley C, et al (2013) Gnuplot 4.6: an interactive plotting program, http://gnuplot.sourceforge.net/
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF Chimera—a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25(13):1605–1612
Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K (1996) Vmd: visual molecular dynamics. J Mol Graph Model 14(1):33–38
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.