Abstract
A density functional theory study was carried out to predict the electrostatic potentials as well as average local ionization energies on both the outer and the inner surfaces of carbon, boron-nitride (BN), boron-phosphide (BP) and silicon-carbide (SiC) single-walled nanotubes. For each nanotube, the effect of tube radius on the surface potentials and calculated average local ionization energies was investigated. It is found that SiC and BN nanotubes have much stronger and more variable surface potentials than do carbon and BP nanotubes. For the SiC, BN and BP nanotubes, there are characteristic patterns of positive and negative sites on the outer lateral surfaces. On the other hand, a general feature of all of the systems studied is that stronger potentials are associated with regions of higher curvature. According to the evaluated surface electrostatic potentials, it is concluded that, for the narrowest tubes, the water solubility of BN tubes is slightly greater than that of SiC followed by carbon and BP nanotubes.

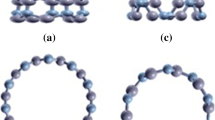
Computed surface electrostatic potential (a) and average ionization potential energy (b) of the (6,0) Si24C24H12 nanotube. Color ranges for VS(r), in kcal mol−1: red >22.91, yellow 3.83–22.91, green −15.25–3.82, blue <−15.25. Color ranges for Ī(r), in eV: red >11.35, yellow 9.63–11.35, green 7.91–9.63, blue <7.91. Black circles Surface maxima, blue surface minima.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iijima S (1991) Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 354:56–58
Malek K, Sahimi M (2010) Molecular dynamics simulations of adsorption and diffusion of gases in silicon-carbide nanotubes. J Chem Phys 132:014310
Teo BK (2003) Doing chemistry on low-dimensional silicon surfaces: silicon nanowires as platforms and templates. Coord Chem Rev 246:229–246
Ahmed R, Fazal-e-Aleem, Hashemifar SJ, Akbarzadeh H (2008) First-principles study of the structural and electronic properties of III-phosphides. Physica B 403:1876–1881
Guo CS, Fan WJ, Chen ZH, Zhang RQ (2006) First-principles study of single-walled armchair Cx(BN)y nanotubes. Solid State Commun 137:549–552
Beheshtian J, Behzadi H, Esrafili MD, Shirvani BB, Hadipour NL (2010) A computational study of water adsorption on boron nitride nanotube. Strut Chem 21:903–908
Hou S, Shen Z, Zhang J, Zhao X, Xue Z (2004) Ab initio calculations on the open end of single-walled BN nanotubes. Chem Phys Lett 393:179–183
Zhang D, Zhang RQ (2003) Ab initio calculations on the open end of single-walled BN nanotubes. Chem Phys Lett 371:426–432
Zhi C, Bando Y, Tang C, Golberg D (2010) Boron nitride nanotubes. Mater Sci Eng 70:92–111
Akdim B, Pachter R, Duan X, Adams WW (2003) Comparative theoretical study of single-wall carbon and boron-nitride nanotubes. Phys Rev B 67:245404
Schroten E, Goossens A, Schoonman J (1998) Photo- and electroreflectance of cubic boron phosphide. J Appl Phys 83:1660–1663
Ferreira VA, Leite Alves HW (2008) Boron phosphide as the buffer-layer for the epitaxial III-nitride growth: a theoretical study. J Cryst Growth 310:3973–3978
Mirzaei M (2011) Carbon doped boron phosphide nanotubes: a computational study. J Mol Model 17:89–96
Menon M, Richter E, Andriotis AN (2004) Structure and stability of SiC nanotubes. Phys Rev B 69:115322
Khan F, Broughton J (1991) Relaxation of icosahedral-cage silicon clusters via tight-binding molecular dynamics. Phys Rev B 43:11754
Menon M, Subbaswamy K (1994) Structure of Si60. Cage versus network structures. Chem Phys Lett 219:219–222
Wu A, Song Q, Yang L, Hao Q (2011) The stability and electronic structures of B or/and N doped SiC nanotubes: a first-principles study. Comput Theor Chem 977:92–96
Gali G, Kang HS (2008) Strain energy and electronic structures of silicon carbide nanotubes: density functional calculations. Phys Rev B 78:165425
Zhang SL (2001) Optimal helicity of single-walled carbon nanotube. Phys Lett A 285:207–211
Zhao MW, Xia YY, Li F, Zhang RQ, Lee ST (2005) Strain energy and electronic structures of silicon carbide nanotubes: density functional calculations. Phys Rev B 71:085312
Zhou Z, Zhao J, Chen Z, Gao X, Yan T, Wen B, Schleyer PR (2006) Comparative study of hydrogen adsorption on carbon and BN nanotubes. J Phys Chem B 110:13363–13369
Gao GH, Kang HS (2008) First principles study of NO and NNO chemisorption on silicon carbide nanotubes and other nanotubes. J Chem Theory Comput 4:1690–1697
Gao GH, Park SH, Kang HS (2009) A first principles study of NO2 chemisorption on silicon carbide nanotubes. Chem Phys 355:50–54
Zhao JX, Ding YH (2009) Can silicon carbide nanotubes sense carbon dioxide? J Chem Theory Comput 5:1099–1105
Cao FL, Xu XY, Ren W, Zao CY (2010) Theoretical study of O2 molecular adsorption and dissociation on silicon carbide nanotubes. J Phys Chem C 114:970–976
Mpourmpakis G, Froudakis GE, Lithoxoos GP, Samios J (2006) SiC nanotubes: a novel material for hydrogen storage. Nano Lett 6:1581–1583
Zhao JX, Ding YH (2008) Silicon carbide nanotubes functionalized by transition metal atoms: a density functional study. J Phys Chem C 112:2558–2564
Li F, Xia YY, Zhao MW, Liu XD, Huang BD, Yang ZH, Ji YJ, Song C (2005) Density-functional theory calculations of XH3-decorated SiC nanotubes (X = {C, Si}): structures, energetics, and electronic structures. J Appl Phys 97:104311
Wang X, Liew KM (2012) Density functional study of fluorinated single-walled silicon carbide nanotubes. J Phys Chem C 116:1702–1708
Naray-Szabo G, Ferenczy GG (1995) Molecular electrostatics. Chem Rev 95:829–847
Sauer J, Ugliengo P, Garrone E, Saunders VR (1994) Theoretical study of van der Waals complexes at surface sites in comparison with the experiment. Chem Rev 94:2095–2160
Peralta-Inga Z, Lane P, Murray JS, Boyd S, Grice ME, O’Connor CJ, Politzer P (2003) Characterization of surface electrostatic potentials of some (5,5) and (n,1) carbon and boron/nitrogen model nanotubes. Nano Lett 3:21–28
Politzer P, Lane P, Murray JS, Concha MC (2005) Comparative analysis of surface electrostatic potentials of carbon, boron/nitrogen and carbon/boron/nitrogen model nanotubes. J Mol Model 11:1–7
Politzer P, Murray JS, Lane P, Concha MC, Jin P, Peralta-Inga Z (2005) An unusual feature of end-substituted model carbon (6,0) nanotubes. J Mol Model 11:258–264
Politzer P, Murray JS, Bulat FA (2010) Average local ionization energy: a review. J Mol Model 16:1731–1742
Politzer P, Lane P, Concha MC, Ma Y, Murray JS (2007) An overview of halogen bonding. J Mol Model 13:305–311
Politzer P, Murray JS, Concha MC (2002) The complementary roles of molecular surface electrostatic potentials and average local ionization energies with respect to electrophilic processes. Int J Quantum Chem 88:19–27
Feynman RP (1939) Forces in molecules. Phys Rev 56:340–343
Hirschfelder JO, Curtiss CF, Bird RB (1954) Molecular theory of gases and liquids. Wiley, New York
Schmidt MW, Baldridge KK, Boatz JA, Elbert ST, Gordon MS, Jensen JH, Koseki S, Matsunaga N, Nguyen KA, Su SJ, Windus TL, Dupuis M, Montgomery JA (1993) General atomic and molecular electronic structure system. J Comput Chem 14:1347–1363
Esrafili MD, Behzadi H (2012) A DFT study on carbon-doping at different sites of (8, 0) boron nitride nanotube. Struct Chem. doi:10.1007/s11224-012-0110-3
Bulat FA, Toro-Labbe A, Brinck T, Murray JS, Politzer P (2010) Quantitative analysis of molecular surfaces: areas, volumes, electrostatic potentials and average local ionization energies. J Mol Model 16:1679–1691
Politzer P, Murray JS, Peralta-Inga Z (2010) Molecular surface electrostatic potentials in relation to noncovalent interactions in biological systems. Int J Quantum Chem 85:676–684
Brinck T, Murray JS, Politzer P (1992) Quantitative determination of the total local polarity (charge separation) in molecules. Mol Phys 76:609–617
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esrafili, M.D., Behzadi, H. A comparative study on carbon, boron-nitride, boron-phosphide and silicon-carbide nanotubes based on surface electrostatic potentials and average local ionization energies. J Mol Model 19, 2375–2382 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-013-1787-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-013-1787-y