Abstract
The Nafion, Dow and Aciplex systems – where the prime differences lies in the side-chain length – have been studied by molecular dynamics (MD) simulation under standard pressure and temperature conditions for two different levels of hydration: 5 and 15 water molecules per (H)SO3 end-group. Structural features such as water clustering, water-channel dimensions and topology, and the dynamics of the hydronium ions and water molecules have all been analysed in relation to the dynamical properties of the polymer backbone and side-chains. It is generally found that mobility is promoted by a high water content, with the side-chains participating actively in the H3O+/H2O transport mechanism. Nafion, whose side-chain length is intermediate of the three polymers studied, is found to have the most mobile polymer side-chains at the higher level of hydration, suggesting that there could be an optimal side-chain length in these systems. There are also some indications that the water-channel network connectivity is optimal for high water-content Nafion system, and that this could explain why Nafion appears to exhibit the most favourable overall hydronium/water mobility.

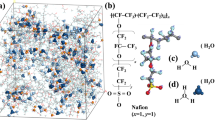
The simulation box for Aciplex with 5 water molecules per sulphonate end-group (yellow spheres). The polymer backbone is black; while side-chains are brown. The water-channel iso-surfaces are represented as blue clouds







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Larminie J, Dicks A (2003) Fuel cell systems explained. Wiley, Chichester, UK
Hickner MA, Ghassemi H, Kim YS, Einsla BR, McGrath JE (2004) Chem Rev 104:4587–4612
Smitha B, Sridher S, Khan AA (2005) J Memb Sci 259:10–26
Mauritz KA, Moore RB (2004) Chem Rev 104:4535–4586
Schuster MFH, Meyer WH, Schuster M, Kreuer KD (2004) Chem Mater 16:329–337
Tsuzuki S, Uchimaru T, Mikami M, Urata S (2004) J Chem Phys 121:9917–9924
Urata S, Tsuzuki S, Mikami M, Takada A, Uchimaru T, Sekiya A (2002) J Comput Chem 23:1472–1479
Urata S, Irisawa J, Takada A, Tsuzuki S, Shinoda W, Mikami M (2005) J Fluorine Chem 126:1312–1320
Urata S, Irisawa J, Takada A, Shinoda W, Tsuzuki S, Mikami M (2005) J Phys Chem B 109:17274–17280
Urata S, Irisawa J, Takada A, Shinoda W, Tsuzuki S, Mikami M (2005) J Phys Chem B 109:4269–4278
Urata S, Irisawa J, Takada A, Tsuzuki S, Shinod W, Mikami M (2004) Phys Chem Chem Phys 6:3325–3332
Goddard WA III, Çağin T, Blanco M, Vaidehi N, Dasgupta S, Floriano W, Belmares M, Kua J, Zamanakos G, Kashihara S, Iotov M, Gao G (2001) Comp and Theor Polym Sci 11:329–343
Deng W-Q, Molinero V, Goddard WA III (2004) J Am Chem Soc 126:15644–15645
Mayo SL, Olafson BD, Goddard WA III (1990) J Phys Chem 94:8897–8909
Jang SS, Molinero V, Çaðin T, Goddard WA III (2004) J Phys Chem B 108:3149–3157
Jang SS, Lin S-T, Çaðin T, Molinero V, Goddard III WA (2005) J Phys Chem B 109:10154–10167
Jang SS, Blanco M, Goddard WA III, Caldwell G, Ross RB (2003) Macromolecules 36:5331–5341
Walbran S, Kornyshev AA (2001) J Chem Phys 114:10039–10048
Spohr E, Commer P, Kornyshev AA (2002) J Phys Chem B 106:10560–10569
Petersen MK, Wang F, Blake NP, Metiu H, Voth GA (2005) J Phys Chem B 109:3727–3730
Petersen MK, Voth GA (2006) J Phys Chem B 110:18594–18600
Seeliger D, Hartnig C, Spohr E (2005) Electrochim Acta 50:4234–4240
Dokmaisrijan S, Spohr E (2006) J Mol Liq 129:92–100
Hektor A, Klintenberg M, Aabloo A, Thomas JO (2003) J Mater Chem 13:214–218
Karo J, Aabloo A, Thomas JO (2005) Solid State Ionics 176:3041–3044
Brandell D (2006) Presentation at the International Symposium on Polymer Electrolytes 10 (ISPE-10), Foz do Iguaçu, Brazil, 15–19 October
Tant MR, Mauritz KA, Wilkes GL (1997) Ionomers. Blackie Academic & Professional, London
Levitt M, Hirshberg M, Sharon R, Laidig KE, Daggett V (1997) J Phys Chem B 101:5051–5061
Brandell D, Ainla A, Liivat A, Aabloo A (2006) Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Li- and Na-Nafion Membranes. In: Proceedings of SPIE – The International Society for Optical Engineering, vol. 6168
Soolo E, Karo J, Kasemägi H, Kruusmaa M, Aabloo A (2006) Application of the Monte Carlo method for creation of initial models of EAP molecules for Molecular Dynamics simulation. In: Proc SPIE – The International Society for Optical Engineering, vol. 6168
Smith W, Forester T, The DL_POLY Project, Daresbury Laboratory, Daresbury, Warrington WA44 AD, England
Gierke TD (1977) J Electrochem Soc 134:319c
Gebel G (2000) Polymer 41:5829–5838
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by grants from The Swedish Research Council (VR); DB gratefully acknowledges a stipend from Fred Anderssons Stiftelse; DB and AL would also like to thank the Nordic Fuel Cell Network for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brandell, D., Karo, J., Liivat, A. et al. Molecular dynamics studies of the Nafion®, Dow® and Aciplex® fuel-cell polymer membrane systems. J Mol Model 13, 1039–1046 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-007-0230-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-007-0230-7