Abstract
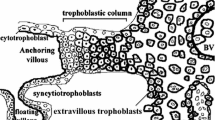
In the human placenta, embryo-derived trophoblasts aggressively invade maternal spiral arteries and transform the arteries to low-resistance large-caliber vessels. This process, which ensures adequate placental perfusion, is called maternal vascular remodeling. Histological examination showed deposition of maternal platelets in the trophoblast aggregates formed in the spiral arteries. Several lines of evidence suggest that these platelets are activated. Soluble factors released from the activated platelets, as a whole, enhanced invasive capacity of isolated trophoblasts in vitro. These findings suggest the importance of nonhemostatic platelet function in maternal vascular remodeling. In contrast, gene knockout studies suggest that maternal platelet defects are compatible with successful pregnancy in mice. Moreover, pregnant women with severe platelet defects usually accomplish an uneventful pregnancy. Thus, promotion of endovascular trophoblast infiltration by maternal platelets might not be the only mechanism that regulates maternal vascular remodeling. The maternal vascular remodeling is an essential component of human reproduction and should be secured by several complementary mechanisms. Future studies should aim to elucidate other mechanisms that could regulate endovascular trophoblast infiltration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Damsky CH, Fitzgerald ML, Fisher SJ (1982) Distribution patterns of extracellular matrix components and adhesion receptors are intricately modulated during first trimester cytotrophoblast differentiation along the invasive pathway, in vivo. J Clin Invest 89(1):210–222
Ramsey EM (1981) The story of the spiral arteries. J Reprod Med 26(8):393–399
Khong TY, De WF, Robertson WB, Brosens I (1986) Inadequate maternal vascular response to placentation in pregnancies complicated by pre-eclampsia and by small-for-gestational age infants. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 93(10):1049–1059
Frank HG, Kaufmann P (2000) Nonvillous parts and trophoblast invasion. In: Benirschke K, Kaufmann P (eds) Pathology of the human placenta. Springer, New York, pp 171–272
Genbacev O, Zhou Y, Ludlow JW, Fisher SJ (1997) Regulation of human placental development by oxygen tension. Science 277(5332):1669–1672
Sato Y, Fujiwara H, Zeng BX, Higuchi T, Yoshioka S, Fujii S (2005) Platelet-derived soluble factors induce human extravillous trophoblast migration and differentiation: platelets are a possible regulator of trophoblast infiltration into maternal spiral arteries. Blood 106(2):428–435
Zarbock A, Polanowska-Grabowska RK, Ley K (2007) Platelet-neutrophil interactions: linking hemostasis and inflammation. Blood Rev 21(2):99–111
Zhou Y, Genbacev O, Damsky CH, Fisher SJ (1998) Oxygen regulates human cytotrophoblast differentiation and invasion: implications for endovascular invasion in normal pregnancy and in pre-eclampsia. J Reprod Immunol 39(1–2):197–213
Sato Y, Higuchi T, Yoshioka S, Tatsumi K, Fujiwara H, Fujii S (2003) Trophoblasts acquire a chemokine receptor, CCR1, as they differentiate towards invasive phenotype. Development (Camb) 130(22):5519–5532
Boehlen F, Clemetson KJ (2001) Platelet chemokines and their receptors: what is their relevance to platelet storage and transfusion practice? Transfus Med 11(6):403–417
Shivdasani RA, Rosenblatt MF, Zucker-Franklin D, Jackson CW, Hunt P, Saris CJ, Orkin SH (1995) Transcription factor NF-E2 is required for platelet formation independent of the actions of thrombopoietin/MGDF in megakaryocyte development. Cell 81(5):695–704
Levin J, Peng JP, Baker GR, Villeval JL, Lecine P, Burstein SA, Shivdasani RA (1999) Pathophysiology of thrombocytopenia and anemia in mice lacking transcription factor NF-E2. Blood 94(9):3037–3047
Palumbo JS, Zogg M, Talmage KE, Degen JL, Weiler H, Isermann BH (2004) Role of fibrinogen- and platelet-mediated hemostasis in mouse embryogenesis and reproduction. J Thromb Haemost 2(8):1368–1379
Offermanns S, Toombs CF, Hu YH, Simon MI (1997) Defective platelet activation in G alpha(q)-deficient mice. Nature (Lond) 389(6647):183–186
Isermann B, Nawroth PP (2006) The role of platelets during reproduction. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb 35(1–2):23–27
James AH, Brancazio LR, Price T (2008) Aspirin and reproductive outcomes. Obstet Gynecol Surv 63(1):49–57
Askie LM, Duley L, Henderson-Smart DJ, Stewart LA, Group PC (2007) Antiplatelet agents for prevention of pre-eclampsia: a metaanalysis of individual patient data. Lancet 369(9575):1791–1798
Isermann B, Sood R, Pawlinski R, Zogg M, Kalloway S, Degen JL, Mackman N, Weiler H (2003) The thrombomodulin-protein C system is essential for the maintenance of pregnancy. Nat Med 9(3):331–337
Strickland S, Richards WG (1992) Invasion of the trophoblasts. Cell 71(3):355–357
Teesalu T, Blasi F, Talarico D (1998) Expression and function of the urokinase type plasminogen activator during mouse hemochorial placental development. Dev Dyn 213(1):27–38
Hu ZY, Liu YX, Liu K, Byrne S, Ny T, Feng Q, Ockleford CD (1999) Expression of tissue type and urokinase type plasminogen activators as well as plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 and type-2 in human and rhesus monkey placenta. J Anat 194:183–195
Nurden AT, Nurden P (2001) Inherited defects of platelet function. Rev Clin Exp Hematol 5(4):314–334; quiz following 431
Khalil A, Seoud M, Tannous R, Usta I, Shamseddine A (1998) Bernard-Soulier syndrome in pregnancy: case report and review of the literature. Clin Lab Haematol 20(2):125–128
Turner RJ, Spencer RA, Miyazawa K (1986) Successful cesarean section in a gravida with the thrombocytopenia with absent radius syndrome. A case report. J Reprod Med 31(4):260–262
Peitsidis P, Datta T, Pafilis I, Otomewo O, Tuddenham EG, Kadir RA (2010) Bernard Soulier syndrome in pregnancy: a systematic review. Haemophilia 16:584–591
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, Y., Fujiwara, H. & Konishi, I. Role of platelets in placentation. Med Mol Morphol 43, 129–133 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-010-0508-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00795-010-0508-1