Abstract
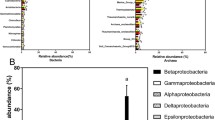
Soda pans of the Pannonian steppe are unique environments regarding their physical and chemical characteristics: shallowness, high turbidity, intermittent character, alkaline pH, polyhumic organic carbon concentration, hypertrophic condition, moderately high salinity, sodium and carbonate ion dominance. The pans are highly productive environments with picophytoplankton predominance. Little is known about the planktonic bacterial communities inhabiting these aquatic habitats; therefore, amplicon sequencing and shotgun metagenomics were applied to reveal their composition and functional properties. Results showed a taxonomically complex bacterial community which was distinct from other soda lakes regarding its composition, e.g. the dominance of class Alphaproteobacteria was observed within phylum Proteobacteria. The shotgun metagenomic analysis revealed several functional gene components related to the harsh and at the same time hypertrophic environmental conditions, e.g. proteins involved in stress response, transport and hydrolase systems targeting phytoplankton-derived organic matter. This is the first detailed report on the indigenous planktonic bacterial communities coping with the multiple extreme conditions present in the unique soda pans of the Pannonian steppe.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anil Kumar P, Srinivas TN, Madhu S et al (2010) Indibacter alkaliphilus gen. nov., sp. nov., an alkaliphilic bacterium isolated from a haloalkaline lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:721–726
Antony CP, Kumaresan D, Hunger S, Drake HL et al (2013) Microbiology of Lonar Lake and other soda lakes. ISME J 7:468–476
Atanasova NS, Oksanen HM, Bamford DH (2015) Haloviruses of archaea, bacteria, and eukaryotes. Curr Opin Microbiol 25:40–48
Banciu HL, Muntyan MS (2015) Adaptive strategies in the double-extremophilic prokaryotes inhabiting soda lakes. Curr Opin Microbiol 25:73–79
Blankenberg D, Kuster GV, Coraor N et al. (2010) Galaxy: a web-based genome analysis tool for experimentalists. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. doi:10.1002/0471142727.mb1910s89
Boros E, Nagy T, Pigniczki Cs et al (2008) The effect of aquatic birds on the nutrient load and water quality of soda pans in Hungary. Acta Zool Hung 54:207–224
Boros E, Horváth Zs, Wolfram G et al (2014) Salinity and ionic composition of the shallow soda pans in the Carpathian Basin. Ann Limnol Int J Lim 50:59–69
Boros E, Pigniczki Cs, Sápi T et al (2016) Waterbird-mediated productivity of two soda pans in the Carpathian Basin in Central Europe. Waterbirds 39:388–401
Boros E, Balogh KV, Vörös L et al (2017) Multiple extreme environmental conditions of intermittent soda pans in the Carpathian Basin (Central Europe). Limnologica 62:38–46
Borsodi AK, Knáb M, Czeibert K et al (2013) Planktonic bacterial community composition of an extremely shallow soda pond during a phytoplankton bloom revealed by cultivation and molecular cloning. Extremophiles 17:575–584
Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT (2005) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, the Proteobacteria, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Buchan A, LeCleir GR, Gulvik CA et al (2014) Master recyclers: features and functions of bacteria associated with phytoplankton blooms. Nat Rev Microbiol 12:686–698
Buchfink B, Xie C, Huson DH (2015) Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat Methods 12:59–60
Cai M, Wang L, Cai H et al (2011) Salinarimonas ramus sp. nov. and Tessaracoccus oleiagri sp. nov., isolated from a crude oil-contaminated saline soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:1767–1775
Chiu HH, Rogozin DY, Huang SP et al (2014) Aliidiomarina shirensis sp. nov., a halophilic bacterium isolated from Shira Lake in Khakasia, southern Siberia, and a proposal to transfer Idiomarina maris to the genus Aliidiomarina. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:1334–1339
Dimitriu PA, Pinkart HC, Peyton BM et al (2008) Spatial and temporal patterns in the microbial diversity of a meromictic soda lake in Washington State. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:4877–4888
Doronina N, Kaparullina E, Trotsenko Y (2014) The Family Methylophilaceae. In: Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Lory S, Stackebrandt E, Thompson T (eds) The Prokaryotes: Alphaproteobacteria and Betaproteobacteria, 4th edn. Springer, Berlin, pp 869–880
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC et al (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27:2194–2200
Eiler A, Zaremba-Niedzwiedzka K, Martínez-García M et al (2014) Productivity and salinity structuring of the microplankton revealed by comparative freshwater metagenomics. Environ Microbiol 16:2682–2698
Felföldi T, Somogyi B, Márialigeti K et al (2009) Characterization of photoautotrophic picoplankton assemblages in turbid, alkaline lakes of the Carpathian Basin (Central Europe). J Limnol 68:385–395
Felföldi T, Somogyi B, Márialigeti K et al (2011) Notes on the biogeography of non-marine planktonic picocyanobacteria: re-evaluating novelty. J Plankton Res 33:1622–1626
Foti M, Sorokin DY, Lomans B et al (2007) Diversity, activity, and abundance of sulfate-reducing bacteria in saline and hypersaline soda lakes. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2093–2100
Giardine B, Riemer C, Hardison RC et al (2005) Galaxy: a platform for interactive large-scale genome analysis. Genome Res 15:1451–1455
Goecks J, Nekrutenko A, Taylor J (2010) Galaxy: a comprehensive approach for supporting accessible, reproducible, and transparent computational research in the life sciences. Genome Biol 11:R86
Goodfellow M, Kämpfer P, Busse HJ et al (2012) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, the Actinobacteria, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Grant WD (2004) Half a lifetime in Soda lakes. In: Vantosa A (ed) Halophilic microorganisms. Springer, Berlin, pp 17–31
Hammer UT (1986) Saline lake ecosystems of the world, vol 59. Springer, New York, p 15
Huson DH, Auch AF, Qi J et al (2007) MEGAN analysis of metagenomic data. Genome Res 17:377–386
Jung YT, Park S, Lee JS et al (2006) Altererythrobacter aestiaquae sp. nov., isolated from seawater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:3943–3949
Kalyuzhnaya MG, Bowerman S, Lara JC et al (2006) Methylotenera mobilis gen. nov., sp. nov., an obligately methylamine-utilizing bacterium within the family Methylophilaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2819–2823
Kirchman DL (2002) The ecology of Cytophaga-Flavobacteria in aquatic environments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 39:91–100
Klindworth A, Pruesse E, Schweer T et al (2013) Evaluation of general 16S ribosomal RNA gene PCR primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res 41:e1
Krieg NR, Staley JT, Brown DR et al (2010) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, the Bacteroidetes, Spirochaetes, Tenericutes, (Mollicutes), Acidobacteria, Fibrobacteres, Fusobacteria, Dictyoglomi, Gemmatimonadetes, Lentisphaerae, Verrucomicrobia, Chlamydiae, and Planctomycetes, 2nd edn. Springer, New York
Krienitz L, Kotut K (2010) Fluctuating algal food populations and the occurrence of Lesser Flamingos (Phoeniconaias minor) in three Kenyan Rift Valley lakes. J Phycol 46:1088–1096
Krulwich TA, Sachs G, Padan E (2011) Molecular aspects of bacterial pH sensing and homeostasis. Nat Rev Microbiol 9:330–343
Kunin V, Engelbrektson A, Ochman H et al (2010) Wrinkles in the rare biosphere: pyrosequencing errors can lead to artificial inflation of diversity estimates. Environ Microbiol 12:118–123
Lanzén A, Simachew A, Gessesse A et al (2013) Surprising prokaryotic and eukaryotic diversity, community structure and biogeography of Ethiopian soda lakes. PLoS One 8:e72577
Liu YP, Wang YX, Li YX et al (2005) Mongoliicoccus roseus gen. nov., sp. nov., an alkaliphilic bacterium isolated from a haloalkaline lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:2206–2212
Lott SC, Voß B, Hess WR et al (2015) CoVennTree: a new method for the comparative analysis of large datasets. Front Genet 6:43
Meyer F, Paarmann D, D’Souza M et al (2008) The metagenomics RAST server—a public resource for the automatic phylogenetic and functional analysis of metagenomes. BMC Bioinform 9:386
Mühling M, Fuller NJ, Millard A et al (2005) Genetic diversity of marine Synechococcus and co-occurring cyanophage communities: evidence for viral control of phytoplankton. Environ Microbiol 7:499–508
Mulkidjanian AY, Dibrov P, Galperin MY (2008) The past and present of sodium energetics: may the sodium-motive force be with you. BBA-Bioenerg 1777:985–992
Muntyan MS, Cherepanov DA, Malinen AM et al (2015) Cytochrome cbb3 of Thioalkalivibrio is a Na+-pumping cytochrome oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci 112:7695–7700
Oh S, Caro-Quintero A, Tsementzi D et al (2011) Metagenomic insights into the evolution, function, and complexity of the planktonic microbial community of Lake Lanier, a temperate freshwater ecosystem. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:6000–6011
Oren A (1999) Bioenergetic aspects of halophilism. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:334–348
Pálffy K, Felföldi T, Mentes A et al (2014) Unique picoeukaryotic algal community under multiple environmental stress conditions in a shallow, alkaline pan. Extremophiles 18:111–119
Paul D, Kumbhare SV, Mhatre SS et al (2016) Exploration of microbial diversity and community structure of Lonar Lake: the only hypersaline meteorite crater lake within basalt rock. Front Microbiol 6:1553
Pruesse E, Peplies J, Glöckner FO (2012) SINA: accurate high-throughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes. Bioinformatics 28:1823–1829
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P et al (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucl Acids Res 41:D590–D596
Raven JA (1998) The twelfth Tansley lecture. Small is beautiful: the picophytoplankton. Funct Ecol 12:503–513
Reyes-Prieto A, Barquera B, Juarez O (2014) Origin and evolution of the sodium-pumping NADH: ubiquinone oxidoreductase. PLoS One 9:e96696
Satomi M, Kimura B, Hamada T et al (2002) Phylogenetic study of the genus Oceanospirillum based on 16S rRNA and gyrB genes: emended description of the genus Oceanospirillum, description of Pseudospirillum gen. nov., Oceanobacter gen. nov. and Terasakiella gen. nov. and transfer of Oceanospirillum jannaschii and Pseudomonas stanieri to Marinobacterium as Marinobacterium jannaschii comb. nov. and Marinobacterium stanieri comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:739–747
Schagerl M, Burian A, Gruber-Dorninger M et al (2015) Algal communities of Kenyan soda lakes with a special focus on Arthrospira fusiformis. Fottea 15:245–257
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T et al (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541
Schloss PD, Gevers D, Westcott SL (2011) Reducing the effects of PCR amplification and sequencing artifacts on 16S rRNA-based studies. PLoS One 6:e27310
Schmieder R, Edwards R (2011) Quality control and preprocessing of metagenomic datasets. Bioinformatics 27:863–864
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O et al (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13:2498–2504
Somogyi B, Felföldi T, Vanyovszki J et al (2009) Winter bloom of picoeukaryotes in Hungarian shallow turbid soda pans and the role of light and temperature. Aquat Ecol 43:735–744
Somogyi B, Felföldi T, Dinka M et al (2010) Periodic picophytoplankton predominance in a large, shallow alkaline lake (Lake Fertő/Neusiedlersee). Ann Limnol Int J Lim 46:9–19
Somogyi B, Felföldi T, Solymosi K et al (2011) Chloroparva pannonica gen. et sp. nov. (Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorophyta)—a new picoplanktonic green alga from a turbid, shallow soda pan. Phycologia 50:1–10
Somogyi B, Felföldi T, V.-Balogh K et al (2016) The role and composition of winter picoeukaryotic assemblages in shallow lakes. J Great Lakes Res 42:1420–1431
Sorokin DY, Berben T, Melton ED et al (2014) Microbial diversity and biogeochemical cycling in soda lakes. Extremophiles 18:791–809
Sorokin DY, Banciu HL, Muyzer G (2015) Functional microbiology of soda lakes. Curr Opin Microbiol 25:88–96
Teeling H, Fuchs BM, Becher D et al (2012) Substrate-controlled succession of marine bacterioplankton populations induced by a phytoplankton bloom. Science 336:608–611
Tindall BJ, Rossello-Mora R, Busse H-J et al (2010) Notes on the characterization of prokaryote strains for taxonomic purposes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:249–266
Van Trappen S, Mergaert J, Swings J (2004) Loktanella salsilacus gen. nov., sp. nov., Loktanella fryxellensis sp. nov. and Loktanella vestfoldensis sp. nov., new members of the Rhodobacter group, isolated from microbial mats in Antarctic lakes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1263–1269
Vavourakis CD, Ghai R, Rodriguez-Valera F et al (2016) Metagenomic insights into the uncultured diversity and physiology of microbes in four hypersaline soda lake brines. Front Microbiol 7:211
V.-Balogh K, Németh B, Vörös L (2009) Specific attenuation coefficients of optically active substances and their contribution to the underwater ultraviolet and visible light climate in shallow lakes and ponds. Hydrobiologia 632:91–105
Vörös L, Somogyi B, Boros E (2008) Birds cause net heterotrophy in shallow lakes. Acta Zool Acad Sci Hung 54:23–34
Vörös L, Mózes A, Somogyi B (2009) A five-year study of autotrophic winter picoplankton in Lake Balaton, Hungary. Aquat Ecol 43:727–734
Weisse T (1993) Dynamics of autotrophic picoplankton in marine and freshwater ecosystems. Adv Microb Ecol 13:327–370
Wilhelm SW, Suttle CA (1999) Viruses and nutrient cycles in the sea. Bioscience 49:781–788
Williams TJ, Wilkins D, Long E et al (2013) The role of planktonic Flavobacteria in processing algal organic matter in coastal East Antarctica revealed using metagenomics and metaproteomics. Environ Microbiol 15:1302–1317
Xing P, Hahnke RL, Unfried F et al (2015) Niches of two polysaccharide-degrading Polaribacter isolates from the North Sea during a spring diatom bloom. ISME J 9:1410–1422
Yoon JH, Kang SJ, Lee SY et al (2009) Seohaeicola saemankumensis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from a tidal flat. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2675–2679
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Emil Boros, Balázs Németh and Tamás Sápi for their assistance during sampling. We are thankful to Annamária Kéri and János Kubisch for their help in establishing the computational environment for the CoVennTree program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Hungarian Scientific Research Fund (Grants OTKA PD105407, PD112449); the Momentum Grant of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences (LP2012-19/2012) to CS.K, and the Bolyai János Research Grant (Hungarian Academy of Sciences) to B.S and T.F. Purchase of equipment was financed by the National Development Agency (Grants KMOP-4.2.1/B-10-2011-0002, TÁMOP-4.2.2/B-10/1-2010-0030).
Additional information
Communicated by A. Oren.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szabó, A., Korponai, K., Kerepesi, C. et al. Soda pans of the Pannonian steppe harbor unique bacterial communities adapted to multiple extreme conditions. Extremophiles 21, 639–649 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-017-0932-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-017-0932-4