Abstract
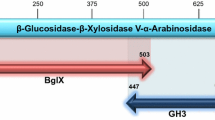
An open reading frame encoding a putative bi-functional β-d-xylosidase/α-l-arabinosidase (Sso3032) was identified on the genome sequence of Sulfolobus solfataricus P2, the predicted gene product showing high amino-acid sequence similarity to bacterial and eukaryal individual β-d-xylosidases and α-l-arabinosidases as well as bi-functional enzymes such as the protein from Thermoanaerobacter ethanolicus and barley. The sequence was PCR amplified from genomic DNA of S. solfataricus P2 and heterologous gene expression obtained in Escherichia coli, under optimal conditions for overproduction. Specific assays performed at 75°C revealed the presence in the transformed E. coli cell extracts of this archaeal activity involved in sugar hydrolysis and specific for both substrates. The recombinant protein was purified by thermal precipitation of the host proteins and ethanol fractionation and other properties, such as high thermal activity and thermostability could be determined. The protein showed a homo-tetrameric structure with a subunit of molecular mass of 82.0 kDa which was in perfect agreement with that deduced from the cloned gene. Northern blot analysis of the xarS gene indicates that it is specifically induced by xylan and repressed by monosaccharides like d-glucose and l-arabinose.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Bedford MR (1995) Mechanism of action and potential environmental benefits from the use of feed enzymes. Anim Feed Sci Tchnol 53:145–155
Beldman G, Searle-van Leeuwen MJF, De Ruiter GA, Siliha HA, Voragen AGJ (1993) Degradation of arabinans by arabinanases from Aspergillus aculeatus and Aspergillus niger. Carbohydr Polym 20:159–168
Bell SD, Kosa PL, Sigler PB, Jackson SP (1999) Orientation of the transcription preinitiation complex in archaea. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13662–13667
Bera-Maillet C, Ribot Y, Forano E (2004) Fiber-degrading systems of different strains of the genus Fibrobacter. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:2172–2179
Biely P, Mislovicova D, Toman R (1985) Soluble chromogenic substrates for the assay of endo-1,4-beta-xylanases and endo-1,4-beta-glucanases. Anal Biochem 144:142–146
Biely P (1985) Microbial xylanolytic system. Trends Biotechnol 3:286–290
Birgisson P, Fridjonsson O, Bahrani-Mougeot FK, Hreggvidsson GO, Kristjansson JK, Mattiasson B (2004) A new thermostable alpha-l-arabinofuranosidase from a novel thermophilic bacterium. Biotechnol Lett 26:1347–1351
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bragger JM, Daniel RM, Coolbear T, Morgan HW (1989) Very stable enzymes from extremely thermophilic archaebacteria and eubacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 31:556–561
Breithaupt H (2001) The hunt for living gold. The search for organisms in extreme environments yields useful enzymes for industry. EMBO Rep 2:968–971
Brent R, Ptashne M (1981) Mechanism of action of the lexA gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:4204–4208
Brock TD, Brock KM, Belly RT, Waiss RL (1972) Sulfolobus: a new genus of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria living at low pH and high temperature. Arch Microbiol 84:54–68
Cannio R, Di Prizito N, Rossi M, Morana A (2004) A xylan-degrading strain of Sulfolobus solfataricus: isolation and characterization of the xylanase activity. Extremophiles 8:117–124
Czjzek M, Ben David A, Bravman T, Shoham G, Henrissat B, Shoham Y (2005) Enzyme-substrate complex structures of a GH39 beta-xylosidase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus. J Mol Biol 353:838–846
De Rosa M, Gambacorta A, Bu’lock JD (1975) Extremely thermophilic acidophilic bacteria convergent with Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J Gen Microbiol 86:156–164
Hain J, Reiter WD, Hudepohl U, Zillig W (1992) Elements of an archaeal promoter defined by mutational analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 20:5423–5428
Haseltine C, Rolfsmeier M, Blum P (1996) The glucose effect and regulation of alpha-amylase synthesis in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus. J Bacteriol 178:945–950
Henrissat B (1991) A classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem J 280:309–316
Hespell RB, Whitehead TR (1990) Physiology and genetics of xylan degradation by gastrointestinal tract bacteria. J Dairy Sci 73:3013–3022
Joseleau JP, Comtat J, Ruel K (1992) Chemical structure of xylans and their interaction in the plant cell walls. In: Visser J, Beldman G, Voragen Mak AGI (eds) Xylans and xylanases. Progress in biotechnology. Elsevier, New York, pp 1–15
Ladenstein R, Antranikian G (1998) Proteins from hyperthermophiles: stability and enzymatic catalysis close to the boiling point of water. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 61:37–85
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nat (Lond) 227:680–685
Lama L, Calandrelli V, Gambacorta A, Nicolaus B (2004) Purification and characterization of thermostable xylanase and beta-xylosidase by the thermophilic bacterium Bacillus thermantarcticus. Res Microbiol 155:283–289
Limauro D, Cannio R, Fiorentino G, Rossi M, Bartolucci S (2001) Identification and molecular characterization of an endoglucanase gene, celS, from the extremely thermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus. Extremophiles 5:213–219
Maat J, Roza M, Verbakel J, Stam H, Santos de Silva MJ, Bosse M, Egmond MR, Hagemans MLD, van Gorcom RFM, Hessing JGM, van der Hondel CAMJJ, Rotterdam C (1992) Xylanase and their application in bakery. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Mai V, Wiegel J, Lorenz WW (2000) Cloning, sequencing, and characterization of the bifunctional β-d-xylosidase/α-l-arabinosidase from the anaerobic thermophile Thermoanaerobacter ethanolicus. Gene 247:137–143
Moracci M, Cobucci Ponzano B, Trincone A, Fusco S, De Rosa M, van Der Oost J, Sensen CW, Charlebois RL, Rossi M (2000) Identification and molecular characterization of the first alpha-xylosidase from an archaeon. J Biol Chem 275:22082–22089
Pisani FM, Rella R, Raia CA, Rozzo C, Nucci R, Gambacorta A, De Rosa M, Rossi M (1990) Thermostable beta-galactosidase from the archaebacterium Sulfolobus solfataricus. Purification and properties. Eur J Biochem 187:321–328
Saiki RK (1990) A guide to methods and applications. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DA, Sninski JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols. Academy Press Inc, San Diego, Calif, pp 13–20
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual. 3 edn. Cold Spring harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
She Q, Sing RH, Confalonieri F, Zivanovic Y, Allard G, Awayez MJ, Chan-Weiher CC, ClausenI G, Curtis BA, De Moors A, Erauso G, Fletcher C, Gordon PM, Heikamp-de Jong PM, Jeffries AC, Kozera CJ, Medina N, Peng X, Thi-Ngoc HP, Redder P, Schenk ME, Theriault C, Tolstrup N, Charlebois RL, Doolittle WF , Duguet M, Gaasterland D, Garret RA, Regan MA, Sensen CW, Van der Oost J (2001) The complete genome of the crenarchaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus P2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:7835–7840
Sunna A, Antranikian G (1997) Xylanolytic enzymes from fungi and bacteria. Crit Rev Biotechnol 17:39–67
Taiz L, Zeiger E (1999) Plant and cell architecture. In: Taiz L, Zeiger E (eds) Plant physiology. Pearson Benjamin cummings, Redwood City, pp 9–25
Uhl AM, Daniel RM (1999) The first description of an archaeal hemicellulase: the xylanase from Thermococcus zilligii strain AN1. Extremophiles 3:263–267
Varghese JN, Hrmova M, Fincher GB (1999) Three-dimensional structure of a barley beta-d-glucan exohydrolase, a family 3 glycosyl hydrolase. Struct Fold Des 7:179–190
Viikari L, Kantelinen A, Sundquist J, Linko M (1994) Xylanase in bleaching. From an idea to industry. FEMS Microbial Rev 13:335–350
Wardlerworth BN, Russel RJ, Bell SD, Taylor GL, White MS (2002) Structure of Alba: an archaeal chromatin protein modulated by acetylation. Embo J 21:4654–4662
Wong KKY, Saddler JN (1993) Application of hemicellulases in the food, feed, and pulp and paper industries. In: Coughlan MP, Hazlewood GP (eds) Hemicellulose and hemicellulases. Portland Press Ltd, London, pp 127–143
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from MIUR (Ministero dell’Istruzione, dell’Università e della Ricerca)-Decreto Direttoriale prot. no. 1105/2002 and by Centro Regionale di Competenza BioTekNet.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Antranikian
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morana, A., Paris, O., Maurelli, L. et al. Gene cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of a bi-functional β-d-xylosidase/α-l-arabinosidase from Sulfolobus solfataricus involved in xylan degradation. Extremophiles 11, 123–132 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-006-0020-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-006-0020-7