Abstract
Objectives
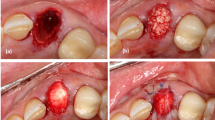
The present study goal was to assess clinically and radiographically using simvastatin (SMV) loaded xenograft for guided bone regeneration (GBR) around simultaneously placed implants with alveolar ridge splitting in patients with horizontally atrophic jaw defect.
Materials and methods
Randomized distribution of the twenty-two patients into two groups (11 patients each) was performed. Group I participants received alveolar ride splitting (ARS) with GBR using SMV gel mixed bone graft and a barrier membrane with simultaneous implant placement. Group II received the same treatment protocol without SMV gel. At the baseline, 6- and 9-months post-surgery, clinical and radiological alterations were assessed.
Results
Six months after therapy, PES records of group I were statistically significantly improved than those of group II (P < .001). Group I exhibited statistically significant expansion of the alveolar ridge over group II after 6 and 9 months (P < .001). When compared to group II over the evaluation interval between 6 and 9 months, group I demonstrated statistically substantially minimal loss of the mean marginal bone level (P < .001). At the 6- and 9-month observation periods, bone density gain was considerably higher in group I than that in group II (P < .001).
Conclusion
Alveolar ridge splitting along with GBR-augmented SMV improve the clinical and radiographical outcomes around dental implant over GBR alone.
Clinical relevance
Augmenting GBR with SMV in alveolar ridge splitting could boost implant osseointegration and enhance peri-implant tissue changes.
Clinical trial registration: NCT05020405.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data are available upon request from the corresponding author.
References
Sakkas A, Schramm A, Karsten W, Gellrich NC, Wilde F (2016) A clinical study of the outcomes and complications associated with zygomatic buttress block bone graft for limited preimplant augmentation procedures. J Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surgery 44(3):249–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2015.12.003
Sculean A, Nikolidakis D, Schwarz F (2008) Regeneration of periodontal tissues: combinations of barrier membranes and grafting materials - biological foundation and preclinical evidence: a systematic review. J Clin Periodontol 35(8 Suppl):106–116. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2008.01263.x
Liñares A, Dopico J, Magrin G, Blanco J (2023) Critical review on bone grafting during immediate implant placement. Periodontolology 2000. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12516. (Advance online publication)
Santana RB, de Mattos CM, Van Dyke T (2009) Efficacy of combined regenerative treatments in human mandibular class II furcation defects. J Periodontol 80(11):1756–1764. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2009.080605
Sculean A, Nikolidakis D, Nikou G, Ivanovic A, Chapple IL, Stavropoulos A (2015) Biomaterials for promoting periodontal regeneration in human intrabony defects: a systematic review. Periodontology 2000 68(1):182–216. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12086
Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Papanikolaou N, Coulthard P, Worthington HV (2009) Enamel matrix derivative (Emdogain(R)) for periodontal tissue regeneration in intrabony defects. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2009(4):CD003875. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD003875.pub3
Stefanini M, Rendón A, Zucchelli A, Sangiorgi M, Zucchelli G (2023) Avoiding errors and complications related to immediate implant placement in the esthetic area with a mucogingival approach. Periodontology 2000 92(1):362–372. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12491
Kheur MG, Kheur S, Lakha T, Jambhekar S, Le B, Jain V (2018) Does graft particle type and size affect ridge dimensional changes after alveolar ridge split procedure? J Oral Maxillofacial Surg 76(4):761–769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms.2017.11.002
Moy PK, Aghaloo T (2019) Risk factors in bone augmentation procedures. Periodontology 2000 81(1):76–90. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12285
Ramanauskaite A, Sader R (2022) Esthetic complications in implant dentistry. Periodontology 2000 88(1):73–85. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12412
Khairnar MS, Khairnar D, Bakshi K (2014) Modified ridge splitting and bone expansion osteotomy for placement of dental implant in esthetic zone. Contemp Clin Dent 5(1):110–114. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-237X.128684
Tatum O (1984) The omni implant system. Clarke’s Clin Dent 5:126–127
Bassetti MA, Bassetti RG, Bosshardt DD (2016) The alveolar ridge splitting/expansion technique: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implant Res 27(3):310–324. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12537
Elamrousy W, Osama M, Issa DR (2021) Autogenous bone and bioactive glass around implants placed simultaneously with ridge splitting for the treatment of horizontal bony defects: a randomised clinical trial. Int J Dent 2021:2457328. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/2457328
Vereanu AD, Tomescu D, Savu MA, Sarafoleanu C (2015) Maxillary sinus augmentation - diagnostic and surgical technique. J Transl Med Res 20(2):94–99. https://doi.org/10.21614/jtmr-20-2-38
Karacayli U, Dikicier ED, Ikicier S (2015) Dental implant placement in inadequate posterior maxilla. Curr Concepts Dental Implantol 491–499. https://doi.org/10.5772/59458
Stricker A, Fleiner J, Stübinger S, Schmelzeisen R, Dard M, Bosshardt DD (2015) Bone loss after ridge expansion with or without reflection of the periosteum. Clin Oral Implant Res 26(5):529–536. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12437
Matys J, Flieger R, Dominiak M (2016) Assessment of temperature rise and time of alveolar ridge splitting by means of Er:YAG laser, piezosurgery, and surgical saw: an ex vivo study. Biomed Res Int 2016:9654975. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9654975
Vercellotti T, De Paoli S, Nevins M (2001) The piezoelectric bony window osteotomy and sinus membrane elevation: introduction of a new technique for simplification of the sinus augmentation procedure. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 21(6):561–567
MoradiHaghgoo J (2018) Effect of implant site preparation by piezoelectric and conventional drilling on autograft cell viability: a clinical trial. J Islamic Dent Assoc IRAN 30(2):52–57
Rajanna S, Lakshmaiahenkatesh P, Suryaprakash M, Varadan K (2011) Pre prosthetic reconstruction of alveolar ridge. J Int Clin Dent Res Organ 3(2):78. https://doi.org/10.4103/2231-0754.121873
Dimova C, Evrosimovska B, Zlatanovska KZJ (2015) Alveolar augmentation using different bone substitutes. Handb Bioceram Biocomposites 1sted Switzerland; Springer, pp l-42. http://link.springer.com/referencework/10.1007/978
Chen ST, Wilson TG Jr, Hämmerle CH (2004) Immediate or early placement of implants following tooth extraction: review of biologic basis, clinical procedures, and outcomes. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 19(Suppl):12–25
Björnsson ES (2017) Hepatotoxicity of statins and other lipid-lowering agents. Liver Int 37(2):173–178. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.13308
Stellaard F, Lütjohann D (2017) The interpretation of cholesterol balance derived synthesis data and surrogate noncholesterol plasma markers for cholesterol synthesis under lipid lowering therapies. Cholesterol 2017:5046294. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5046294
Tai IC, Wang YH, Chen CH, Chuang SC, Chang JK, Ho ML (2015) Simvastatin enhances Rho/actin/cell rigidity pathway contributing to mesenchymal stem cells’ osteogenic differentiation. Int J Nanomed 10:5881–5894. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S84273
Yue X, Niu M, Zhang T et al (2016) In vivo evaluation of a simvastatin-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier for bone tissue regeneration. Nanotechnology 27(11). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/27/11/115708
Sendyk DI, Deboni MC, Pannuti CM, Naclério-Homem MG, Wennerberg A (2016) The influence of statins on osseointegration: a systematic review of animal model studies. J Oral Rehabil 43(11):873–882. https://doi.org/10.1111/joor.12438
Xue Y, Wu M, Liu Z, Song J, Luo S, Li H, Li Y, Jin L, Guan B, Lin M, Chen F, Jin C, Liu D, Li Y, Zhang X (2019) In vitro and in vivo evaluation of chitosan scaffolds combined with simvastatin-loaded nanoparticles for guided bone regeneration. J Mater Sci Mate Med 30(4):47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-019-6249-3
Caton JG, Armitage G, Berglundh T, Chapple ILC, Jepsen S, Kornman KS, Mealey BL, Papapanou PN, Sanz M, Tonetti MS (2018) A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri-implant diseases and conditions - introduction and key changes from the 1999 classification. J Clin Periodontol 45(Suppl 20):S1–S8. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12935
Farré-Pagés N, Augé-Castro ML, Alaejos-Algarra F, Mareque-Bueno J, Ferrés-Padró E, Hernández-Alfaro F (2011) Relation between bone density and primary implant stability. Med Oral Patol Oral y Cirugia Bucal 16(1):e62–e67. https://doi.org/10.4317/medoral.16.e62
Wu D, Zhou L, Lin J, Chen J, Huang W, Chen Y (2019) Immediate implant placement in anterior teeth with grafting material of autogenous tooth bone vs xenogenic bone. BMC Oral Health 19(1):266. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-019-0970-7
Thylin MR, McConnell JC, Schmid MJ, Reckling RR, Ojha J, Bhattacharyya I, Marx DB, Reinhardt RA (2002) Effects of simvastatin gels on murine calvarial bone. J Periodontol 73(10):1141–1148. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2002.73.10.1141
Gehrke P, Lobert M, Dhom G (2008) Reproducibility of the pink esthetic score–rating soft tissue esthetics around single-implant restorations with regard to dental observer specialization. J Esthet Restor Dent 20(6):375–385. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1708-8240.2008.00212.x
Ayukawa Y, Yasukawa E, Moriyama Y, Ogino Y, Wada H, Atsuta I, Koyano K (2009) Local application of statin promotes bone repair through the suppression of osteoclasts and the enhancement of osteoblasts at bone-healing sites in rats. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 107(3):336–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tripleo.2008.07.013
Chen S, Yang JY, Zhang SY, Feng L, Ren J (2011) Effects of simvastatin gel on bone regeneration in alveolar defects in miniature pigs. Chin Med J 124(23):3953–3958
Pradeep AR, Priyanka N, Kalra N, Naik SB, Singh SP, Martande S (2012) Clinical efficacy of subgingivally delivered 1.2-mg simvastatin in the treatment of individuals with Class II furcation defects: a randomized controlled clinical trial. J Periodontol 83(12):1472–1479. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2012.110716
Gao X, Zhou J, Bian Y, Huang S, Zhang D (2021) Simvastatin intervention mitigates hypercholesterolemia-induced alveolar bone resorption in rats. Exp Ther Med 21(6):628. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2021.10060
Baek KH, Lee WY, Oh KW, Tae HJ, Lee JM, Lee EJ, Han JH, Kang MI, Cha BY, Lee KW, Son HY, Kang SK (2005) The effect of simvastatin on the proliferation and differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells. J Korean Med Sci 20(3):438–444. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2005.20.3.438
Zhao S, Wen F, He F, Liu L, Yang G (2014) In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the osteogenic ability of implant surfaces with a local delivery of simvastatin. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 29(1):211–220. https://doi.org/10.11607/jomi.3147
Zhou Y, Ni Y, Liu Y, Zeng B, Xu Y, Ge W (2010) The role of simvastatin in the osteogenesis of injectable tissue-engineered bone based on human adipose-derived stromal cells and platelet-rich plasma. Biomaterials 31(20):5325–5335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.03.03738
Niu J, Ding G, Zhang L (2015) Effects of simvastatin on the osteogenic differentiation and immunomodulation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Med Rep 12(6):8237–8240
Gutierrez GE, Lalka D, Garrett IR, Rossini G, Mundy GR (2006) Transdermal application of lovastatin to rats causes profound increases in bone formation and plasma concentrations. Osteopor Int: J Establ Result Cooperation Between Eur Found Osteopor Natl Osteopor Foundation USA 17(7):1033–1042. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-006-0079-0
Xu R, Shi G, Xu L, Gu Q, Fu Y, Zhang P, Cheng J, Jiang H (2018) Simvastatin improves oral implant osseointegration via enhanced autophagy and osteogenesis of BMSCs and inhibited osteoclast activity. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 12(5):1209–1219. https://doi.org/10.1002/term.2652
Nyan M, Hao J, Miyahara T, Noritake K, Rodriguez R, Kasugai S (2014) Accelerated and enhanced bone formation on novel simvastatin-loaded porous titanium oxide surfaces. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 16(5):675–683. https://doi.org/10.1111/cid.12045
Mansour G, Al Ashwah A, Koura A (2014) Evaluation of simvastatin grafting around immediate dental implants in dogs. Implant Dent 23(2):195–199. https://doi.org/10.1097/ID.0000000000000051
Hwang R, Lee EJ, Kim MH, Li SZ, Jin YJ, Rhee Y, Kim YM, Lim SK (2004) Calcyclin, a Ca2+ ion-binding protein, contributes to the anabolic effects of simvastatin on bone. J Biol Chem 279(20):21239–21247. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M312771200
Fang W, Zhao S, He F, Liu L, Yang G (2015) Influence of simvastatin-loaded implants on osseointegration in an ovariectomized animal model. Biomed Res Int 2015:831504. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/831504
Gouda A, Helal E, Ali S, Bakry S, Yassin S (2018) Maxillary sinus lift using osteoinductive simvastatin combined with β-TCP versus β-TCP - a comparative pilot study to evaluate simvastatin enhanced and accelerated bone formation. Acta Odontol Scand 76(1):39–47. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016357.2017.1381345
Xu XC, Chen H, Zhang X, Zhai ZJ, Liu XQ, Qin A, Lu EY (2014) Simvastatin prevents alveolar bone loss in an experimental rat model of periodontitis after ovariectomy. J Transl Med 12:284. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-014-0284-0
Cruz R, Moraschini V, Calasans-Maia MD, de Almeida DCF, Sartoretto SC, Granjeiro JM (2021) Clinical efficacy of simvastatin gel combined with polypropylene membrane on the healing of extraction sockets: a triple-blind, randomized clinical trial. Clin Oral Implant Res 32(6):711–720. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.13740
Moraschini V, de Almeida D (2020) Simvastatin enhances bone regeneration in post-extraction sockets: a triple-blind, parallel-arm, randomized clinical trial. Clin Oral Implant Res 31:241–242. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.181_13644
Chauhan AS, Maria A, Managutti A (2015) Efficacy of simvastatin in bone regeneration after surgical removal of mandibular third molars: a clinical pilot study. J Maxillofac Oral Surg 14(3):578–585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-014-0697-6
Pişkin E, Işoğlu IA, Bölgen N, Vargel I, Griffiths S, Cavuşoğlu T, Korkusuz P, Güzel E, Cartmell S (2009) In vivo performance of simvastatin-loaded electrospun spiral-wound polycaprolactone scaffolds in reconstruction of cranial bone defects in the rat model. J Biomed Mater Res, Part A 90(4):1137–1151. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.32157
Maritz FJ, Conradie MM, Hulley PA, Gopal R, Hough S (2001) Effect of statins on bone mineral density and bone histomorphometry in rodents. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 21(10):1636–1641. https://doi.org/10.1161/hq1001.097781
Pénzes D, Simon F, Mijiritsky E, Németh O, Kivovics M (2020) A Modified ridge splitting technique using autogenous bone blocks-A case series. Mater (Basel, Switzerland) 13(18):4036. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13184036
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dalia Rasheed Issa and Ahmed Y. Gamal conceived the idea; Walid Elamrousy performed the surgeries; Dalia Rasheed Issa and Walid Elamrousy analyzed the data; and Dalia Rasheed Issa and Ahmed Y. Gamal led the writing.
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The present study has been approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Kafrelsheikh University, Egypt (KFSIRB200-22). The investigation was conducted according to the revised principles of the Helsinki Declaration.
Consent to participate
Research procedures were explained to all patients, and they agreed to participate in the study and signed the appropriate informed consent form before beginning of the study.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Issa, D.R., Elamrousy, W. & Gamal, A.Y. Alveolar ridge splitting and simvastatin loaded xenograft for guided bone regeneration and simultaneous implant placement: randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin Oral Invest 28, 71 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-023-05427-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-023-05427-y