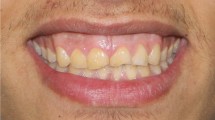
Abstract
Objectives
The objective of this study is to minimize gingival display by surgical repositioning of the upper lip and to suggest this technique as an alternative treatment modality to orthognatic surgery for treatment of excessive gingival display.
Materials and methods
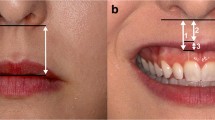
Forty-eight patients were selected with gingival display of more than 2 mm during maximal smiling. All patients underwent surgical repositioning of the upper lip, aimed at limiting elevator muscle activity to treat excessive gum exposure. Patients were regathered in 1 week for the follow-up postoperative symptoms according to VAS scale to evaluate pain and swelling. Reference values were given to patients.
Results
The study has indicated good results and stability especially to patients with skeletal class I classification along with medium and thick biotype of attached gingiva without hypermobile upper lip.
Conclusion
Surgical repositioning of the upper lip is an effective way to improve a patient’s gingival smile caused by degree I and II VME in combination with HUL as an alternative treatment modality to orthognathic surgery. This method is less invasive and cost-effective, causes minimal postoperative complications, and provides faster recovery.
Clinical relevance
Excessive gingival display (EGD) with various etiologies requires several proper treatment modalities. The proposed modified method of lip repositioning to reduce the degree of gingival display is less aggressive, reliable, and causes fewer postoperative complications compared to orthognathic surgery.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EGD:
-
Excessive gingival display
- VME:
-
Vertical maxillary excess
- HUL:
-
Hyperactive upper lip
- CEJ:
-
Cemento enamel junction
- MGJ:
-
Mucogingival junction
- NSAIDs:
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- MCPF:
-
Mucosal coronally positioned flap
References
Garber DA, Salama MA (2000) The aesthetic smile: diagnosis and treatment. Periodontol 1996(11):18–28
Gupta KK et al (2010) An innovative cosmetic technique called lip repositioning. J Indian Soc Periodontol 14(4):266–269
Haddadi P, Zare H, Azadikhah A (2021) Lip repositioning, a solution for gummy smile. Front Dent. https://doi.org/10.18502/fid.v18i15.6140
Tjan AH, Miller GD, The JG (1984) Some esthetic factors in a smile. J Prosthet Dent 51:24–28
Geron WA (2005) Influence of sex on the perception of oral and smile esthetics with different gingival display and incisal plane inclination angle. Orthod 75:778–784
Kokich V, Kiyak HA, Shapiro PA (1999) Comparing the perception of dentists and lay people to altered dental esthetics. J Esthet Dent 11:311–324
Gupta KK et al (2011) Lip repositioning with crown lengthening & gingival depigmentation. J Periodontol Implant Dent 3(1):38–42
Garguilo A, Wenz F, Orban B (1961) Dimensions and relations at the dentogingival junction in humans. J Periodontal 132:261–267
Kokich V (1996) Esthetics: the orthodontic-periodontic restorative connection. Seminars in Orthodontics 2(I1):21–30
Simon Z, Rosenblatt A, Dorfman W (2007) Eliminating a gummy smile with surgical lip repositioning. Cosmet Dent 2007:100–108
Chu SJ, Karabin S, Mistry S (2004) Short tooth syndrome: diagnosis, etiology, and treatment management. J Calif Dent Assoc 32(2):143–152
Robbins JW (1999) Differential diagnosis and treatment of excess gingival display. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent 11:265–272. quiz 273
Oliveira M, Molina G, Furtado A, Ghizorin J, Pereira J (2015) Gummy smile: a contemporary and multidisciplinary overview. Dent Hypotheses 2015:55–60
Bhola M, Fairbairn PJ, Kolhatkar S, Chu SJ, Morris T, de Campos M (2015) LipStaT: the lip stabilization technique — indications and guidelines for case selection and classification of excessive gingival display. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 35(549):559
Robbins JW (1999) Differential diagnosis and treatment of excess gingival display. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent 11:265–272
Storrer CL, Valverde FK, Santos FR, Deliberador TM (2014) Treatment of gummy smile: gingival recontouring with the containment of the elevator muscle of the upper lip and wing of nose. A surgery innovation technique. J Indian Soc Periodontol 18(5):656–660
Simon Z, Rosenblatt A (2007) Eliminating a gummy smile with surgical lip repositioning. Cosmet Dent 23:100–108
Rosenblatt A, Simon Z (2006) Lip repositioning for reduction of excessive gingival display. Int J Perio Rest Dent 26:433–437
Hao Wu et al (2010) Classification and craniofacial features of gummy smile in adolescents. J Craniofac Surg 21:1474–1479
Peck S, Peck L, Kataja M (1992) The gingival smile line. Angle Orthod 62:91–100
Miskinyar SA (1983) A new method for correcting a gummy smile. Plast Reconstr Surg 72:397–400
Rubinstein AM, Kostianovsky AS (1973) Cosmetic surgery for the malformation of the laugh: original technique (in Spanish). Prensa Med Argent 60:952
Litton C, Fournier P (1979) Simple surgical correction of the gummy smile. Plast Reconstr Surg 63:372–373
Polo M (2016) Commentary on: Botulinum toxin for the treatment of excessive gingival display: a systematic review. Aesthetic Surg J 36(1):89–92
Rees TD, La Trenta GS (1989) The long face syndrome and rhinoplasty. Semin Plast Surg 3(2):1–23
Kim SG, Park SS (2007) Incidence of complications and problems related to orthognathic surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65(12):2438–2444
Foudah MA (2019) Lip repositioning: an alternative to invasive surgery a 4 year follow up case report. Saudi Dent J 31:78–84
Humayun N, Kolhatkar S, Souiyas J, Bhola M (2010) Mucosal coronally positioned flap for the management of excessive gingival display in the presence of hypermobility of the upper lip and vertical maxillary excess: a case report. J Periodontol 81:1858–1863
Ezquerra F, Berrazueta MJ, Ruiz-Capillas A, Arregui JS (1999) New approach to the gummy smile. Plast Reconstr Surg 104(4):1143–50
Faus-Matoses V, Faus-Matoses I, Jorques-Zafrilla A, Faus-Llácer VJ (2018) Lip repositioning technique. A simple surgical procedure to improve the smile harmony. J Clin Exp Dent 10(4):408–412
Gabrić Pandurić D, Blašković M, Brozović J, Sušić M (2014) Surgical treatment of excessive gingival display using lip repositioning technique and laser gingivectomy as an alternative to orthognathic surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 72(2):404.1–11
Abdullah WA, Khalil HS, Alhindi MM, Marzook H (2014) Modifying gummy smile: a minimally invasive approach. J Contemp Dent Pract 15(6):821–826
Kamer F (1979) “How do I do it”—plastic surgery, practical suggestions on facial plastic surgery, smile surgery. Laryngoscope 89:1528–1532
Gabrić Pandurić D, Blasković M, Brozović J, Sušić M (2014) Surgical treatment of excessive gingival display using lip repositioning technique and laser gingivectomy as an alternative to orthognathic surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 72:4041–4051
Foudah MA (2019) Lip repositioning: an alternative to invasive surgery a 4 year follow up case report. Saudi Dent J 31:78–84
Sybaite J, Sharma P, Fine P, Blizard R, Leung A (2020) The influence of varying gingival display of maxillary anterior teeth on the perceptions of smile aesthetics. J Dent 103:103504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdent.2020.103504
Ozturan S, Ay E, Sagir S (2014) Case series of laser-assisted treatment of excessive gingival display: an alternative treatment. Photomed Laser Surg 32:517–523
Mantovani MB, Souza EC, Marson FC, Corrêa GO, Progiante PS, Silva CO (2016) Use of modified lip repositioning technique associated with esthetic crown lengthening for treatment of excessive gingival display: a case report of multiple etiologies. J Indian Soc Periodontol 20(1):82–87
Dinker S, Anitha A, Sorake A, Kumar K (2014) Management of gummy smile with botulinum toxin type-A: a case report. J Int Oral Health 6(1):111–115
Suber JS, Dinh TP, Prince MD, Smith PD (2014) OnabotulinumtoxinA for the treatment of a “gummy smile.” Aesthet Surg J 34:432–437
Ishida LH, Ishida LC, Ishida J, Grynglas J, Alonso N, Ferreira MC (2010) Myotomy of the levator labii superioris muscle and lip repositioning: a combined approach for the correction of gummy smile. Plast Reconstr Surg 126:1014–1019
Silva CO, Ribeiro-Junior NV, Campos TV, Rodrigues JG, Tatakis DN (2013) Excessive gingival display: treatment by a modified lip repositioning technique. J Clin Periodontol 40:260–265
Storrer CL, Valverde FK, Santos FR, Deliberador TM (2014) Treatment of gummy smile: gingival recontouring with the containment of the elevator muscle of the upper lip and wing of nose. A surgery innovation technique. J Indian Soc Periodontol 18:656–660
Grover HS, Gupta A, Luthra S (2014) Lip repositioning surgery: a pioneering technique for perio-esthetics. Contemp Clin Dent 5:142–145
Ellenbogen R, Swara N (1984) The improvement of the gummy smile using the implant spacer technique. Ann Plast Surg 12:16–24
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The study was reviewed and approved by the local Ethics Committee and in accordance with the norms of the World Medical Association and the Helsinki Declaration.
Consent to participate
The patients were informed about the study both verbally and in writing and provided their written consent for participation.
Consent for publication
The patient was properly informed and provided his/her written consent for publication of this case report and accompanying images.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hakobyan, G., Boyadjian, A., Boyadjian, M. et al. Clinical advantages of improving the excessive gingival display (EGD) by surgical repositioning of the upper lip. Clin Oral Invest 26, 7265–7275 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-022-04687-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-022-04687-4