Abstract
Objectives
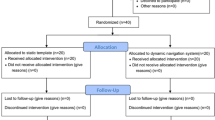
To compare the accuracy and primary stability of tapered and straight implants undergoing immediate implant placement with dynamic navigation.
Materials and methods
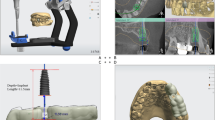
Patients with compromised anterior teeth in maxilla were recruited and allocated randomly into (1) tapered implant group (TI group) and (2) straight implant group (SI group). Implants were inserted into fresh sockets with dynamic navigation. Three-dimensional platform deviation, apex deviation, angular deviation, insertion torque value (ITV) and implant stability quotient (ISQ) were recorded.
Results
Twenty patients with 20 implants were included. The overall platform, apex, and angular deviation were 0.87 ± 0.35 mm, 0.81 ± 0.34 mm, and 2.40 ± 1.31°, respectively. The accuracy was 0.86 ± 0.26 mm, 0.76 ± 0.33 mm, and 2.49 ± 1.54° for TI, and 0.89 ± 0.44 mm, 0.88 ± 0.36 mm, and 2.31 ± 1.01° for SI, with no significant difference (p = 0.85, 0.45, 0.76). Sagittal root position classification (SRP) class I may obtain greater error in numerical values in straight implants (0.97 ± 0.47 mm vs. 0.6 ± 0.16 mm, 0.92 ± 0.36 mm vs. 0.73 ± 0.36 mm, 2.48 ± 1.19° vs. 1.71 ± 0.14°). The overall ISQ was 60.74. ISQ was 60.48 for TI and 60.96 for SI, with no significant difference. Acceptable ITV (> 15 Ncm) was achieved in most of the included patients (SI 7/10, TI 9/10).
Conclusions
High accuracy and primary stability of immediate implant placement could be achieved both in tapered and straight implants with dynamic navigation systems.
Clinical relevance
Tapered and straight implants did not reach a consensus on which was better in immediate implant regarding to accuracy and primary stability. Our study demonstrated implant macrodesign did not affect accuracy and primary stability in immediate implant using dynamic navigation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
D’Haese J, Ackhurst J, Wismeijer D (2000) De Bruyn H and Tahmaseb A (2017) Current state of the art of computer-guided implant surgery. Periodontol 73:121–133. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12175
Jung RE, Schneider D, Ganeles J, Wismeijer D, Zwahlen M, Hämmerle CH, Tahmaseb A (2009) Computer technology applications in surgical implant dentistry: a systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 24(Suppl):92–109
Vercruyssen M, Fortin T, Widmann G (2000) Jacobs R and Quirynen M (2014) Different techniques of static/dynamic guided implant surgery: modalities and indications. Periodontol 66:214–227. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12056
Wei SM, Zhu Y, Wei JX, Zhang CN, Shi JY, Lai HC (2021) Accuracy of dynamic navigation in implant surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res 32:383–393. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.13719
Kaewsiri D, Panmekiate S, Subbalekha K, Mattheos N, Pimkhaokham A (2019) The accuracy of static vs. dynamic computer-assisted implant surgery in single tooth space: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Oral Implants Res 30:505–514. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.13435
Buser D, Chappuis V (2000) Belser UC and Chen S (2017) Implant placement post extraction in esthetic single tooth sites: when immediate, when early, when late? Periodontol 73:84–102. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12170
Shi JY, Wang R, Zhuang LF, Gu YX, Qiao SC, Lai HC (2015) Esthetic outcome of single implant crowns following type 1 and type 3 implant placement: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res 26:768–774. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12334
Testori T, Weinstein T, Scutellà F (2000) Wang HL and Zucchelli G (2018) Implant placement in the esthetic area: criteria for positioning single and multiple implants. Periodontol 77:176–196. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12211
Blanco J, Carral C (2000) Argibay O and Liñares A (2019) Implant placement in fresh extraction sockets. Periodontol 79:151–167. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12253
Kotsakis GA, Olmedo DG (2000) (2021) Peri-implantitis is not periodontitis: scientific discoveries shed light on microbiome-biomaterial interactions that may determine disease phenotype. Periodontol 86:231–240. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12372
Decker AM (2000) Kapila YL and Wang HL (2021) The psychobiological links between chronic stress-related diseases, periodontal/peri-implant diseases, and wound healing. Periodontol 87:94–106. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12381
Feine J, Abou-Ayash S, Al Mardini M, de Santana RB, Bjelke-Holtermann T, Bornstein MM, Braegger U, Cao O, Cordaro L, Eycken D, Fillion M, Gebran G, Huynh-Ba G, Joda T, Levine R, Mattheos N, Oates TW, Abd-Ul-Salam H, Santosa R, Shahdad S, Storelli S, Sykaras N, Treviño Santos A, Stephanie Webersberger U, Williams MAH, Wilson TG Jr, Wismeijer D, Wittneben JG, Yao CJ, Zubiria JPV (2018) Group 3 ITI Consensus Report: patient-reported outcome measures associated with implant dentistry. Clin Oral Implants Res 29(Suppl 16):270–275. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.13299
Block MS, Emery RW, Lank K, Ryan J (2017) Implant Placement Accuracy Using Dynamic Navigation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 32:92–99. https://doi.org/10.11607/jomi.5004
Pellegrino G, Bellini P, Cavallini PF, Ferri A, Zacchino A, Taraschi V, Marchetti C and Consolo U (2020) Dynamic navigation in dental implantology: the influence of surgical experience on implant placement accuracy and operating time. An in Vitro Study. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:2153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17062153
Aydemir CA, Arısan V (2020) Accuracy of dental implant placement via dynamic navigation or the freehand method: A split-mouth randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res 31:255–263. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.13563
Kan JY, Roe P, Rungcharassaeng K (2015) Effects of implant morphology on rotational stability during immediate implant placement in the esthetic zone. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 30:667–670. https://doi.org/10.11607/jomi.3885
El Kholy K, Ebenezer S, Wittneben JG, Lazarin R, Rousson D, Buser D (2019) Influence of implant macrodesign and insertion connection technology on the accuracy of static computer-assisted implant surgery. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 21:1073–1079. https://doi.org/10.1111/cid.12836
Schnutenhaus S, Edelmann C, Rudolph H (2021) Does the macro design of an implant affect the accuracy of template-guided implantation? A prospective clinical study. Int J Implant Dent 7:42. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40729-021-00320-3
Esposito M, Hirsch JM, Lekholm U, Thomsen P (1998) Biological factors contributing to failures of osseointegrated oral implants. (II) Etiopathogenesis. Eur J Oral Sci 106:721–764. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0909-8836.t01-6-.x
Lang NP, Tonetti MS, Suvan JE, Pierre Bernard J, Botticelli D, Fourmousis I, Hallund M, Jung R, Laurell L, Salvi GE, Shafer D, Weber HP (2007) Immediate implant placement with transmucosal healing in areas of aesthetic priority. A multicentre randomized-controlled clinical trial I. Surgical outcomes Clin Oral Implants Res 18:188–196. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2006.01371.x
West JD, Oates TW (2007) Identification of stability changes for immediately placed dental implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 22:623–630
Ellis R, Chen S, Davies H, Fitzgerald W, Xu J, Darby I (2020) Primary stability and healing outcomes of apically tapered and straight implants placed into fresh extraction sockets. A pre-clinical in vivo study. Clin Oral Implants Res 31:705–714. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.13618
Shi JY, Lv XL, Gu YX, Lai HC (2020) Angulated screw-retained and cemented implant crowns following flapless immediate implant placement in the aesthetic region: a 1-year prospective cohort study. Int J Oral Implantol (Berl) 13:269–277
Kan JYK, Rungcharassaeng K, Deflorian M, Weinstein T (2000) Wang H-L and Testori T (2018) Immediate implant placement and provisionalization of maxillary anterior single implants. Periodontol 77:197–212. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12212
Chen CK, Yuh DY, Huang RY, Fu E, Tsai CF, Chiang CY (2018) Accuracy of implant placement with a navigation system, a laboratory guide, and freehand drilling. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 33:1213–1218. https://doi.org/10.11607/jomi.6585
Mediavilla Guzmán A, Riad Deglow E, Zubizarreta-Macho Á, Agustín-Panadero R and Hernández Montero S (2019) Accuracy of computer-aided dynamic navigation compared to computer-aided static navigation for dental implant placement: an in vitro study. J Clin Med 8:2123. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122123
Gargallo-Albiol J, Barootchi S, Salomó-Coll O, Wang HL (2019) Advantages and disadvantages of implant navigation surgery. A systematic review Ann Anat 225:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aanat.2019.04.005
Schnutenhaus S, Brunken L, Edelmann C, Dreyhaupt J, Rudolph H, Luthardt RG (2020) Alveolar ridge preservation and primary stability as influencing factors on the transfer accuracy of static guided implant placement: a prospective clinical trial. BMC Oral Health 20:178. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-020-01155-x
Chen Z, Li J, Sinjab K, Mendonca G, Yu H, Wang HL (2018) Accuracy of flapless immediate implant placement in anterior maxilla using computer-assisted versus freehand surgery: A cadaver study. Clin Oral Implants Res 29:1186–1194. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.13382
Kan JY, Roe P, Rungcharassaeng K, Patel RD, Waki T, Lozada JL, Zimmerman G (2011) Classification of sagittal root position in relation to the anterior maxillary osseous housing for immediate implant placement: a cone beam computed tomography study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 26:873–876
Sakoh J, Wahlmann U, Stender E, Nat R, Al-Nawas B, Wagner W (2006) Primary stability of a conical implant and a hybrid, cylindric screw-type implant in vitro. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 21:560–566
Torroella-Saura G, Mareque-Bueno J, Cabratosa-Termes J, Hernández-Alfaro F, Ferrés-Padró E, Calvo-Guirado JL (2015) Effect of implant design in immediate loading. A randomized, controlled, split-mouth, prospective clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res 26:240–244. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12506
Kim Y-Y, Song YW, Kim MJ, Cha J-K, Park J-M, Kim J-H and Jung U-W Immediate loading of fixed partial prostheses reconstructed using either tapered or straight implants in the posterior area: a randomized clinical trial. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 23:703-715. https://doi.org/10.1111/cid.13039
Chrcanovic BR, Albrektsson T, Wennerberg A (2014) Reasons for failures of oral implants. J Oral Rehabil 41:443–476. https://doi.org/10.1111/joor.12157
Pozzi A, Arcuri L, Carosi P, Nardi A, Kan J (2021) Clinical and radiological outcomes of novel digital workflow and dynamic navigation for single-implant immediate loading in aesthetic zone: 1-year prospective case series. Clin Oral Implants Res. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.13839
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Xuhui Zhang (Stanford University, Ph.D. in Operation Research) for statistical consulting and language editing.
Funding
This work was financially supported by Shanghai Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases (19411950100) and Clinical Research Program of Ninth People’s Hospital affiliated Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine (JYLJ201909).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Concept/design: X.M.Z, H.C.L, and S.M.W. Surgery operation: J.Y.S. Data analysis/interpretation: S.M.W. Drafting article: S.M.W, J.Y.S, S.C.Q, and X.Z. Critical revision of article: X.M.Z and H.C.L. Statistics: X.Z. Data collection: S.C.Q. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of Shanghai Ninth People’s Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University (approval number: SH9H-2020-T410-2) and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, SM., Shi, JY., Qiao, SC. et al. Accuracy and primary stability of tapered or straight implants placed into fresh extraction socket using dynamic navigation: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin Oral Invest 26, 2733–2741 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-021-04247-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-021-04247-2