Abstract
Objectives
The objective of this study is to evaluate the effects of treatment modalities on titanium surface characteristics and surrounding tissues.
Materials and methods
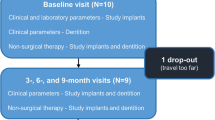
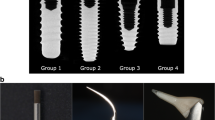
Eighteen participants each had four titanium healing caps (HC) attached to four newly inserted implants. After healing, each HC was randomly assigned to either (1) titanium curettes (TC), (2) stainless steel ultrasonic tip (PS), (3) erythritol air-polishing powder (EP), or (4) only rubber cup polishing (CON). Probing depths (PD), bleeding on probing (BOP), matrix metalloproteinase 8 (MMP-8), and periopathogens were recorded before and 3 months following instrumentation. After final assessments, HCs were removed, cleaned, and subjected to (a) bacterial colonization (Streptococcus gordonii, 24 h; mixed culture, 24 h) and (b) gingival fibroblasts (5 days). HC surfaces were analyzed with a scanning electron microscope (SEM).
Results
No significant differences between the groups were evident before or after instrumentation for PD and BOP (except TC showed a significant decrease in PD; p = 0.049). MMP-8 levels and bacterial loads were always very low. MMP-8 decreased further after instrumentation, while bacteria levels showed no change. No significant differences (p > 0.05) were evident in bacterial colonization or fibroblast attachment. A comparison of the overall mean SEM surface roughness scores showed a significant difference between all groups (p < 0.0001) with the lowest roughness after EP.
Conclusions
All treatments performed yielded comparable outcomes and may be implemented safely.
Clinical relevance
Clinicians may fear implant surface damage, but all instrumentation types are safe and non-damaging. They can be implemented as needed upon considering the presence of staining and soft and hard deposits.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Derks J, Tomasi C (2015) Peri-implant health and disease. A systematic review of current epidemiology. J Clin Periodontol 42(Suppl 16):S158–S171. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpe.12334
Renvert S, Roos-Jansåker A-M, Claffey N (2008) Non-surgical treatment of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis: a literature review. J Clin Periodontol 35(8 Suppl):305–315. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2008.01276.x
Armitage GC, Xenoudi P (2016) Post-treatment supportive care for the natural dentition and dental implants. Periodontol 71(1):164–184. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12122
Louropoulou A, Slot DE, Van der Weijden FA (2012) Titanium surface alterations following the use of different mechanical instruments: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res 23(6):643–658. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2011.02208.x
Louropoulou A, Slot DE, Van der Weijden FA (2015) Influence of mechanical instruments on the biocompatibility of titanium dental implants surfaces: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res 26(7):841–850. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12365
Quirynen M, Bollen CM (1995) The influence of surface roughness and surface-free energy on supra- and subgingival plaque formation in man. A review of the literature. J Clin Periodontol 22(1):1–14
Teughels W, Van Assche N, Sliepen I, Quirynen M (2006) Effect of material characteristics and/or surface topography on biofilm development. Clin Oral Implants Res 17(S2):68–81. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2006.01353.x
Duarte PM, Reis AF, de Freitas PM, Ota-Tsuzuki C (2009) Bacterial adhesion on smooth and rough titanium surfaces after treatment with different instruments. J Periodontol 80(11):1824–1832. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2009.090273
Bollen CM, Papaioanno W, Van Eldere J, Schepers E, Quirynen M, van Steenberghe D (1996) The influence of abutment surface roughness on plaque accumulation and peri-implant mucositis. Clin Oral Implants Res 7(3):201–211. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0501.1996.070302.x
Marín-Pareja N, Salvagni E, Guillem-Marti J, Aparicio C, Ginebra MP (2014) Collagen-functionalised titanium surfaces for biological sealing of dental implants: effect of immobilisation process on fibroblasts response. Colloids Surf B Biointerface 122:601–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2014.07.038
Zhao B, van der Mei HC, Subbiahdoss G, de Vries J, Rustema-Abbing M, Kuijer R, Busscher HJ, Ren Y (2014) Soft tissue integration versus early biofilm formation on different dental implant materials. Dent Mater 30(7):716–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2014.04.001
Guillem-Marti J, Delgado L, Godoy-Gallardo M, Pegueroles M, Herrero M, Gil FJ (2013) Fibroblast adhesion and activation onto micro-machined titanium surfaces. Clin Oral Implants Res 24(7):770–780. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2012.02451.x
Figuero E, Graziani F, Sanz I, Herrera D, Sanz M (2014) Management of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis. Periodontol 66(1):255–273. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12049
Schwarz F, Schmucker A, Becker J (2015) Efficacy of alternative or adjunctive measures to conventional treatment of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Implant Dent 1(1):22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40729-015-0023-1
Schmidt KE, Auschill TM, Heumann C, Frankenberger R, Eick S, Sculean A, Arweiler NB (2017) Influence of different instrumentation modalities on the surface characteristics and biofilm formation on dental implant neck, in vitro. Clin Oral Implants Res 28(4):483–490. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.12823
Eick S, Bender P, Flury S, Lussi A, Sculean A (2013) In vitro evaluation of surface roughness, adhesion of periodontal ligament fibroblasts, and Streptococcus gordonii following root instrumentation with Gracey curettes and subsequent polishing with diamond-coated curettes. Clin Oral Investig 17(2):397–404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-012-0719-z
Bain CA (1998) An in vitro and in vivo evaluation of various implant-cleaning instruments. Quintessence Int 29(7):423–427
Pontoriero R, Tonelli MP, Carnevale G, Mombelli A, Nyman SR, Lang NP (1994) Experimentally induced peri-implant mucositis. A clinical study in humans. Clin Oral Implants Res 5(4):254–259. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0501.1994.050409.x
Salvi GE, Aglietta M, Eick S, Sculean A, Lang NP (2012) Reversibility of experimental peri-implant mucositis compared with experimental gingivitis in humans. Clin Oral Implants Res 23(2):182–190. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2011.02220.x
Máximo MB, de Mendonça AC, Renata Santos V, Figueiredo LC, Feres M, Duarte PM (2009) Short-term clinical and microbiological evaluations of peri-implant diseases before and after mechanical anti-infective therapies. Clin Oral Implants Res 20(1):99–108. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2008.01618.x
Cochis A, Fini M, Carrassi A, Migliario M, Visai L, Rimondini L (2013) Effect of air polishing with glycine powder on titanium abutment surfaces. Clin Oral Implants Res 24(8):904–909. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2012.02490.x
Brägger U, Bürgin WB, Hämmerle CH, Lang NP (1997) Associations between clinical parameters assessed around implants and teeth. Clin Oral Implants Res 8(5):412–421. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0501.1997.080508.x
Papaioannou W, Quirynen M, Van Steenberghe D (1996) The influence of periodontitis on the subgingival flora around implants in partially edentulous patients. Clin Oral Implants Res 7(4):405–409. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0501.1996.070415.x
Quirynen M, Papaioannou W, van Steenberghe D (1996) Intraoral transmission and the colonization of oral hard surfaces. J Periodontol 67(10):986–993. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.1996.67.10.986
Quirynen M, Vogels R, Peeters W, van Steenberghe D, Naert I, Haffajee A (2006) Dynamics of initial subgingival colonization of ‘pristine’ peri-implant pockets. Clin Oral Implants Res 17(1):25–37. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2005.01194.x
Porras R, Anderson GB, Caffesse R, Narendran S, Trejo PM (2002) Clinical response to 2 different therapeutic regimens to treat peri-implant mucositis. J Periodontol 73(10):1118–1125. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2002.73.10.1118
Trejo PM, Bonaventura G, Weng D, Caffesse RG, Bragger U, Lang NP (2006) Effect of mechanical and antiseptic therapy on peri-implant mucositis: an experimental study in monkeys. Clin Oral Implants Res 17(3):294–304. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0501.2005.01226.x
Gonçalves PF, Huang H, McAninley S, Alfant B, Harrison P, Aukhil I, Walker C, Shaddox LM (2013) Periodontal treatment reduces matrix metalloproteinase levels in localized aggressive periodontitis. J Periodontol 84(12):1801–1808. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2013.130002
Gupta N, Gupta ND, Gupta A, Khan S, Bansal N (2015) Role of salivary matrix metalloproteinase-8 (MMP-8) in chronic periodontitis diagnosis. Front Med 9(1):72–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-014-0347-x
Chen HY, Cox SW, Eley BM, Mäntylä P, Rönkä H, Sorsa T (2000) Matrix metalloproteinase-8 levels and elastase activities in gingival crevicular fluid from chronic adult periodontitis patients. J Clin Periodontol 27(5):366–369. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-051x.2000.027005366.x
Sorsa T, Gursoy UK, Nwhator S, Hernandez M, Tervahartiala T, Leppilahti J, Gursoy M, Könönen E, Emingil G, Pussinen PJ, Mäntylä P (2016) Analysis of matrix metalloproteinases, especially MMP-8, in gingival creviclular fluid, mouthrinse and saliva for monitoring periodontal diseases. Periodontol 70(1):142–163. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12101
Rickard AH, Gilbert P, High NJ, Kolenbrander PE, Handley PS (2003) Bacterial coaggregation: an integral process in the development of multi-species biofilms. Trends Microbiol 11(2):94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0966-842X(02)00034-3
Subramani K, Jung RE, Molenberg A, Hammerle CH (2009) Biofilm on dental implants: a review of the literature. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 24(4):616–626
Quirynen M, Marechal M, Busscher HJ, Weerkamp AH, Darius PL, van Steenberghe D (1990) The influence of surface free energy and surface roughness on early plaque formation. An in vivo study in man. J Clin Periodontol 17(3):138–144. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.1990.tb01077.x
Dmytryk JJ, Fox SC, Moriarty JD (1990) The effects of scaling titanium implant surfaces with metal and plastic instruments on cell attachment. J Periodontol 61(8):491–496. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.1990.61.8.491
Schwarz F, Rothamel D, Sculean A, Georg T, Scherbaum W, Becker J (2003) Effects of an Er:YAG laser and the Vector ultrasonic system on the biocompatibility of titanium implants in cultures of human osteoblast-like cells. Clin Oral Implants Res 14(6):784–792. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0905-7161.2003.00954.x
Arweiler NB, Auschill TM, Sculean A (2017) Patient self-care of periodontal pocket infections. Periodontol 2000 76(1):164–179. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12152
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to Dr. Ralf Rössler for inserting the dental implants.
Funding
This study was partially supported by an unrestricted grant from the Oral Reconstruction Foundation (previously Camlog Foundation), Basel, Switzerland (Grant CF41203), who also provided the dental implants and the specially constructed titanium healing caps for the experimental investigation. The design, documentation, and analyses of this study were carried out independently.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The protocol of the study was reviewed and approved by the Medical Ethics Committee, Philipps-University Marburg in Germany (no. 159/12). The study was conducted in accordance with the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) and Good Clinical Practice guidelines as well as the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed consent
All participants gave their informed consent prior to their inclusion in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, K.E., Auschill, T.M., Heumann, C. et al. Clinical and laboratory evaluation of the effects of different treatment modalities on titanium healing caps: a randomized, controlled clinical trial. Clin Oral Invest 22, 2149–2160 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-017-2287-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-017-2287-8