Abstract
Objectives
The aim of this article was to review the dental implications of X-linked hypophosphataemic rickets (XLHR) and to provide suggestions regarding the dental treatment of these patients.
Materials and methods
The following search items “x-linked hypophosphataemia, hypophosphataemic rickets, vitamin D-resistant rickets” were used for literature search. Only full-text articles were analysed and summarized to get an overview of the different treatments and outcomes of hypophosphataemic patients.
Results
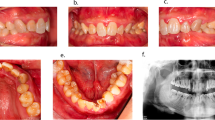
Radiographically, very large pulp chambers with an abnormally high pulp volume/tooth volume ratio, suggesting taurodontism, are often evident. The affected teeth are characterised by a thin enamel layer and dentinal defects. The gender distribution of hypophosphataemic patients is almost equal, but postpubertary males seem to show a trend to develop more severe dental symptoms of the disease. Abscesses without any signs of dental caries or trauma are frequent findings. The most often affected teeth are incisors followed by molars and premolars.
Conclusions
Treatment options include frequent dental examination, application of topical fluoride varnish and sealing of pits and fissures to prevent microbial invasion that may result in pulpitis and further endodontic complications.
Clinical relevance
X-linked hypophosphataemic rickets is associated with marked structural alterations of dental hard tissues and the development of multiple abscesses and sinus tracts of dental origin. Therefore, profound knowledge of the various dental implications of XLHR is required to provide these patients with the best possible treatment options.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beaton GH, Bengoa JM (1976) Nutrition in preventive medicine. World Health Organization Monograph Series No. 62 Chapter 6
Uriu-Adams JY, Obican SG, Keen CL (2013) Vitamin D and maternal and child health: overview and implications for dietary requirements. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today 99:24–44
Masuyama R (2014) Role of local vitamin D signalling and cellular calcium transport system in bone homeostasis. J Bone Miner Metab 32:1–9
Holick MF (2007) Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med 357:266–281
Souza MA, Valente Soares LAV Jr, Alves dos Santos M, Vaisbich MH (2010) Dental abnormalities and oral health in patients with Hypophosphatemic rickets. Clinics 65:1023–1026
Feng JQ, Clinkenbeard EL, Yuan B, White KE, Drezner MK (2013) Osteocyte regulation of phosphate homeostasis and bone mineralization underlies the pathophysiology of the heritable disorders of rickets and osteomalacia. Bone 54:213–221
Bowden SA, Patel HP, Beebe A, McBride KL (2013) Successful medical therapy for hypophosphatemic rickets due to mitochondrial complex I deficiency induced de Toni-Debré-Fanconi Syndrome. Case Rep Pediatr 2013:354314
Root AW, Diamond FB (2002) Disorders of calcium metabolism in the child and adolescent. In: Sperling MA (ed) Pediatric endocrinology. Saunders, Philadelphia, p 646
Albright F, Butler AA, Bloomberg E (1937) Rickets resistant to vitamin D therapy. Am J Dis Child 54:529–547
Al-Jundi SH, Dabous IM, Al-Jamal GA (2009) Craniofacial morphology in patients with hypophosphataemic vitamin-D-resistant rickets: a cephalometric study. J Oral Rehabil 36:483–490
Reid IR, Hardy DC, Murphy WA, Teitelbaum SL, Bergfeld MA, Whyte MP (1989) X-linked hypophosphatemia: a clinical, biochemical, and histopathologic assessment of morbidity in adults. Medicine (Baltimore) 68:336–352
Petersen DJ, Boniface AM, Schranck FW, Rupich RC, Whyte MP (1992) X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets: a study (with literature review) of linear growth response to calcitriol and phosphate therapy. J Bone Miner Res 7:583–597
Holm IA, Nelson AE, Robinson BG, Mason RS, Marsh DJ, Cowell CT, Carpenter TO (2001) Mutational analysis and genotype-phenotype correlation of the PHEX gene in X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:3889–3899
Durmaz E, Zou M, Al-Rijjal RA, Baitei EY, Hammami S, Bircan İ, Akçurin S, Meyer B, Shi Y (2013) Novel and de novo PHEX mutations in patients with hypophosphatemic rickets. Bone 52:286–291
Carpenter TO (1997) New perspectives on the biology and treatment of X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. Pediatr Clin N Am 44:443–466
Souza AP, Kobayashi TY, LourenҫoNeto N, Silva SMB, Machado MAAM, Oliveira M (2013) Dental manifestations of patient with vitamin-D resistant rickets. J Appl Oral Sci 21:601–606
The HYP Consortium (1995) A gene (PEX) with homologies to endopeptidases is mutated in patients with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. Nat Genet 11:130–136
Rowe PSN, Oudet CL, Francis F, Sinding C, Pannetier S, Econs MJ, Strom TM, Meitinger T, Garabedian M, David A, Macher MA, Questiaux E, Popowska E, Pronicka E, Read AP, Mokrzycki A, Glorieux FH, Drezner MK, Hanauer A, Lehrach H, Goulding JN, O’Riordan JLH (1997) Distribution of mutations in the PEX gene in families with X-linked hypophosphataemic rickets (HYP). Hum Mol Genet 6:539–549
Nesbitt T, Fujiwara I, Thomas R, Xiao ZS, Quarles LD, Drezner MK (1999) Coordinated maturational regulation of PHEX and renal phosphate transport inhibitory activity: evidence for the pathophysiological role of PHEX in X-linked hypophosphatemia. J Bone Miner Res 14:2027–2035
Kelly A, Levine MA (2010) Disorders of bone and mineral metabolism. In: Kappy MS, Allen DB, Mitchell EG (eds) Pediatric practice endocrinology. McGraw Hill, New York
Carpenter TO (2012) The expanding family of hypophosphatemic syndromes. J Bone Miner Metab 30:1–9
Rafaelsen SH, Ræder H, Fagerheim AK, Knappskog P, Carpenter TO, Johansson S, Bjerknes R (2013) Exome sequencing reveals FAM20c mutations associated with fibroblast growth factor 23–related hypophosphatemia, dental anomalies, and ectopic calcification. J Bone Miner Res 28:1378–1385
Tenenhouse HS (1999) X-linked hypophosphataemia: a homologous disorder in humans and mice. Nephrol Dial Transplant 14:333–341
Brewer ED (2006) Panproximal tubular dysfunction (Fanconi Syndrome). In: McMilan JA, Feigin RD, DeAngelis C, Jones MD (eds) Oski’spediatrics, 4th edn. Lippincott & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Fadavi S, Rowold E (1990) Familial hypophosphatemic vitamin D-resistant rickets: review of the literature and report of case. ASDC J Dent Child 57:212–215
Harris R, Sullivan HR (1960) Dental sequelae in deciduous dentition in vitamin D-resistant rickets, case report. Aust Dent J 5:200–203
Bender IB, Naidorf IJ (1985) Dental observations in vitamin D-resistant rickets with special reference to periapical lesions. J Endod 11:514–520
Cohen S, Becker GL (1976) Origin, diagnosis, and treatment of the dental manifestations of vitamin D-resistant rickets: review of the literature and report of case. J Am Dent Assoc 92:120–129
Opsahl Vitala S, Gauchera C, Bardeta C, Rowed PS, Georgee A, Linglartf A, Chaussain C (2012) Tooth dentin defects reflect genetic disorders affecting bone mineralization. Bone 50:989–997
Witkop CJ Jr (1971) Manifestations of genetic diseases in the human pulp. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 32:278–316
Sauk JJ Jr, Witkop CJ Jr (1973) Electron optic analysis of human dentin in hypophosphatemic vitamin D-resistant rickets (report of a kindred with consanguinity). J Oral Pathol 2:203–214
Shellis RP (1983) Structural organization of calcospherites in normal and rachitic human dentine. Arch Oral Biol 28:85–95
Abe K, Ooshima T, Lily TS, Yasufuku Y, Sobue S (1988) Structural deformities of deciduous teeth in patients with hypophosphatemic vitamin D-resistant rickets. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 65:191–198
Schwartz S, Scriver CR, Reade TM, Shields ED (1988) Oral findings in patients with autosomal dominant hypophosphatemic bone disease and X-linked hypophosphatemia: further evidence that they are different diseases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 66:310–314
Daley TD, Jarvis A, Wysocki GP, Kogon SL (1990) X-ray microanalysis of teeth from healthy patients and patients with familial hypophosphatemia. Calcif Tissue Int 47:350–355
Shields ED, Scriver CR, Reade T, Fujiwara TM, Morgan K, Ciampi A, Schwartz S (1990) X-linked hypophosphatemia: the mutant gene is expressed in teeth as well as in kidney. Am J Hum Genet 46:434–442
Hillmann G, Geurtsen W (1996) Pathohistology of undecalcified primary teeth in vitamin D-resistant rickets: review and report of two cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 82:218–224
Goodman JR, Gelbier MJ, Bennett JH, Winter GB (1998) Dental problems associated with hypophosphataemic vitamin D resistant rickets. Int J Paediatr Dent 8:19–28
Murayama T, Iwatsubo R, Akiyama S, Amano A, Morisaki I (2000) Familial hypophosphatemic vitamin D-resistant rickets: dental findings and histologic study of teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 90:310–316
Zambrano M, Nikitakis NG, Sanchez-Quevedo MC, Sauk JJ, Sedano H, Rivera H (2003) Oral and dental manifestations of vitamin D-dependent rickets type I: report of a pediatric case. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 95:705–709
Chaussain-Miller C, Sinding C, Wolikow M, Lasfargues J-J, Godeau G, Garabédian M (2003) Dental abnormalities in patients with familial hypophosphatemic vitamin D-resistant rickets: prevention by early treatment with 1-hydroxyvitamin D. J Pediatr 142:324–331
Seow WK (2003) Diagnosis and management of unusual dental abscesses in children. Aust Dent J 48:156–168
Batra P, Tejani Z, Mars M (2006) X-linked hypophosphatemia: dental and histologic findings. J Can Dent Assoc 72:69–72
Chaussain-Miller C, Sinding C, Septier D, Wolikow M, Goldberg M, Garabedian M (2007) Dentin structure in familial hypophosphatemic rickets: benefits of vitamin D and phosphate treatment. Oral Dis 13:482–489
Douyere D, Joseph C, Gaucher C, Chaussain C, Courson F (2009) Familial hypophosphatemic vitamin D-resistant rickets-prevention of spontaneous dental abscesses on primary teeth: a case report. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 107:525–530
Rabbani A, Rahmani P, Ziaee V, Ghodoosi S (2012) Dental problems in hypophosphatemic rickets, a cross sectional study. Iran J Pediatr 22:531–534
Andersen MG, Beck-Nielsen SS, Haubek D, Hintze H, Gjørup H, Poulsen S (2012) Periapical and endodontic status of permanent teeth in patients with hypophosphatemic rickets. J Oral Rehabil 39:144–150
Rathore R, Nalawade TM, Pateel D, Mallikarjuna R (2013) Oral manifestations of vitamin D resistant rickets in orthopantomogram. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2012-008318
Studart Soares EC, Gurgel Costa FW, Rodrigues Ribeiro T, NegreirosNunes Alves AP, SáRorizFonteles C (2013) Clinical approach in familial hypophosphatemic rickets: report of three generations. Spec Care Dentist 33:304–307
Larmas M, Hietala EL, Simila S, Pajari U (1991) Oral manifestations of familial hypophosphatemic rickets after phosphate supplement therapy: a review of the literature and report of case. ASDC J Dent Child 58:328–334
Seow WK, Needleman HL, Holm IA (1995) Effect of familial hypophosphatemic rickets on dental development: a controlled, longitudinal study. Pediatr Dent 17:346–350
Salmon B, Bardet C, Khaddam M, Naji J, Coyac BR, Baroukh B, Letourneur F, Lesieur J, Decup F, Le Denmat D, Nicoletti A, Poliard A, Rowe PS, Huet E, Opsahl Vital S, Linglart A, McKee MD, Chaussain C (2013) MEPE-derived ASARM peptide inhibits odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells and impairs mineralization in tooth models of X-linked hypophosphatemia. PLoS One 8:e56749
Seeto E, Seow WK (1991) Scanning electron microscopic analysis of dentin in vitamin D-resistant rickets–assessment of mineralization and correlation with clinical findings. Pediatr Dent 13:43–48
Goldberg M, Septier D, Bourd K, Hall R, Jeanny JC, Jonet L, Colin S, Tager F, Chaussain-Miller C, Garabédian M, George A, Goldberg H, Menashi S (2002) The dentino-enamel junction revisited. Connect Tissue Res 43:482–489
Via WF Jr (1967) “Spontaneous” degeneration of the dental pulp associated with phosphate diabetes. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 24:623–628
Pliskin ME, Brown AM, Baden EE, Kimball HG (1975) Vitamin D resistant rickets of a young adult patient. A review and case report. J Oral Med 30:77–80
McWhorter AG, Seale NS (1991) Prevalence of dental abscess in a population of children with vitamin D-resistant rickets. Pediatr Dent 13:91–96
Cehreli ZC, Turgut M, Olmez S, Dagdeviren A, Atilla P (2000) Short term human primary pulpal response after direct pulp capping with fourth-generation dentin adhesives. J Clin Pediatr Dent 25:65–71
Fusayama T, Nakamura M, Kurosaki N, Iwaku M (1979) Non-pressure adhesion of a new adhesive restorative resin. J Dent Res 58:1364–1370
Liu S, Gupta A, Quarles LD (2007) Emerging role of fibroblast growth factor 23 in a bone–kidney axis regulating systemic phosphate homeostasis and extracellular matrix mineralization. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 16:329–335
Seow WK, Romaniuk K, Sclavos S (1989) Micromorphologic features of dentin in vitamin D-resistant rickets: correlation with clinical grading of severity. Pediatr Dent 11:203–208
Seow WK, Latham SC (1986) The spectrum of dental manifestations in vitamin D-resistant rickets: implications for management. Pediatr Dent 8:245–250
Rakocz M, Keating J III, Johnson R (1982) Management of the primary dentition in vitamin D-resistant rickets. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 54:166–171
Shroff DV, McWhorter AG, Seale NS (2002) Evaluation of aggressive pulp therapy in a population of vitamin D-resistant rickets patients: a follow-up of 4 cases. Pediatr Dent 24:347–349
Mireku AS, Romberg E, Fuoad AF, Arola D (2010) Vertical fracture of root filled teeth restored with posts: the effects of patient age and dentine thickness. Int Endod J 43:218–225
Foster BL, Ramnitz MS, Gafni RI, Burke AB, Boyce AM, Lee JS, Wright JT, Akintoye SO, Somerman MJ, Collins MT (2014) Rare bone diseases and their dental, oral, and craniofacial manifestations. J Dent Res 93:7S–19S
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabandal, M.M.I., Robotta, P., Bürklein, S. et al. Review of the dental implications of X-linked hypophosphataemic rickets (XLHR). Clin Oral Invest 19, 759–768 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-015-1425-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-015-1425-4