Abstract
Objectives
The purpose of this study is to investigate the contribution of selected variables to the occurrence of severe early childhood caries (S-ECC) in 3- to 5-year-old kindergarten children.
Methods
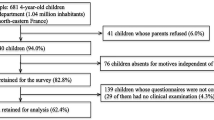
A cross-sectional study was conducted in 2010 in 30 randomly selected kindergartens in the German Rhein-Neckar district. After informed consent, parents were asked to complete a questionnaire. The oral examinations took place in the selected kindergartens and the WHO methods as well as the criteria proposed by the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry were followed. Logistic regression was applied to explore the main factors contributing to S-ECC in a multivariate model.
Results
In all, 1,007 children aged 3 to 5 years with an average age of 4.1 (SD = 0.8) years were examined. Five variables were associated significantly with the occurrence of S-ECC: breastfeeding for more than 12 months (OR = 3.27), use of the nursing bottle in bed (OR = 3.08), start of tooth brushing after the first anniversary (OR = 2.42), regular visits at the dentists (OR = 0.14) and mother with immigration background (OR = 4.05). Prevalence rate of S-ECC was 9.5 %. The mean d3+4mft values were 5.69 (S-ECC group) and 0.23 (non-S-ECC group).
Conclusion
These results show that occurrence of S-ECC is a complex interaction between socioeconomic, psychological and behavioural factors of parents. New and specific ways to provide preventive dental care for toddlers and infants of caries risk groups have to be developed.
Clinical relevance
Parents of newborn children have to receive information about timely start of tooth brushing and adequate use of nursing bottles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harris R, Nicoll AD, Adair PM, Pine CM (2004) Risk factors for dental caries in young children: a systematic review of the literature. Community Dent Health 21(Supplement):71–85
Drury TF, Horowitz AM, Ismail AI, Maertens MP, Rozier RG, Selwitz RH (1999) Diagnosing and reporting early childhood caries for research purposes. J Public Health Dent 59:192–197
American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (2008) Policy on early childhood caries (ECC): classifications, consequences, and preventive strategies. Pediatr Dent 30(Suppl 7):40–43
Tickle M, Blinkhorn AS, Milsom KM (2008) The occurrence of dental pain and extractions over a 3-year period in a cohort of children aged 3–6 years. J Public Health Dent 68:63–69
Leake J, Jozzy S, Uswak G (2008) Severe dental caries, impacts and determinants among children 2–6 years of age in Inuvik Region, Northwest Territories, Canada. J Can Dent Assoc 74:519
Wong HM, McGrath CPJ, King NM, Lo ECM (2011) Oral health-related quality of life in Hong Kong preschool children. Caries Res 45:370–376
Martins-Júnior PA, Vieira-Andrade RG, Corrêa-Faria P, Oliveira-Ferreira F, Marques LS, Ramos-Jorge ML (2013) Impact of early childhood caries on the oral health-related quality of life of preschool children and their parents. Caries Res 47:211–218
Clarke M, Locker D, Berall G, Pencharz P, Kenny DJ, Judd P (2006) Malnourishment in a population of young children with severe early childhood caries. Pediatr Dent 28:254–259
Hallett KB, O’Rourke PK (2006) Pattern and severity of early childhood caries. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 34:25–35
Ismail A, Lim S, Sohn W, Willem JM (2008) Determinants of early childhood caries in low income African American young children. Pediatr Dent 30:289–296
Feldens CA, Giugliani ERJ, Vigo A, Vitolo MR (2010) Early feeding practices and severe early childhood caries in four-year-old children from Southern Brazil: a birth cohort study. Caries Res 44:445–452
Slabsinskiene E, Milciuviene S, Narbutaite J, Vasiliauskiene I, Andruskeviciene V, Bendoraitiene EA, Saldūnaite K (2010) Severe early childhood caries and behavioral risk factors among 3-year-old children in Lithuania. Medicina (Kaunas) 46:135–141
Hsieh H, Huang S, Tsai C, Hsiao S (2012) Toothbrushing habits and risk indicators of severe early childhood caries among aboriginal Taiwanese. Asia Pac J Public Health. doi:10.1177/1010539511430721
Seow WK (2012) Environmental, maternal, and child factors which contribute to early childhood caries: a unifying conceptual model. Int J Paediatr Dent 22:157–168
Wennhall I, Matsson L, Schröder U, Twetman S (2002) Caries prevalence in 3-year-old children in a low socio-economic multicultural urban area in southern Sweden. Swed Dent J 26:167–172
Stecksen-Blicks C, Sunnegardh K, Borssen E (2004) Caries experience and background factors in 4-year-old children: time trends 1967–2002. Caries Res 38:149–155
Iida H, Auinger P, Billings RG, Weitzman M (2007) Association Between Infant Breastfeeding and Early Childhood Caries in the United States. Pediatrics 120:944–952
WHO (1997) Oral health surveys; basic methods, 4th edn. WHO, Geneva
Robke FJ (2008) Effects of nursing bottle misuse on oral health. Prevalence of caries, tooth malalignments and malocclusions in North-German preschool children. J Orofac Orthop 69:5–19. doi:10.1007/s00056-008-0724-7
Schulte AG, Momeni A, Pieper K (2006) Caries prevalence in 12-year-old children from Germany. Results of the 2004 national survey. Community Dent Health 23:197–202
Pieper K (2010) Epidemiologische Begleituntersuchungen zur Gruppenprophylaxe 2009. Gutachten. Deutsche Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Jugendzahnpflege e.V. (DAJ), Bonn
Kruger E, Dyson K, Tennant M (2005) Pre-school child oral health in rural Western Australia. Aust Dent J 50:258–262
Pieper K, Dressler S, Heinzel-Gutenbrenner M, Neuhäuser A, Krecker M, Wunderlich K, Jablonski-Momeni A (2012) The influence of social status on pre-school children’s eating habits, caries experience and caries prevention behaviour. Int J Public Health 5:207–215
Helfenstein U, Steiner M (1994) Fluoride varnishes (Duraphat): a meta-analysis. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 22:1–5
Marinho VC, Higgins JP, Logan S, Sheiham A (2003) Topical fluoride (toothpastes, mouth rinses, gels or varnishes for preventing dental caries in children and adolescents). Cochrane Database Syst Rev 4:CD002782
Pieper K, Weber K, Margraf-Stiksrud J, Stein S, Heinzel-Gutenbrenner M, Jablonski-Momeni A (2012) Evaluation of an intensified preventive program aimed at 12-year-olds with increased caries risk. J Public Health 20:151–157
Weintraub JA, Ramos-Gomez F, Jue B, Shain S, Hoover CI, Featherstone JDB, Gansky SA (2006) Fluoride varnish efficacy in preventing early childhood caries. J Dent Res 85:172–176
Plutzer K, Spencer AJ (2008) Efficacy of an oral health promotion intervention in the prevention of early childhood caries. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 36:335–346
Feldens CA, Giugliani ERJ, Duncan BB, Drachler ML, Vitolo MR (2010) Long-term effectiveness of a nutritional program in reducing early childhood caries: a randomized trial. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 38:324–332
Schulte AG (2005) Salt fluoridation in Germany since 1991. Schweiz Monatsschr Zahnmed 115:659–662
Conflict of interest
The authors declare to have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bissar, A., Schiller, P., Wolff, A. et al. Factors contributing to severe early childhood caries in south-west Germany. Clin Oral Invest 18, 1411–1418 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-013-1116-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-013-1116-y