Abstract
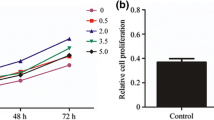
This study explores the effects of C-myc gene silencing on cell proliferation, apoptosis and cytokine expression in interleukin (IL)-1β-induced rat chondrocytes. Primary chondrocytes were obtained from 40 Sprague-Dawley rats. For in vitro C-myc3-shRNA transfection, chondrocytes were assigned to a blank 1, model 1, IL-1β + C-myc3-shRNA, C-myc3-shRNA, (IL-1β + C-myc3-shRNA) + C-myc overexpression, C-myc3-shRNA + C-myc overexpression or IL-1β + C-myc-Con group. Western blotting and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) were performed to detect C-myc, PCNA and cyclin D1 mRNA and protein expression. Cell proliferation was analyzed via CCK-8 assay and cell cycle while apoptosis was measured through flow cytometry. ELISA was utilized to assess the levels of metallopeptidase 13 (MMP-13), IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). Both the qRT-PCR and Western blotting results demonstrated that C-myc3-shRNA transfection inhibits C-myc expression and promotes PCNA and cyclin D1 expression. In comparison to the model 1 group, all groups except the (IL-1β + C-myc3-shRNA) + C-myc overexpression and IL-1β + C-myc-Con groups showed increases in cell proliferation and S phase cell count and decreases in G0/G1 phase cell count, cell apoptosis and MMP-13, IL-6 and TNF-α levels. The model 1, C-myc3-shRNA and C-myc3-shRNA + C-myc overexpression groups displayed higher cell proliferation and S phase cell count and reduced G0/G1 phase cell count, cell apoptosis and MMP-13, IL-6 and TNF-α levels than the IL-1β + C-myc3-shRNA group. In comparison to the model 1 and C-myc3-shRNA + C-myc overexpression groups, the C-myc3-shRNA group promoted cell proliferation and S phase cell counts but suppressed G0/G1 phase cell count, cell apoptosis and MMP-13, IL-6 and TNF-α levels. In conclusion, the study demonstrates that C-myc gene silencing can promote cell proliferation and inhibit cell apoptosis and cytokine expression in IL-1β-induced rat chondrocytes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neogi T, Zhang Y (2013) Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 39:1–19
Kim C, Linsenmeyer KD, Vlad SC, Guermazi A, Clancy MM, Niu J, Felson DT (2014) Prevalence of radiographic and symptomatic hip osteoarthritis in an urban United States community: the Framingham osteoarthritis study. Arthritis Rheumatol 66:3013–3017
Goldring MB, Goldring SR (2007) Osteoarthritis. J Cell Physiol 213:626–634
McAlindon TE, Nuite M, Krishnan N, Ruthazer R, Price LL, Burstein D, Griffith J, Flechsenhar K (2011) Change in knee osteoarthritis cartilage detected by delayed gadolinium enhanced magnetic resonance imaging following treatment with collagen hydrolysate: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 19:399–405
Zhu M, Tang D, Wu Q, Hao S, Chen M, Xie C, Rosier RN, O’Keefe RJ, Zuscik M, Chen D (2009) Activation of beta-catenin signaling in articular chondrocytes leads to osteoarthritis-like phenotype in adult beta-catenin conditional activation mice. J Bone Miner Res 24:12–21
O’Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang CV, Mendell JT (2005) c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1 expression. Nature 435:839–843
Kalra N, Kumar V (2004) c-Fos is a mediator of the c-myc-induced apoptotic signaling in serum-deprived hepatoma cells via the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Biol Chem 279:25313–25319
Perera PM, Wypasek E, Madhavan S, Rath-Deschner B, Liu J, Nam J, Rath B, Huang Y, Deschner J, Piesco N, Wu C, Agarwal S (2010) Mechanical signals control SOX-9, VEGF, and c-Myc expression and cell proliferation during inflammation via integrin-linked kinase, B-Raf, and ERK1/2-dependent signaling in articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther 12:R106
Delmore JE, Issa GC et al (2011) BET bromodomain inhibition as a therapeutic strategy to target c-Myc. Cell 146:904–917
Lewis BC, Klimstra DS, Varmus HE (2003) The c-myc and PyMT oncogenes induce different tumor types in a somatic mouse model for pancreatic cancer. Genes Dev 17:3127–3138
Beroukhim R, Mermel CH et al (2010) The landscape of somatic copy-number alteration across human cancers. Nature 463:899–905
Fukazawa T, Maeda Y, Matsuoka J, Yamatsuji T, Shigemitsu K, Morita I, Faiola F, Durbin ML, Soucek L, Naomoto Y (2010) Inhibition of Myc effectively targets KRAS mutation-positive lung cancer expressing high levels of Myc. Anticancer Res 30:4193–4200
Tuo YL, Li XM, Luo J (2015) Long noncoding RNA UCA1 modulates breast cancer cell growth and apoptosis through decreasing tumor suppressive miR-143. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 19:3403–3411
Arden N, Nevitt MC (2006) Osteoarthritis: epidemiology. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 20:3–25
Goldring MB, Otero M (2011) Inflammation in osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 23:471–478
Ikegawa S (2007) New gene associations in osteoarthritis: what do they provide, and where are we going? Curr Opin Rheumatol 19:429–434
Rao DD, Vorhies JS, Senzer N, Nemunaitis J (2009) siRNA vs. shRNA: similarities and differences. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 61:746–759
Hao H, Nancai Y, Lei F, Xiong W, Wen S, Guofu H, Yanxia W, Hanju H, Qian L, Hong X (2008) siRNA directed against c-Myc inhibits proliferation and downregulates human telomerase reverse transcriptase in human colon cancer Colo 320 cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 27:27
Wang H, Mannava S, Grachtchouk V, Zhuang D, Soengas MS, Gudkov AV, Prochownik EV, Nikiforov MA (2008) c-Myc depletion inhibits proliferation of human tumor cells at various stages of the cell cycle. Oncogene 27:1905–1915
Hwang HW, Mendell JT (2006) MicroRNAs in cell proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer 94:776–780
Elouil H, Cardozo AK, Eizirik DL, Henquin JC, Jonas JC (2005) High glucose and hydrogen peroxide increase c-Myc and haeme-oxygenase 1 mRNA levels in rat pancreatic islets without activating NFkappaB. Diabetologia 48:496–505
Li FY, Cheng NS, Cheng JQ, Mao H, Jiang LS, Li N, He S (2009) Treatment of chronic proliferative cholangitis with c-myc shRNA. World J Gastroenterol 15:95–101
Nilkaeo A, Bhuvanath S (2006) Interleukin-1 modulation of human placental trophoblast proliferation. Mediators Inflamm 2006:79359
Gordan JD, Thompson CB, Simon MC (2007) HIF and c-Myc: sibling rivals for control of cancer cell metabolism and proliferation. Cancer Cell 12:108–113
Shchors K, Shchors E, Rostker F, Lawlor ER, Brown-Swigart L, Evan GI (2006) The Myc-dependent angiogenic switch in tumors is mediated by interleukin 1beta. Genes Dev 20:2527–2538
Takaishi H, Kimura T, Dalal S, Okada Y, D’Armiento J (2008) Joint diseases and matrix metalloproteinases: a role for MMP-13. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 9:47–54
Woodell-May J, Matuska A, Oyster M, Welch Z, O’Shaughnessey K, Hoeppner J (2011) Autologous protein solution inhibits MMP-13 production by IL-1beta and TNFalpha-stimulated human articular chondrocytes. J Orthop Res 29:1320–1326
Stannus O, Jones G, Cicuttini F, Parameswaran V, Quinn S, Burgess J, Ding C (2010) Circulating levels of IL-6 and TNF-alpha are associated with knee radiographic osteoarthritis and knee cartilage loss in older adults. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 18:1441–1447
Chen B, Tsui S, Smith TJ (2005) IL-1 beta induces IL-6 expression in human orbital fibroblasts: identification of an anatomic-site specific phenotypic attribute relevant to thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy. J Immunol 175:1310–1319
Lopez-Armada MJ, Carames B, Lires-Dean M, Cillero-Pastor B, Ruiz-Romero C, Galdo F, Blanco FJ (2006) Cytokines, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta, differentially regulate apoptosis in osteoarthritis cultured human chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 14:660–669
Husari AW, Dbaibo GS, Bitar H, Khayat A, Panjarian S, Nasser M, Bitar FF, El-Sabban M, Zaatari G, Mroueh SM (2006) Apoptosis and the activity of ceramide, Bax and Bcl-2 in the lungs of neonatal rats exposed to limited and prolonged hyperoxia. Respir Res 7:100
Huang Y, Wu D, Fan W (2014) Protection of ginsenoside Rg1 on chondrocyte from IL-1beta-induced mitochondria-activated apoptosis through PI3 K/Akt signaling. Mol Cell Biochem 392:249–257
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the reviewers for their useful comments on this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, J., Li, XL., Shi, ZM. et al. Effects of C-myc gene silencing on interleukin-1β-induced rat chondrocyte cell proliferation, apoptosis and cytokine expression . J Bone Miner Metab 36, 286–296 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-017-0845-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-017-0845-4