Abstract
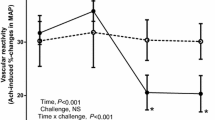
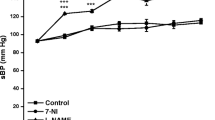
This study investigates the effects of chronic methionine intake on bradykinin (BK)-relaxation. Vascular reactivity experiments were performed on carotid rings from male Wistar rats. Treatment with methionine (0.1, 1 or 2 g kg−1 per day) for 8 and 16 weeks, but not for 2 and 4 weeks, reduced the relaxation induced by BK. Indomethacin, a non-selective cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitor, and SQ29548, a selective thromboxane A2 (TXA2)/prostaglandin H2 (PGH2) receptor antagonist prevented the reduction in BK-relaxation observed in the carotid from methionine-treated rats. Conversely, AH6809, a selective prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) receptor antagonist did not alter BK-relaxation in the carotid from methionine-treated rats. The nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitors L-NAME, L-NNA and 7-nitroindazole reduced the relaxation induced by BK in carotids from control and methionine-treated rats. In summary, we found that chronic methionine intake impairs the endothelium-dependent relaxation induced by BK and this effect is due to an increased production of endothelial vasoconstrictor prostanoids (possibly TXA2) that counteracts the relaxant action displayed by the peptide.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abahji TN, Nill L, Ide N, Keller C, Hoffmann U, Weiss N (2007) Acute hyperhomocysteinemia induces microvascular and macrocvascular endothelial dysfunction. Arch Med Res 38:408–416. doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2007.01.004
Abularrage CJ, Sidawy AN, White PW, Aidinian G, DeZee KJ, Weiswasser JM et al (2007) Effect of folic acida and vitamin B6 and B12 on microcirculatory vasoreactivity in patients with hyperhomocysteinemia. Vasc Endovascular Surg 41:339–345. doi:10.1177/1538574407301692
Accorsi-Mendonca D, Correa FM, Paiva TB, de Souza HP, Laurindo FR, de Oliveira AM (2004) The balloon catheter induces an increase in contralateral carotid artery reactivity to angiotensin II and phenylephrine. Br J Pharmacol 142:79–88. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0705732
Akamine EH, Urakawa TA, de Oliveira MA, Nigro D, De Carvalho MH, Tostes RC et al (2006) Decreased endothelium-dependent vasodilation in diabetic female rats: role of prostanoids. J Vasc Res 43:401–410. doi:10.1159/000094790
Alexander RW (1995) Hypertension and the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: oxidative stress and the mediation of arterial inflammatory response: a new perspective. Hypertension 25:155–161
Bagi Z, Ungvari Z, Szollar L, Koller A (2001) Flow-induced constriction in arterioles from hyperhomocysteinemic rats is due to imapried nitric oxide and enhanced thromboxane A2 mediation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 21:233–237
Birney Y, Redmond EM, Sitzmann JV, Cahill PA (2003) Eicosanoids in cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 72:3–18. doi:10.1016/S1098-8823(03)00080-7
Bonaventura D, Tirapelli CR, Haddad R, Hoehr NF, Eberlin MN, de Oliveira AM (2004) Chronic methionine load-induced hyperhomocysteinemia enhances rat carotid responsiveness for angiotensin II. Pharmacology 70:91–99. doi:10.1159/000074673
Chen C, Conklin BS, Ren Z, Zhong DS (2002) Homocysteine decreases endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation in porcine arteries. J Surg Res 102:22–30. doi:10.1006/jsre.2001.6304
Davì G, Dimino G, Coppola A, Andrea G, Cerbone AM, Madonna P et al (2001) Oxidative stress and platelet activation in homozygous homocysteinuria. Circulation 104:1124–1128. doi:10.1161/hc3501.095287
De Andrade CR, Fukada SY, Olivon VC, de Goody MA, Haddad R, Eberlin MN et al (2006) Alpha1D-adrenoceptor-induced relaxation on rat carotid artery is impaired during the endothelial dysfunction evoked in the early stages of hyperhomocysteinemia. Eur J Pharmacol 543:83–91. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.06.003
Fredriksson R, Lagerström MC, Lundin LG, Schiöth HB (2003) The G-protein-coupled receptors in the human genome form five main families. Phylogenetic analysis, paralogon groups, and fingerprints. Mol Pharmacol 63(6):1256–1272. doi:10.1124/mol.63.6.1256
Gonzalez C, Corbacho AM, Eiserich JP, Garcia C, Lopez-Barrera F, Morales-Tlalpan V et al (2004) 16K-prolactin inhibits activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase, intracellular calcium mobilization, and endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation. Endocrinology 145:5714–5722. doi:10.1210/en.2004-0647
Graeber JE, Slott JH, Ulane RE, Schulman JD, Stuart MJ (1982) Effect of homocysteine on platelet and vascular arachidonic acid metabolism. Pediatr Res 16:490–493. doi:10.1203/00006450-198206000-00018
Gris JC, Schved JF, Aguilar-Martinez P, Arnaud A, Sanchez N (1991) Endothelial mediators regulating vascular tonus. Presse Med 20:303–308
Hanratty CG, McAuley DF, McGrath LT, Yuong IS, Johnston GD (2001a) Hyperhomocysteinemia in young adults is not associated with impaired endothelial dysfunction. Clin Sci 100:67–72. doi:10.1042/CS20000138
Hanratty CG, McGrath LT, McAuley DF, Young IS, Johnston GD (2001b) The effects of oral methionine and homocysteine on endothelial function. Heart 85:326–330. doi:10.1136/heart.85.3.326
Harker LA, Ross R, Slichter SJ, Scott CR (1976) Homocysteine-induced arteriosclerosis. The role of endothelial cell injury and platelet response in its genesis. J Clin Invest 58:731–741. doi:10.1172/JCI108520
Hernanz R, Briones AM, Alonso MJ, Vila E, Salaices M (2004) Hypertension alters role of iNOS, COX-2, and oxidative stress in bradykinin relaxation impairment after LPS in rat cerebral arteries. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 287:H225–H234. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00548.2003
Horn F, Bettler E, Oliveira L, Campagne F, Cohen FE, Vriend G (2003) GPCRDB information system for G protein-coupled receptors. Nucleic Acids Res 31(1):294–297. doi:10.1093/nar/gkg103
Leeb-Lundberg LM, Marceau F, Muller-Esterl W, Pettibone DJ, Zuraw BL (2005) International union of pharmacology. XLV. Classification of the kinin receptor family: from molecular mechanisms to pathophysiological consequences. Pharmacol Rev 57:27–77. doi:10.1124/pr.57.1.2
Liao JK, Homcy CJ (1993) The G proteins of the G alpha i and G alpha q family couple the bradykinin receptor to the release of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. J Clin Invest 92(5):2168–2172. doi:10.1172/JCI116818
Loeb AL, Izzo NJ Jr, Johnson RM, Garrison JC, Peach MJ (1988) Endothelium-derived relaxing factor release associated with increased endothelial cell inositol trisphosphate and intracellular calcium. Am J Cardiol 62(11):36G–40G. doi:10.1016/0002-9149(88)90030-6
Luscher TF, Tanner FC, Tschundi MR, Noll G (1993) Endothelial dysfunction in coronary artery disease. Annu Rev Med 44:395–418. doi:10.1146/annurev.me.44.020193.002143
Miyamoto A, Laufs U, Pardo C, Liao JK (1997) Modulation of bradykinin receptor ligand binding affinity and its coupled G-proteins by nitric oxide. J Biol Chem 272(31):19601–19608. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.31.19601
Perry DJ (1999) Hyperhomocysteinemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 12:451–477. doi:10.1053/beha.1999.0036
Rodgers GM, Conn MT (1990) Homocysteine, an atherogenic stimulus, reduces protein C activation by arterial and venous endothelial cells. Blood 75:895–901
Rubanyi GM (1993) The role of endothelium in cardiovascular homeostasis and diseases. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 22(Suppl 4):S1–S14. doi:10.1097/00005344-199304000-00002
Scholkens BA (1996) Kinins in the cardiovascular system. Immunopharmacology 33:209–216. doi:10.1016/0162-3109(96)00061-6
Selhub J (1999) Homocysteine metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr 19:217–246. doi:10.1146/annurev.nutr.19.1.217
Sellke FW, Boyle EM Jr, Verrier ED (1996) Endothelial cell injury in cardiovascular surgery: the pathophysiology of vasomotor dysfunction. Ann Thorac Surg 62:1222–1228. doi:10.1016/0003-4975(96)00538-3
Sharma JM, Sharma J (2002) Cardiovascular properties of the kallikrein–kinin system. Curr Med Res Opin 18:10–17. doi:10.1185/03007990212500093
Sharma JN, Thani RB (2004) Therapeutic prospects for bradykinin receptor agonists in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Drugs 7:926–934
Shukla N, Koupparis A, Jones RAW, Angelini GD, Persad R, Jeremy JY (2006) Penicillamine administration reverses the inhibitory effect of hyperhomocysteinemia on endothelium-dependent relaxation and superoxide formation in the aorta of the rabbit. Eur J Pharmacol 531:201–208. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.12.003
Signorello MG, Pascale R, Leoncini G (2002) Effect of homocysteine on arachidonic acid in human platelets. Eur J Clin Invest 32:279–284. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2362.2002.00971.x
Smrcka AV, Hepler JR, Brown KO, Sternweis PC (1991) Regulation of polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C activity by purified Gq. Science 251(4995):804–807. doi:10.1126/science.1846707
Spillmann F, Van Linthout S, Schulteiss HP, Tshope C (2006) Cardioprotective mechanisms of the kallikrein–kinin system in diabetic cardiopathy. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 15:22–29. doi:10.1097/01.mnh.0000199009.56799.2b
Starr MS, West GB (1966) The effect of bradykinin and anti-inflammatory agents on isolated arteries. J Pharm Pharmacol 18:838–840
Stuhlinger MC, Tsao PS, Her JH, Kimoto M, Balint RF, Cooke JP (2001) Homocysteine impairs the nitric oxide synthase pathway: role of asymmetric dimethylarginine. Circulation 104:2569–2575. doi:10.1161/hc4601.098514
Symons JD, Mullick AE, Ensunsa JL, Ma AA, Rutledge JC (2002) Hyperhomocysteinemia evoked by folate depletion: effects on coronary and carotid arterial function. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 22:772–780. doi:10.1161/01.ATV.0000014588.71807.0A
Taylor SJ, Chae HZ, Rhee SG, Exton JH (1991) Activation of the beta 1 isozyme of phospholipase C by alpha subunits of the Gq class of G proteins. Nature 350(6318):516–518. doi:10.1038/350516a0
Tirapelli CR, De Andrade CR, Lieberman M, Laurindo FR, De Souza HP, de Oliveira AM (2006) Vitamin K1 (phylloquinone) induces vascular endothelial dysfunction: role of oxidative stress. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 213:10–17. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2005.09.001
Tirapelli CR, Bonaventura D, De Oliveira AM (2007) Functional characterization of the mechanisms underlying bradykinin-induced relaxation in the isolated rat carotid artery. Life Sci 80:1799–1805. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2007.02.012
Ungvari Z, Pacher P, Rischak K, Szollar L, Koller A (1999) Dysfunction of nitric oxide mediation in isolated rat arterioles with methionine diet-induced hyperhomocysteinemia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19:1899–1904
Ungvari Z, Sarkadi-nagy E, Bagi Z, Szollar L, Koller A (2000) Simultaneously increase TXA2 activity in isolated arterioles and plaquetes of rats with hyperhomocysteinemia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:1203–1208
Wang J, Dudman NP, Wicken DE (1993) Effects of homocysteine related compounds on prostacyclin production by cultured human vascular endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost 70:1047–1052
Weiss N (2005) Mechanisms of increased vascular oxidant stress in hyperhomocysteinemia and its impact on endothelial function. Curr Drug Metab 6:27–36. doi:10.2174/1389200052997357
Wigg SJ, Tare M, Tonta MA, O’Brien RC, Meredith IT, Parkington HC (2001) Comparison of effects of diabetes mellitus on an EDHF-dependent and an EDHF-independent artery. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 281:H232–H240
Wimalasundera R, Fexby S, Regan L, Thom SA, Hughes AD (2003) Effect of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin 1beta on endothelium-dependent relaxation in rat mesenteric resistance arteries in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 138:1285–1294. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0705168
Acknowledgments
We are most grateful to Mirian C. C. de Melo, Juliana A. Vercesi and Mayara S. Gomes for their technical assistance. We thank FAPESP for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonaventura, D., Tirapelli, C.R. & de Oliveira, A.M. Chronic methionine load-induced hyperhomocysteinemia impairs the relaxation induced by bradykinin in the isolated rat carotid. Amino Acids 37, 617–627 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-008-0181-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-008-0181-z