Abstract
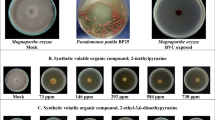
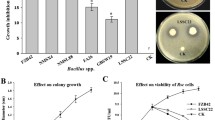
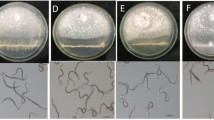
Rice bacterial blight, caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo), is a severe disease of rice plants. Upon pathogen infection, rice biosynthesizes phytoalexins, including diterpenoids such as momilactones, phytocassanes, and oryzalexins. However, information on headspace volatiles in response to Xoo infection is limited. We have examined headspace volatile terpenes, induced by the infection of Xoo, and investigated their biological roles in the rice plant. Monoterpenes α-thujene, α-pinene, sabinene, myrcene, α-terpene, and (S)-limonene and sesquiterpenes cyclosativene, α-copaene, and β-elemene were detected from 1-week-old Xoo-infected rice seedlings, by solid-phase microextraction–gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. All monoterpenes were constitutively released from rice seedlings before Xoo infection. However, (S)-limonene emission was further elicited after exposure of the seedlings to Xoo in coincidence with upregulation of limonene synthase gene (OsTPS20) transcripts. Only the stereospecific (S)-limonene [and not (R)-limonene or other monoterpenes] severely inhibited Xoo growth, as confirmed by disc diffusion and liquid culture assays. Rice seedlings showed suppressed pathogenic symptoms suggestive of resistance to Xoo infection after foliar treatment with (S)-limonene. Collectively, our findings suggest that (S)-limonene is a volatile phytoanticipin, which plays a significant role in suppressing Xoo growth in rice seedlings.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arimura G et al (2008) Herbivore-induced terpenoid emission in Medicago truncatula: concerted action of jasmonate, ethylene and calcium signaling. Planta 227:453–464
Bajpai VK, Kang S, Xu H, Lee S-G, Baek K-H, Kang SC (2011) Potential roles of essential oils on controlling plant pathogenic bacteria Xanthomonas species. Plant Pathol J 27:207–224
Bohlmann J, Meyer-Gauen G, Croteau R (1998) Plant terpenoid synthases: molecular biology and phylogenetic analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:4126–4133
Cartwright DW, Langcake P, Pryce RJ, Leworthy DP, Ride JP (1981) Isolation and characterization of two phytoalexins from rice as momilactones A and B. Phytochemistry 20:535–537
Chen F, Tholl D, Bohlmann J, Pichersky E (2011) The family of terpene synthases in plants: a mid-size family of genes for specialized metabolism that is highly diversified throughout the kingdom. Plant J 66:212–229
Hasegawa M et al (2010) Phytoalexin accumulation in the interaction between rice and the blast fungus. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 23:1000–1011
Horino O, Kaku H (1989) Defense mechanisms of rice against bacterial blight caused by Xanthomonas campestris pv. oryzae. pp. 135–152. In: Bacterial blight of rice. IRRI, Los Banos, Philippines
Karagnilla A, Paris-Natural M, Ou SH (1973) A comparative study of culture media for Xanthomonas oryzae. Philipp Agric 57:141–152
Kato T et al (1973) Momilactones, growth inhibitors from rice, Oryza sativa L. Tetrahedron Lett 14:3861–3864
Kato H, Kodama O, Akatsuka T (1994) Oryzalexin F, a diterpene phytoalexin from UV-irradiated rice leaves. Phytochemistry 36:299–301
Kauffman H, Reddy A, Hsieh S, Merca S (1973) Improved technique for evaluating resistance of rice varieties to Xanthomonas oryzae. Plant Disease Reporter
Kodama O, Miyakawa J, Akatsuka T, Kiyosawa S (1992) Sakuranetin, a flavanone phytoalexin from ultraviolet-irradiated rice leaves. Phytochemistry 31:3807–3809
Koga J, Shimura M, Oshima K, Ogawa N, Yamauchi T, Ogasawara N (1995) Phytocassanes A, B, C and D, novel diterpene phytoalexins from rice, Oryza sativa L. Tetrahedron 51:7907–7918
Kono Y et al (1991) Structures of oryzalides A and B, and oryzalic acid A, a group of novel antimicrobial diterpenes, isolated from healthy leaves of a bacterial leaf blight-resistant cultivar of rice plant. Agric Biol Chem 55:803–811
Kotan R, Kordali S, Cakir A (2007) Screening of antibacterial activities of twenty-one oxygenated monoterpenes. Z Naturforsch C 62:507–513
Lee G, Lee S, Chung M-S, Jeong Y, Chung B (2015) Rice terpene synthase 20 (OsTPS20) plays an important role in producing terpene volatiles in response to abiotic stresses. Protoplasma 252:997–1007
Lichtenthaler HK (1999) The 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50:47–65
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Loreto F, Förster A, Dürr M, Csiky O, Seufert G (1998) On the monoterpene emission under heat stress and on the increased thermotolerance of leaves of Quercus ilex L. fumigated with selected monoterpenes. Plant Cell Environ 21:101–107
Mew T (1987) Current status and future prospects of research on bacterial blight of rice. Annu Rev Phytopathol 25:359–382
Mew T, Alvarez A, Leach J, Swings J (1993) Focus on bacterial blight of rice. Plant Dis 77:5–12
Pare PW, Tumlinson JH (1999) Plant volatiles as a defense against insect herbivores. Plant Physiol 121:325–332
Reimers PJ, Guo A, Leach JE (1992) Increased activity of a cationic peroxidase associated with an incompatible interaction between Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and rice (Oryza sativa). Plant Physiol 99:1044–1050
Rodríguez A et al (2011) The monoterpene limonene in orange peels attracts pests and microorganisms. Plant Signal Behav 6:1820–1823
Rodríguez A et al (2014) Terpene down-regulation triggers defense responses in transgenic orange leading to resistance against fungal pathogens. Plant Physiol 164:321–339
Taniguchi S, Hosokawa-Shinonaga Y, Tamaoki D, Yamada S, Akimitsu K, Gomi K (2014a) Jasmonate induction of the monoterpene linalool confers resistance to rice bacterial blight and its biosynthesis is regulated by JAZ protein in rice. Plant Cell Environ 37:451–461
Taniguchi S et al (2014b) Isolation of jasmonate-induced sesquiterpene synthase of rice: product of which has an antifungal activity against Magnaporthe oryzae. J Plant Physiol 171:625–632
Tholl D (2006) Terpene synthases and the regulation, diversity and biological roles of terpene metabolism. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9:297–304
Watanabe M et al (1990) Novel C19-kaurane type of diterpene (oryzalide A), a new antimicrobial compound isolated from healthy leaves of a bacterial leaf blight-resistant cultivar of rice plant. Agric Biol Chem 54:1103–1105
Watanabe M et al (1992) Structures of oryzalic acid B and three related compounds, a group of novel antibacterial diterpenes, isolated from leaves of a bacterial leaf blight-resistant cultivar of rice. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 56:113–117
Yuan JS, Köllner TG, Wiggins G, Grant J, Degenhardt J, Chen F (2008) Molecular and genomic basis of volatile-mediated indirect defense against insects in rice. Plant J 55:491–503
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Nuclear R&D Program of the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning (MSIP), Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Bhumi Nath Tripathi
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, G.W., Chung, MS., Kang, M. et al. Direct suppression of a rice bacterial blight (Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae) by monoterpene (S)-limonene. Protoplasma 253, 683–690 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-015-0904-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-015-0904-4