Abstract
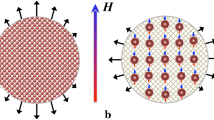
Magneto-active elastomers are smart materials composed of a rubber-like matrix material containing a distribution of magneto active particles. The large elastic deformations possible in the rubber-like matrix allow the mechanical properties of magneto-active elastomers to be changed significantly by the application of external magnetic fields. In this paper, we provide a theoretical basis for the description of the nonlinear properties of a particular class of these materials, namely transversely isotropic magneto-active elastomers. The transversely isotropic character of these materials is produced by the application of a magnetic field during the curing process, when the magneto active particles are distributed within the rubber. As a result the particles are aligned in chains that generated a preferred direction in the material. Available experimental data suggest that this enhances the stiffness of the material in the presence of an external magnetic field by comparison with the situation in which no external field is applied during curing, which leads to an essentially random (isotropic) distribution of particles. Herein, we develop a general form of the constitutive law for such magnetoelastic solids. This is then used in the solution of two simple problems involving homogeneous deformations, namely simple shear of a slab and simple tension of a cylinder. Using these results and the experimental available data we develop a prototype constitutive equation, which is used in order to solve two boundary-value problems involving non-homogeneous deformations—the extension and inflation of a circular cylindrical tube and the extension and torsion of a solid circular cylinder.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farshad M., Le Roux M.: A new active noise abatement barrier system. Polym. Test. 23, 855–860 (2004)
Jolly M.R., Carlson J.D., Muñoz B.C.: A model of the behaviour of magnetorheological materials. Smart Mater. Struct. 5, 607–614 (1996)
Kari L., Blom P.: Magneto-sensitive rubber in a noise reduction context-exploring the potential. Plast. Rubber Compos. 34, 365–371 (2005)
Bellan C., Bossis G.: Field dependence of viscoelastic properties of MR elastomers. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 16, 2447–2453 (2002)
Bossis G., Abbo C., Cutillas S.: Electroactive and electrostructured elastomers. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 15, 564–573 (2001)
Farshad M., Benine A.: Magnetoactive elastomer composites. Polym. Test. 23, 347–357 (2004)
Farshad M., Le Roux M.: Compression properties of magnetostrictive polymer composite gels. Polym. Test. 24, 163–168 (2005)
Ginder J.M., Nichols M.E., Elie L.D., Tardiff J.L.: Magnetorheological elastomers: properties and applications. Proc. Smart Struct. Mater. SPIE 3675, 131–138 (1999)
Varga Z., Filipcsei G., Szilággi A., Zríngi M.: Electric and magnetic field-structured smart composites. Macromol. Symp. 227, 123–133 (2005)
Varga Z., Filipcsei G., Zríngi M.: Magnetic field sensitive functional elastomers with tuneable modulus. Polymer 47, 227–233 (2006)
Dorfmann A., Ogden R.W.: Magnetoelastic modelling of elastomer. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids 22, 497–507 (2003)
Dorfmann A., Ogden R.W.: Nonlinear magnetoelastic deformations. Q. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 57, 599–622 (2004)
Dorfmann A., Ogden R.W.: Nonlinear magnetoelastic deformations of elastomers. Acta Mech. 167, 13–28 (2003)
Dorfmann A., Ogden R.W., Saccomandi G.: The effect of rotation on the nonlinear magnetoelastic response of a circular cylindrical tube. Int. J. Solids Struct. 42, 3700–3715 (2005)
Dorfmann A., Ogden R.W.: Some problems in nonlinear magnetoelasticity. Z. Angew. Math. Phys. 56, 718–745 (2005)
Brown W.F.: Magnetoelastic Interactions. Springer, Berlin (1966)
Hutter K.: On thermodynamics and thermostatics of viscous thermoelastic solids in the electromagnetic fields. A Lagrangian formulation. Arch. Rat. Mech. Anal. 54, 339–366 (1975)
Hutter K.: A thermodynamic theory of fluids and solids in the electromagnetic fields. Arch. Rat. Mech. Anal. 64, 269–289 (1977)
Eringen A.C., Maugin G.A.: Electrodynamics of Continua I. Foundations and Solid Media. Springer, Berlin (1990)
Kovetz A.: Electromagnetic Theory. Oxford University Press, NY (2000)
Hutter, K., van de Ven , A.A.: Field Matter Interactions in Thermoelastic Solids. Lectures Notes in Physics vol. 88. Springer, Berlin (1978)
Pao, Y. H.: Electromagnetic forces in deformable continua. In: Nemat-Nasser S. (ed.), Mechanics Today, vol. 4, pp. 209–306 (1978)
Borcea L., Bruno O.: On the magneto-elastic properties of elastomer-ferromagnet composites. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 49, 2877–2919 (2001)
Yin H.M., Sun L.Z., Chen J.S.: Magneto-elastic modeling of composites containing chain-structured magnetostrictive particles. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 54, 975–1003 (2006)
Kankanala S.V., Triantafyllidis N.: On finitely strained magnetorheological elastomers. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 52, 2869–2908 (2004)
Bustamante, R.: Transversely isotropic non-linear electro-active elastomers. Acta Mech. doi:10.1007/s00033-007-7145-0 (2008)
Singh M., Pipkin A.C.: Controllable states of elastic dielectrics. Arch. Rat. Mech. Anal. 21, 169–210 (1966)
Pucci E., Saccomandi G.: On the controllable states of elastic dielectric and magnetoelastic solids. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 31, 251–256 (1993)
Bustamante R., Dorfmann A., Ogden R.W.: Universal relations in isotropic nonlinear magnetoelasticity. Q. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 59, 435–450 (2006)
Bustamante, R.: Mathematical modelling of non-linear magneto- and electro-elastic rubber-like materials. Ph.D. thesis, University of Glasgow (2007)
Ogden R.W.: Non-linear elastic deformations. Dover, New York (1997)
Steigmann D.J.: Equilibrium theory for magnetic elastomers and magnetoelastic membranes. Int. J. Non Linear Mech. 39, 1193–1216 (2004)
Bustamante R., Dorfmann A., Ogden R.W.: On variational formulations in nonlinear magnetoelastostatics. Math. Mech. Solids 13, 725–745 (2008)
Spencer A.J.M.: Theory of invariants. In: Eringen, A.C. (eds) Continuum Physics, vol. 1, pp. 239–353. Academic, New York (1971)
Zheng Q.S.: Theory of representations for tensor functions. A unified invariant approach to constitutive equations. Appl. Mech. Rev. 47, 545–587 (1994)
Maugin, G.A.: Continuum mechanics of Electromagnetic Solids. North Holland Series in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, vol. 33. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1988)
Brigadnov I.A., Dorfmann A.: Mathematical modeling of magneto-sensitive elastomers. Int. J. Solids Struct. 40, 4659–4674 (2003)
Bustamante R., Dorfmann A., Ogden R.W.: A nonlinear magnetoelastic tube under extension and inflation in an axial magnetic field: numerical solution. J. Eng. Math. 59, 139–153 (2007)
Saccomandi, G., Ogden, R. W. (eds.): Mechanics and Thermomechanics of Rubberlike Solids. CISM Courses and Lectures Series, vol. 452. Springer, Wien (2004)
Merodio J., Ogden R.W.: Instabilities and loss of ellipticity in fiber-reinforced compressible non-linearly elastic solids under plane deformation. Int. J. Solids Struct. 40, 4704–4727 (2003)
Merodio J., Ogden R.W.: Mechanical response of fiber-reinforced incompressible non-linearly elastics solids. Int. J. Non Linear Mech. 40, 213–227 (2005)
Jiang X., Ogden R.W.: On azimuthal shear of a circular cylindrical tube of compressible elastic material. Q. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 51, 143–158 (1998)
Varga Z., Filipcsei G., Zríngi M.: Smart composites with controlled anisotropy. Polymer 46, 7779–7787 (2005)
Bustamante, R.: Mathematical modelling of boundary conditions for magneto-sensitive elastomers: variational formulations. J. Eng. Math. doi:10.1007/s10665-008-9263-x (2009)
Coquelle E., Bossis G.: Mullins effect in elastomers filled with particles aligned by a magnetic field. Int. J. Solids Struct. 43, 7659–7672 (2006)
Criscione J.C.: Rivlin’s representation formula is ill-conceived for the determination of response functions via biaxial testing. J. Elast. 70, 129–147 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bustamante, R. Transversely isotropic nonlinear magneto-active elastomers. Acta Mech 210, 183–214 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-009-0193-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-009-0193-0