Abstract
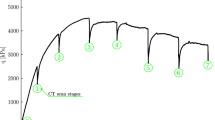
We investigate the strength and failure properties of a model cemented granular material under simple compressive deformation. The particles are lightweight expanded clay aggregate beads coated by a controlled volume fraction of silicone. The beads are mixed with a joint seal paste (the matrix) and molded to obtain dense cemented granular samples of cylindrical shape. Several samples are prepared for different volume fractions of the matrix, controlling the porosity, and silicone coating upon which depends the effective particle–matrix adhesion. Interestingly, the compressive strength is found to be an affine function of the product of the matrix volume fraction and effective particle–matrix adhesion. On the other hand, it is shown that particle damage occurs beyond a critical value of the contact debonding energy. The experiments suggest three regimes of crack propagation corresponding to no particle damage, particle abrasion and particle fragmentation, respectively, depending on the matrix volume fraction and effective particle–matrix adhesion. We also use a sub-particle lattice discretization method to simulate cemented granular materials in two dimensions. The numerical results for crack regimes and the compressive strength are in excellent agreement with the experiments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benhamida A., Bouchelaghem F., Dumontet H.: Effective properties of a cemented or an injected granular material. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 29, 187–208 (2005)
Buyukozturk O., Hearing B.: Crack propagation in concrete composites influenced by interface fracture parameters. Int. J. Solids Struct. 35(31–32), 4055–4066 (1998)
Castellanos A.: The relationship between attractive interparticle forces and bulk behaviour in dry and uncharged fine powders. Adv. Phys. 54(114), 263–376 (2005)
Chiaia B.M., Vervuurt A., Van Mier J.G.M.: Lattice model evaluation of progressive failure in disordered particle composites. Eng. Fract. Mech. 57(2–3), 301–309 (1997)
de Larrard F., Belloc A.: The influence of aggregate on the compressive strength of normal and high-strength concrete. ACI Mater. J. 94, 417–426 (1997)
Delaplace A., Pijaudier-Cabot G., Roux S.: Progressive damage in discrete models and consequences on continuum modelling. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 44(1), 99–136 (1996)
Delenne J.-Y., El Youssoufi M.S., Cherblanc F., Benet J.-C.: Mechanical behaviour and failure of cohesive granular materials. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 28(15), 1577–1594 (2004)
Delenne J.Y., Haddad Y., Benet J.C., Abecassis J.: Use of mechanics of cohesive granular media for analysis of hardness and vitreousness of wheat endosperm. J. Cereal Sci. 47(3), 438–444 (2008)
El Youssoufi M.S., Delenne J.-Y., Radjaï F.: Self-stresses and crack formation by particle swelling in cohesive granular media. Phys. Rev. E 71, 051307 (2005)
Elata D., Dvorkin J.: Pressure sensitivity of cemented granular materials. Mech. Mater. 23(2), 147–154 (1996)
Fitoussi J., Guo G., Baptiste D.: A statistical micromechanical model of anisotropic damage for s.m.c. composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 58(5), 759–763 (1998)
Goddard J.D.: Microstructural origins of continuum stress fields—a brief history and some unresolved issues. In: DeKee, D., Kaloni, P.N. (eds.) Recent Developments in Structured Continua. Pitman Research Notes in Mathematics No. 143, p 179. Longman, J. Wiley, New York (1986)
He M.-Y., Hutchinson J.W.: Crack deflection at an interface between dissimilar elastic materials. Int. J. Solids Struct. 25(9), 1053–1067 (1989)
Herrmann, H.J., Roux, S. (eds): Statistical Models for Fracture in Disordered Media. North Holland, Amsterdam (1990)
Johnson K.L.: Contact Mechanics. University Press, Cambridge (1999)
Kendall K., Alford N.McN., Birchall J.D.: The strength of green bodies. Br. Ceram. Proc. 37, 255–265 (1986)
Liu, A.J., Nagel, S.R. (eds): Jamming and Rheology. Taylor & Francis, New York (2001)
Merchant I.J., Macphee D.E., Chandler H.W., Henderson R.J.: Toughening cement-based materials through the control of interfacial bonding. Cement Concrete Res. 31(12), 1873–1880 (2001)
Mishnaevsky L. Jr, Derrien K., Baptiste D.: Effect of microstructure of particle reinforced composites on the damage evolution: probabilistic and numerical analysis. Compos. Sci. Technol. 64(12), 1805–1818 (2004)
Morris C.F.: Puroindolines: the molecular genetic basis of wheat grain hardness. Plant Mol. Biol. 48, 633–647 (2002)
Nadot-Martin C., Trumel H., Dragon A.: Morphology-based homogenization for viscoelastic particulate composites: Part I: Viscoelasticity sole. Eur. J. Mech. A Solids 22(1), 89–106 (2003)
Ouadfel H., Rothenburg L.: Stress–force–fabric relationship for assemblies of ellipsoids. Mech. Mater. 33(4), 201–221 (2001)
Radjaï F., Preechawuttipong I., Peyroux R.: Cohesive granular texture. In: Vermeer, P.A., Diebels, S., Ehlers, W., Herrmann, H.J., Luding, S., Ramm, E. (eds) Continuous and Discontinuous Modelling of Cohesive Frictional Materials, pp. 148–159. Springer, Berlin (2000)
Richefeu V., El Youssoufi M.S., Radjai F.: Shear strength properties of wet granular materials. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys.) 73(5), 051304 (2006)
Roux, S.: Statistical models for fracture in disordered media. In: Continuum and Discrete Description Of Elasticity and Other Rheological Behavior. pp. 87–114. North Holland, Amsterdam (1990)
Sahimi M.: Heterogeneous Materials II. Springer, New York (2003)
Schlangen E., van Mier J.G.M.: Experimental and numerical analysis of micromechanisms of fracture of cement-based composites. Cement Concrete Compos. 14(2), 105–118 (1992)
Sienkiewicz F., Shukla A., Sadd M., Zhang Z., Dvorkin J.: A combined experimental and numerical scheme for the determination of contact loads between cemented particles. Mech. Mater. 22(1), 43–50 (1996)
Tan H., Huang Y., Liu C., Geubelle P.H.: The mori-tanaka method for composite materials with nonlinear interface debonding. Int. J. Plast. 21(10), 1890–1918 (2005)
Tan H., Huang Y., Liu C., Ravichandran G., Inglis H.M., Geubelle P.H.: The uniaxial tension of particulate composite materials with nonlinear interface debonding. Int. J. Solids Struct. 44(6), 1809–1822 (2007)
Tarbuck E.J., Lutgens F.K.: Earth—An Introduction to Physical Geology. Pearson Education, New Jersey (2005)
Topin V., Delenne J.-Y., Radjai F., Brendel L., Mabille F.: Strength and fracture of cemented granular matter. Eur. Phys. J. E 23, 413–429 (2007)
Topin V., Radjai F., Delenne J.-Y., Mabille F.: Mechanical modeling of wheat hardness and fragmentation. Powder Technol. 190(1–2), 215–220 (2009)
Topin V., Radjai F., Delenne J.-Y., Sadoudi A., Mabille F.: Wheat endosperm as a cohesive granular material. J. Cereal Sci. 47(2), 347–356 (2008)
Troadec H., Radjai F., Roux S., Charmet J.C.: Model for granular texture with steric exclusion. Phys. Rev. E 66(41), 041305-1 (2002)
Turnbull K.M., Rahman S.: Endosperm texture in wheat. J. Cereal Sci. 36(3), 327–337 (2002)
Van Mier J.G.M., Chiaia B.M., Vervuurt A.: Numerical simulation of chaotic and self-organizing damage in brittle disordered materials. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 142(1–2), 189–201 (1997)
Voivret C., Radjai F., Delenne J.-Y., El Youssoufi M.S.: Space-filling properties of polydisperse granular media. Phys. Rev. E 76(2), 021301–021312 (2007)
Zhonghua L., Schmauder S.: Phase-stress partition and residual stress in metal matrix composites. Comput. Mater. Sci. 18(3–4), 295–302 (2000)
Zhou C.W., Yang W., Fang D.N.: Mesofracture of metal matrix composites reinforced by particles of large volume fraction. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 41(1–3), 311–326 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delenne, J.Y., Topin, V. & Radjai, F. Failure of cemented granular materials under simple compression: experiments and numerical simulations. Acta Mech 205, 9–21 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-009-0160-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-009-0160-9