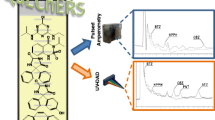
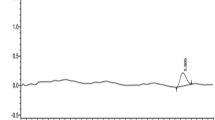
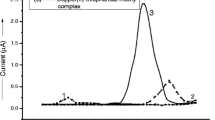
Abstract
The azoles (represented by penconazole, cyproconazole, and tebuconazole in this study) are frequently used agrochemicals to protect various crops against mildew and fungi. They are considered as endocrine disruptors, because they block the biosynthesis (on the level of enzymes inhibition) of biochemicals with steroid structure. Besides targeted impacts, they can partly get into the soil with the rainfall or litter fall and influence/block the biosynthesis of sterols of non-target organisms. In this sense, the risk of disruption of rhizosphere plant–microbial symbiosis and dynamic processes in the soil solution by azoles is of high importance to be evaluated. We have developed an analytical methodology for determination of penconazole, cyproconazole, and tebuconazole in soil solution using capillary electrophoresis with a photodiode array detector at UV-214 nm and acidic electrolyte solution (pH 1.48). The results were also compared with mass spectrometric measurements using μ-TOF mass spectrometry. There approx. 90% of present azoles were bound in the soil solution matrix. The detection limit for these azoles is about 10–7 mol dm−3. Because of very low pKa of azoles, we have to consider deprotonation of azoles and consequently the high affinity to create complexes with cations. The majority of present azoles in soil solution might form neutral adducts with mono-cations, making them invisible in electrospray mass spectra.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zarn JA, Bruschweiler BJ, Schlatter JR (2003) Environ Health Perspect 111:255
Trösken ER, Fischer K, Völkel W, Lutz WK (2006) Toxicology 219:33
Jakl M, Fanfrlík J, Jaklová Dytrtová J (2017) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 31:2043
Jaklová Dytrtová J, Fanfrlík J, Norková R, Jakl M, Hobza P (2014) Int J Mass Spectrom 359:38
Jaklová Dytrtová J, Straka M, Bělonožníková K, Jakl M, Ryšlavá H (2018) Food Chem 262:221
Rugova A, Puschenreiter M, Koellensperger G, Hann S (2017) Anal Chim Acta 956:1
Neumann G, George TS, Plassard C (2009) Plant Soil 321:431
Jaklová Dytrtová J, Šestáková I, Jakl M, Navrátil T (2009) Electroanalysis 21:573
Grossmann J, Udluft P (1991) J Soil Sci 42:83
McGahan DG, Southard RJ, Zasoski RJ (2014) Geoderma 226:340
Jaklová Dytrtová J, Jakl M, Schröder D, Navrátil T (2011) Curr Org Chem 15:2970
Jones DL (1998) Plant Soil 205:25
Norková R, Jaklová Dytrtová J, Jakl M, Schröder D (2012) Water Air Soil Pollut 223:2633
Kim KR, Owens G, Naidu R, Kwon SI (2010) Geoderma 155:86
Huang QX, Yu YY, Tang CM, Peng XZ (2010) J Chromatogr A 1217:3481
Ekiert RJ, Krzek J, Talik P (2010) Talanta 82:1090
Chicharro M, Zapardiel A, Bermejo E, Moreno M (2003) Talanta 59:37
Pavlíček V, Tůma P, Matějčková J, Samcová E (2014) Electrophoresis 35:956
Glatz Z (2013) Electrophoresis 34:631
Konášová R, Jaklová Dytrtová J, Kašička V (2015) J Chromatogr A 1408:243
Nowak PM, Wozniakiewicz M, Gladysz M, Janus M, Koscielniak P (2017) Anal Bioanal Chem 409:4383
Jakl M, Jaklová Dytrtová J, Miholová D, Kolihová D, Száková J, Tlustoš P (2009) Chem Speciat Bioavail 21:111
Antoniadis V, Levizou E, Shaheen SM, Ok YS, Sebastian A, Baum C, Prasad MNV, Wenzel WW, Rinklebe J (2017) Earth Sci Rev 171:621
Jaklová Dytrtová J, Jakl M, Schröder D, Čadková E, Komárek M (2011) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 25:1037
Jaklová Dytrtová J, Šestáková I, Jakl M, Száková J, Miholová D, Tlustoš P (2008) Cent Eur J Chem 6:71
Gordien JB, Pigneux A, Vigouroux S, Tabrizi R, Accoceberry I, Bernadou JM, Rouault A, Saux MC, Breilh D (2009) J Pharm Biomed Anal 50:932
Acknowledgements
This work was supported (J. Jaklová Dytrtová) by the Czech Science Foundation (18-01710S).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takala, N., Sirén, H., Jakl, M. et al. Determination of important azoles in soil solution using CE. Monatsh Chem 150, 1625–1631 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-019-02447-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-019-02447-x