Abstract
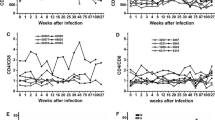
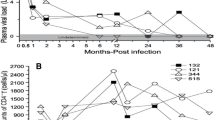
The cytokine interleukin-21 (IL-21) regulates viral pathogenesis in individuals infected with human and simian immunodeficiency viruses. However, because the time of initial infection with HIV in humans is rarely known, the dynamics of IL-21 production during the first weeks have not been adequately explored. In the present study, we used rhesus macaques to model the first stages of infection. Twenty-two rhesus macaques were infected rectally with simian-human immunodeficiency virus (SHIV)-1157ipd3N4, and for 12 weeks, replication of the virus, the numbers of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and the levels of plasma IL-21 were monitored. Our study demonstrated that plasma levels of IL-21 increased during the early phase of SHIV infection when compared with the values observed before inoculation. We conclude that IL-21 has a likely role in the immunopathogenesis of HIV/SIV/SHIV.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parrish-Novak J, Dillon SR, Nelson A, Hammond A, Sprecher C et al (2000) Interleukin 21 and its receptor are involved in NK cell expansion and regulation of lymphocyte function. Nature 408:57–63
Alter G, Heckerman D, Schneidewind A, Fadda L, Kadie CM et al (2011) HIV-1 adaptation to NK-cell-mediated immune pressure. Nature 476:96–100
Iannello A, Boulassel MR, Samarani S, Tremblay C, Toma E et al (2010) IL-21 enhances NK cell functions and survival in healthy and HIV-infected patients with minimal stimulation of viral replication. J Leukoc Biol 87:857–867
Williams LD, Bansal A, Sabbaj S, Heath SL, Song W et al (2011) Interleukin-21-producing HIV-1-specific CD8 T cells are preferentially seen in elite controllers. J Virol 85:2316–2324
Chevalier MF, Julg B, Pyo A, Flanders M, Ranasinghe S et al (2011) HIV-1-specific interleukin-21+ CD4+ T cell responses contribute to durable viral control through the modulation of HIV-specific CD8+ T cell function. J Virol 85:733–741
Yue FY, Lo C, Sakhdari A, Lee EY, Kovacs CM et al (2010) HIV-specific IL-21 producing CD4+ T cells are induced in acute and chronic progressive HIV infection and are associated with relative viral control. J Immunol 185:498–506
Porichis F, Kwon DS, Zupkosky J, Tighe DP, McMullen A et al (2011) Responsiveness of HIV-specific CD4 T cells to PD-1 blockade. Blood 118:965–974
Thompson JA, Curti BD, Redman BG, Bhatia S, Weber JS et al (2008) Phase I study of recombinant interleukin-21 in patients with metastatic melanoma and renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 26:2034–2039
Frederiksen KS, Lundsgaard D, Freeman JA, Hughes SD, Holm TL et al (2008) IL-21 induces in vivo immune activation of NK cells and CD8(+) T cells in patients with metastatic melanoma and renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother 57:1439–1449
Zheng L, Diallo M, Chen X, Zheng Y, He Y et al (2011) IL-21 level in Chinese HIV infected individuals and its dynamics undergoing HAART. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 36:1059–1064
Iannello A, Tremblay C, Routy JP, Boulassel MR, Toma E et al (2008) Decreased levels of circulating IL-21 in HIV-infected AIDS patients: correlation with CD4+ T-cell counts. Viral Immunol 21:385–388
Garcia A, Siddappa NB, Li Q, Haase AT, Paul K et al (2010) AIDS and optic neuritis in a rhesus monkey infected with the R5 clade C SHIV-1157ipd3N4. J Med Primatol 39:356–360
Santosuosso M, Righi E, Hill ED, Leblanc PR, Kodish B et al (2011) R5-SHIV induces multiple defects in T cell function during early infection of rhesus macaques including accumulation of T reg cells in lymph nodes. PLoS One 6:e18465
Humbert M, Rasmussen RA, Song R, Ong H, Sharma P et al (2008) SHIV-1157i and passaged progeny viruses encoding R5 HIV-1 clade C env cause AIDS in rhesus monkeys. Retrovirology 5:94
Leutenegger CM, Higgins J, Matthews TB, Tarantal AF, Luciw PA et al (2001) Real-time TaqMan PCR as a specific and more sensitive alternative to the branched-chain DNA assay for quantitation of simian immunodeficiency virus RNA. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 17:243–251
Niu MT, Bethel J, Holodniy M, Standiford HC (1998) Zidovudine treatment in patients with primary (acute) human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. DATRI 002 Study Group. Division of AIDS Treatment Research Initiative. J Infect Dis 178:80–91
Pasquier C, Saune K, Raymond S, Moinard N, Daudin M et al (2009) Determining seminal plasma human immunodeficiency virus type 1 load in the context of efficient highly active antiretroviral therapy. J Clin Microbiol 47:2883–2887
Halfon P, Giorgetti C, Khiri H, Penaranda G, Terriou P et al (2010) Semen may harbor HIV despite effective HAART: another piece in the puzzle. PLoS One 5:e10569
Butler DM, Delport W, Kosakovsky Pond SL, Lakdawala MK, Cheng PM et al (2010) The origins of sexually transmitted HIV among men who have sex with men. Sci Transl Med 2:18re11
Iannello A, Boulassel MR, Samarani S, Debbeche O, Tremblay C et al (2010) Dynamics and consequences of IL-21 production in HIV-infected individuals: a longitudinal and cross-sectional study. J Immunol 184:114–126
Kim HP, Korn LL, Gamero AM (2005) Leonard WJ Calcium-dependent activation of interleukin-21 gene expression in T cells. J Biol Chem 280:25291–25297
Zhu X, Ma D, Zhang J, Peng J, Qu X et al (2010) Elevated interleukin-21 correlated to Th17 and Th1 cells in patients with immune thrombocytopenia. J Clin Immunol 30:253–259
Petersen CM, Christensen EI, Andresen BS (1992) Moller BK Internalization, lysosomal degradation and new synthesis of surface membrane CD4 in phorbol ester-activated T-lymphocytes and U-937 cells. Exp Cell Res 201:160–173
Barker BR, Parvani JG, Meyer D, Hey AS, Skak K et al (2007) IL-21 induces apoptosis of antigen-specific CD8+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol 179:3596–3603
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Prof. Ruth Ruprecht at the Dana Farber Cancer Institute, USA, for her kind provision of SHIV-1157ipd3N4. We are grateful to Drs. Zhigang Yao, Dongmei Wang, Pingsen Zhao, and Hao Gu for their technical support. Funding: This study was supported by grants from the National Science and Technology Major projects of Infectious Disease (2012 2×10004-501, 2012 2×10001-007, and 2012 2×10001-006). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Cc., Xue, J., Cong, Z. et al. Circulating IL-21 levels increase during early simian-human immunodeficiency virus infection in macaques. Arch Virol 158, 853–858 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-012-1534-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-012-1534-1