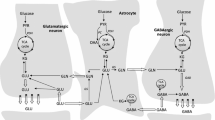
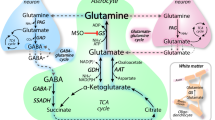
Abstract
In this study, the relationship between endogenous brain GABA concentration and glutamate–glutamine cycling flux (V cyc) was investigated using in vivo 1H and 1H{13C} magnetic resonance spectroscopy techniques. Graded elevations of brain GABA levels were induced in rat brain after administration of the highly specific GABA-transaminase inhibitor vigabatrin (γ-vinyl-GABA). The glial-specific substrate [2-13C]acetate and 1H{13C} magnetic resonance spectroscopy were used to measure V cyc at different GABA levels. Significantly reduced V cyc was found in rats pretreated with vigabatrin. The reduction in group mean V cyc over the range of GABA concentrations investigated in this study (1.0 ± 0.3–5.1 ± 0.5 μmol/g) was found to be nonlinear: ΔV cyc/V cyc = [GABA (μmol/g)]−0.35 − 1.0 (r 2 = 0.98). The results demonstrate that V cyc is modulated by endogenous GABA levels, and that glutamatergic and GABAergic interactions can be studied in vivo using noninvasive magnetic resonance spectroscopy techniques.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banay-Schwartz M, Palkovits M, Lajtha A (1993) Heterogeneous distribution of functionally important amino acids in brain areas of adult and aging humans. Neurochem Res 18:417–423
Bergin AM, Connolly M (2002) New antiepileptic drug therapies. Neurol Clin 20:82–1163
Blüml S, Moreno-Torres A, Shic F, Nguy CH, Ross BD (2002) Tricarboxylic acid cycle of glia in the in vivo human brain. NMR Biomed 15:1–5
Boumezbeur F, Petersen KF, de Graaf RA, Cline GW, Behar KL, Shulman GI, Rothman DL, Mason GF (2008) Combination of datasets from [2-13C]acetate and [1-13C]glucose experiments improve accuracy of metabolite rates determination in humans. Proc Intl Soc Magn Reson Med, Abstract # 196, Toronto
Bradford HF (1995) Glutamate, GABA and epilepsy. Prog Neurobiol 47:477–511
Chapman AG, Riley K, Evens MC, Meldrum BS (1982) Acute effects of sodium valproate and γ-vinyl GABA on regional amino acid metabolism in the rat brain: incorporation of 2-[14C]glucose into amino acids. Neurochem Res 7:1089–1105
Chen Z, Li SS, Yang J, Letizia D, Shen J (2004) Measurement and automatic correction of high order B0 inhomogeneity in the rat brain at 11.7 Tesla. Magn Reson Imaging 22:835–842
Crowder JM, Bradford HF (1987) Inhibitory effects of noradrenaline and dopamine on calcium influx and neurotransmitter glutamate release in mammalian brain slices. Eur J Pharmacol 143:52–343
Danbolt NC, Storm-Mathisen J, Kanner BI (1992) An [Na+–K+]coupled l-glutamate transporter purified from rat brain is located in glial cell processes. Neuroscience 51:295–310
Hasler G, van der Veen JW, Tumonis T, Meyers N, Shen J, Drevets WC (2007) Reduced prefrontal glutamate/glutamine and gamma-aminobutyric acid levels in major depression determined using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64:193–200
Hertz L (2004) Intercellular metabolic compartmentation in the brain: past, present and future. Neurochem Int 45:285–296
Jackson MF, Esplin B, Capek R (2000) Reversal of the activity-dependent suppression of GABA-mediated inhibition in hippocampal slices from gamma-vinyl GABA (vigabatrin)-pretreated rats. Neuropharmacology 39:65–74
Kendell SF, Krystal JH, Sanacora G (2005) GABA and glutamate systems as therapeutic targets in depression and mood disorders. Expert Opin Ther Targets 9:153–168
Kuzniecky R, Ho S, Pan J, Martin R, Gilliam F, Faught E, Hetherington H (2002) Modulation of cerebral GABA by topiramate, lamotrigine, and gabapentin in healthy adults. Neurology 58:368–372
Lebon V, Petersen KF, Cline GW, Shen J, Mason GF, Dufour S, Behar KL, Shulman GI, Rothman DL (2002) Astroglial contribution to brain energy metabolism in humans revealed by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: elucidation of the dominant pathway for neurotransmitter glutamate repletion and measurement of astrocytic oxidative metabolism. J Neurosci 22:1523–1531
Manor D, Rothman DL, Mason GF, Hyder F, Petroff OA, Behar KL (1996) The rate of turnover of cortical GABA from [1–13C]glucose is reduced in rats treated with the GABA-transaminase inhibitor vigabatrin (gamma-vinyl GABA). Neurochem Res 21:1031–1041
Maura G, Marcoli M, Tortarolo M, Andrioli GC, Raiteri M (1998) Glutamate release in human cerebral cortex and its modulation by 5-hydroxytryptamine acting at h 5-HT1D receptors. Br J Pharmacol 123:45–50
McDonald DG, Najam Y, Keegan MB, Whooley M, Madden D, McMenamin JB (2005) The use of lamotrigine, vigabatrin and gabapentin as add-on therapy in intractable epilepsy of childhood. Seizure 14:112–116
Michaelis T, Merboldt KD, Bruhn H, Hanicke W, Frahm J (1993) Absolute concentrations of metabolites in the adult human brain in vivo: quantification of localized proton MR spectra. Radiology 187:219–227
Michael-Titus AT, Bains S, Jeetle J, Whelpton R (2000) Imipramine and phenelzine decrease glutamate overflow in the prefrontal cortex-a possible mechanism of neuroprotection in major depression? Neuroscience 100:681–684
Miller JM, Jope RS, Ferraro TN, Hare TA (1990) Brain amino acid concentrations in rats killed by decapitation and microwave irradiation. J Neurosci Methods 31:187–192
Parent MB, Habib MK, Baker GB (2000) Time-dependent changes in brain monoamine oxidase activity and in brain levels of monoamines and amino acids following acute administration of the antidepressant/antipanic drug phenelzine. Biochem Pharmacol 59:63–1253
Parent MB, Master S, Kashlub S, Baker GB (2002) Effects of the antidepressant/antipanic drug phenelzine and its putative metabolite phenylethylidenehydrazine on extracellular gamma-aminobutyric acid levels in the striatum. Biochem Pharmacol 63:57–64
Patel AB, de Graaf RA, Martin DL, Battaglioli G, Behar KL (2006) Evidence that GAD65 mediates increased GABA synthesis during intense neuronal activity in vivo. J Neurochem 97:385–396
Petroff OA, Hyder F, Collins T, Mattson RH, Rothman DL (1999) Acute effects of vigabatrin on brain GABA and homocarnosine in patients with complex partial seizures. Epilepsia 40:64–958
Piérard C, Pérès M, Satabin P, Guezennec CY, Lagarde D (1999) Effects of GABA-transaminase inhibition on brain metabolism and amino-acid compartmentation: an in vivo study by 2D 1H-NMR spectroscopy coupled with microdialysis. Exp Brain Res 127:321–327
Post RM, Denicoff KD, Frye MA, Dunn RT, Leverich GS, Osuch E, Speer A (1998) A history of the use of anticonvulsants as mood stabilizers in the last two decades of the 20th century. Neuropsychobiology 38:66–152
Preece NE, Cerdan S (1996) Metabolic precursors and compartmentation of cerebral GABA in vigabatrin-treated rats. J Neurochem 67:1718–1725
Provencher SW (2001) Automatic quantification of localized in vivo 1H spectra with LCModel. NMR Biomed 14:260–264
Qume M, Whitton PS, Fowler LJ (1995) The effect of chronic treatment with the GABA transaminase inhibitors gamma-vinyl-GABA and ethanolamine-O-sulphate on the in vivo release of GABA from rat hippocampus. J Neurochem 64:2256–2261
Sanacora G, Mason GF, Rothman DL, Behar KL, Hyder F, Petroff OA, Berman RM, Charney DS, Krystal JH (1999) Reduced cortical gamma-aminobutyric acid levels in depressed patients determined by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Arch Gen Psychiatry 56:1043–1047
Schumann WC, Magnusson I, Chandramouli V, Kumaran K, Wahren J, Landau BR (1991) Metabolism of [2–14C]acetate and its use in assessing hepatic Krebs cycle activity and gluconeogenesis. J Biol Chem 266:90–6985
Shen J (2006) 13C magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies of alterations in glutamate neurotransmission. Biol Psychiatry 59:883–887
Shen J, Petersen KF, Behar KL, Brown P, Nixon TW, Mason GF, Petroff OA, Shulman GI, Shulman RG, Rothman DL (1999) Determination of the rate of the glutamate/glutamine cycle in the human brain by in vivo 13C NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:8235–8240
Shen J, Yang J, Choi I-Y, Li SS, Chen Z (2004) A new strategy for in vivo spectral editing Application to GABA editing using selective homonuclear polarization transfer spectroscopy. J Magn Reson 170:290–298
Sibson NR, Dhankhar A, Mason GF, Behar KL, Rothman DL, Shulman RG (1997) In vivo 13C NMR measurements of cerebral glutamine synthesis as evidence for glutamate-glutamine cycling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:2699–2704
Slotboom J, Bovée WMMJ (1995) Adiabatic slice-selective rf pulses and a single-shot adiabatic localization pulse sequence. Concept Magn Reson 7:193–217
Smolders I, Khan GM, Lindekens H, Prikken S, Marvin CA, Manil J, Ebinger G, Michotte Y (1997) Effectiveness of vigabatrin against focally evoked pilocarpine-induced seizures and concomitant changes in extracellular hippocampal and cerebellar glutamate, gamma-aminobutyric acid and dopamine levels, a microdialysis-electrocorticography study in freely moving rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 283:1239–1248
Waniewski RA, Martin DL (1998) Preferential utilization of acetate by astrocytes is attributable to transport. J Neurosci 18:5225–5233
Wood JD, Kurylo E, Lane R (1988) Gamma-Aminobutyric acid release from synaptosomes prepared from rats treated with isonicotinic acid hydrazide and gabaculine. J Neurochem 50:1839–1843
Wu Y, Wang W, Richerson GB (2003) Vigabatrin induces tonic inhibition via GABA transporter reversal without increasing vesicular GABA release. J Neurophysiol 89:2021–2034
Yang J, Shen J (2005) In vivo evidence for reduced cortical glutamate–glutamine cycling in rats treated with the antidepressant/antipanic drug phenelzine. Neuroscience 135:37–927
Yang J, Li SS, Bacher J, Shen J (2007) Quantification of cortical GABA-glutamine cycling rate using in vivo magnetic resonance signal of [2-13C]GABA derived from glia-specific substrate [2-13C]acetate. Neurochem Int 50:371–378
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Mr. Christopher Johnson, Drs. Steve Li, Steve Fox and Su Xu for valuable help and Ms. Ioline Henter for editing the manuscript. This work was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the NIH, NIMH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Shen, J. Elevated endogenous GABA concentration attenuates glutamate–glutamine cycling between neurons and astroglia. J Neural Transm 116, 291–300 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0186-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0186-0