Abstract
Objective
Surgery and radiosurgery represent the most common treatment options for vestibular schwannoma. A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted to compare the outcomes of surgery versus stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS).
Methods
The Cochrane library, PubMed, Embase, and clinicaltrials.gov were searched through 01/2021 to find all studies on surgical and stereotactic procedures performed to treat vestibular schwannoma. Using a random-effects model, pooled odds ratios (OR) and their 95% confidence intervals (CI) comparing post- to pre-intervention were derived for pre-post studies, and pooled incidence of adverse events post-intervention were calculated for case series and stratified by intervention type.
Results
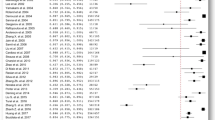
Twenty-one studies (18 pre-post design; three case series) with 987 patients were included in the final analysis. Comparing post- to pre-intervention, both surgery (OR: 3.52, 95%CI 2.13, 5.81) and SRS (OR: 3.30, 95%CI 1.39, 7.80) resulted in greater odds of hearing loss, lower odds of dizziness (surgery OR: 0.10; 95%CI 0.02, 0.47 vs. SRS OR: 0.22; 95%CI 0.05, 0.99), and tinnitus (surgery OR: 0.23; 95%CI 0.00, 37.9; two studies vs. SRS OR: 0.11; 95%CI 0.01, 1.07; one study). Pooled incidence of facial symmetry loss was larger post-surgery (14.3%, 95%CI 6.8%, 22.7%) than post-SRS (7%, 95%CI 1%, 36%). Tumor control was larger in the surgery (94%, 95%CI 83%, 98%) than the SRS group (80%, 95%CI 31%, 97%) for small-to-medium size tumors.
Conclusion
Both surgery and SRS resulted in similar odds of hearing loss and similar improvements in dizziness and tinnitus among patients with vestibular schwannoma; however, facial symmetry loss appeared higher post-surgery.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aihara N, Murakami S (2015) Enlargement of the internal auditory canal and hearing preservation in the middle fossa approach for intracanalicular vestibular schwannomas. World Neurosurg 84:1950–1955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2015.08.041
Ansari SF, Terry C, Cohen-Gadol AA (2012) Surgery for vestibular schwannomas: a systematic review of complications by approach. Neurosurg Focus 33:E14. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.6.Focus12163
Asthagiri AR, Parry DM, Butman JA, Kim HJ, Tsilou ET, Zhuang Z, Lonser RR (2009) Neurofibromatosis type 2. Lancet 373:1974–1986. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(09)60259-2
Begg CB, Mazumdar M (1994) Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 50:1088–1101
Carlson ML, Link MJ, Driscoll CLW, Haynes DS, Billings HA, Lohse CM, Hall ER, Agazzi S, Barker FG 3rd, Brackmann DE, Cueva RA, Golfinos JG, Gurgel RK, Kondziolka D, Kutz JW Jr, Neff BA, Sheehan JP, Van Gompel JJ, Yu CP (2020) Working toward consensus on sporadic vestibular schwannoma care: a modified Delphi study. Otol Neurotol 41:e1360–e1371. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0000000000002917
Chamoun R, MacDonald J, Shelton C, Couldwell WT (2012) Surgical approaches for resection of vestibular schwannomas: translabyrinthine, retrosigmoid, and middle fossa approaches. Neurosurg Focus 33:E9. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.6.Focus12190
DeMonte F, Gidley PW (2012) Hearing preservation surgery for vestibular schwannoma: experience with the middle fossa approach. Neurosurg Focus 33:E10. https://doi.org/10.3171/2012.7.Focus12172
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials 7:177–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2
Dhanachai M, Theerapancharoen V, Laothamatas J, Jariengprasert C, Kraiphibul P, Yongvithisatid P (2004) Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for bilateral vestibular schwannomas associated with neurofibromatosis type 2: early experiences in Ramathibodi Hospital. J Med Assoc Thai 87:1076–1081
Dowling EM, Patel NS, Lohse CM, Driscoll CLW, Neff BA, Van Gompel JJ, Link MJ, Carlson ML (2019) Durability of hearing preservation following microsurgical resection of vestibular schwannoma. Otol Neurotol 40:1363–1372. https://doi.org/10.1097/mao.0000000000002378
Gurgel RK, Jackler RK, Dobie RA, Popelka GR (2012) A new standardized format for reporting hearing outcome in clinical trials. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 147:803–807. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599812458401
Hani U, Bakhshi S, Shamim MS (2020) Steriotactic radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas. J Pak Med Assoc 70:939–941
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. Bmj 327:557–560. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Hirsch A, Norén G, Anderson H (1979) Audiologic findings after stereotactic radiosurgery in nine cases of acoustic neurinomas. Acta Otolaryngol 88:155–160. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016487909137155
House JW, Brackmann DE (1985) Facial nerve grading system. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 93:146–147. https://doi.org/10.1177/019459988509300202
House F, Hitselberger WE (1969) The middle fossa approach for removal of small acoustic tumors. Acta Otolaryngol 67:413–427. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016486909125467
Inoue Y, Kanzaki J, Ogawa K, Hoya N, Takei S, Shiobara R (2000) The long-term outcome of hearing preservation following vestibular schwannoma surgery. Auris Nasus Larynx 27:9–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0385-8146(99)00046-2
Johnson S, Kano H, Faramand A, Pease M, Nakamura A, Hassib M, Spencer D, Sisterson N, Faraji AH, Arai Y, Monaco E, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2019) Long term results of primary radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas. J Neurooncol 145:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-019-03290-0
Kang WS, Kim SA, Yang CJ, Nam SH, Chung JW (2017) Surgical outcomes of middle fossa approach in intracanalicular vestibular schwannoma. Acta Otolaryngol 137:352–355. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016489.2016.1255992
Kanzaki J, Ogawa K, Inoue Y, Shiobara R (1997) Hearing preservation surgery in acoustic neuroma patients with normal hearing. Skull Base Surg 7:109–113. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1058601
Kaylie DM, Horgan MJ, Delashaw JB, McMenomey SO (2000) A meta-analysis comparing outcomes of microsurgery and gamma knife radiosurgery. Laryngoscope 110:1850–1856. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200011000-00016
Koos WT, Day JD, Matula C, Levy DI (1998) Neurotopographic considerations in the microsurgical treatment of small acoustic neurinomas. J Neurosurg 88:506–512. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1998.88.3.0506
Kunimoto Y, Lauda L, Falcioni M, Taibah A, Hasegawa K, Sanna M (2015) Staged resection for vestibular schwannoma. Acta Otolaryngol 135:895–900. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016489.2015.1040170
Kuo YH, Roos D, Brophy BP (2008) Linear accelerator radiosurgery for treatment of vestibular schwannomas in neurofibromatosis 2. J Clin Neurosci 15:744–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2007.07.078
Leon J, Lehrer EJ, Peterson J, Vallow L, Ruiz-Garcia H, Hadley A, Herchko S, Lundy L, Chaichana K, Vibhute P, Sheehan JP, Trifiletti DM (2019) Observation or stereotactic radiosurgery for newly diagnosed vestibular schwannomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Radiosurg SBRT 6:91–100
Maniakas A, Saliba I (2012) Microsurgery versus stereotactic radiation for small vestibular schwannomas: a meta-analysis of patients with more than 5 years’ follow-up. Otol Neurotol 33:1611–1620. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0b013e31826dbd02
Master AN, Roberts DS, Wilkinson EP, Slattery WH, Lekovic GP (2018) Endoscope-assisted middle fossa craniotomy for resection of inferior vestibular nerve schwannoma extending lateral to transverse crest. Neurosurg Focus 44:E7. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.12.Focus17663
Mathew GD, Facer GW, Suh KW, Houser OW (1921) O’Brien PC (1978) Symptoms, findings, and methods of diagnosis in patients with acoustic neuroma. Laryngoscope 88:1893–1903. https://doi.org/10.1288/00005537-197812000-00001
Milligan BD, Pollock BE, Foote RL, Link MJ (2012) Long-term tumor control and cranial nerve outcomes following gamma knife surgery for larger-volume vestibular schwannomas. J Neurosurg 116:598–604. https://doi.org/10.3171/2011.11.JNS11811
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6:e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Mohr G, Sade B, Dufour JJ, Rappaport JM (2005) Preservation of hearing in patients undergoing microsurgery for vestibular schwannoma: degree of meatal filling. J Neurosurg 102:1–5. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2005.102.1.0001
Monfared A, Corrales CE, Theodosopoulos PV, Blevins NH, Oghalai JS, Selesnick SH, Lee H, Gurgel RK, Hansen MR, Nelson RF, Gantz BJ, Kutz JW Jr, Isaacson B, Roland PS, Amdur R, Jackler RK (2016) Facial nerve outcome and tumor control rate as a function of degree of resection in treatment of large acoustic neuromas: preliminary report of the acoustic neuroma subtotal resection study (ANSRS). Neurosurgery 79:194–203. https://doi.org/10.1227/neu.0000000000001162
Nakamizo A, Mori M, Inoue D, Amano T, Mizoguchi M, Yoshimoto K, Sasaki T (2013) Long-term hearing outcome after retrosigmoid removal of vestibular schwannoma. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 53:688–694. https://doi.org/10.2176/nmc.oa2012-0351
Park CK, Jung HW, Kim JE, Son YJ, Paek SH, Kim DG (2006) Therapeutic strategy for large vestibular schwannomas. J Neurooncol 77:167–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-005-9015-y
Peters JL, Sutton AJ, Jones DR, Abrams KR, Rushton L (2007) Performance of the trim and fill method in the presence of publication bias and between-study heterogeneity. Stat Med 26:4544–4562. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.2889
Prabhu V, Kondziolka D, Hill TC, Benjamin CG, Shinseki MS, Golfinos JG, Roland JT Jr, Fatterpekar GM (2018) Preserved cochlear CISS signal is a predictor for hearing preservation in patients treated for vestibular schwannoma with stereotactic radiosurgery. Otol Neurotol 39:628–631. https://doi.org/10.1097/mao.0000000000001762
Sampath P, Holliday MJ, Brem H, Niparko JK, Long DM (1997) Facial nerve injury in acoustic neuroma (vestibular schwannoma) surgery: etiology and prevention. J Neurosurg 87:60–66. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1997.87.1.0060
Santa Maria PL, Shi Y, Gurgel RK, Corrales CE, Soltys SG, Santa Maria C, Murray K, Chang SD, Blevins NH, Gibbs IC, Jackler RK (2019) Long-term hearing outcomes following stereotactic radiosurgery in vestibular schwannoma patients—a retrospective cohort study. Neurosurgery 85:550–559. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuros/nyy407
Santa Maria PL, Shi Y, Aaron KA, Gurgel RK, Corrales CE, Soltys SG, Santa Maria C, Chang SD, Blevins NH, Jackler RK, Gibbs IC (2021) Tumor control following stereotactic radiosurgery in patients with vestibular schwannomas—a retrospective cohort study. Otol Neurotol 42:e1548–e1559. https://doi.org/10.1097/mao.0000000000003285
Savardekar AR, Terrell D, Lele SJ, Diaz R, Keesari PR, Trosclair K, Kosty J, Wang CJ, Gardner G, Guthikonda B (2021) Primary treatment of small-to-medium (<3cm) sporadic vestibular schwannomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis on hearing preservation and tumor control rates for microsurgery versus radiosurgery. World Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2021.11.083
Sepehrnia A, Borghei-Razavi H (2015) Vestibular schwannoma between 1 and 3 cm: importance of the tumor size in surgical and functional outcome. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 129:21–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2014.11.020
Shaffer BT, Cohen MS, Bigelow DC, Ruckenstein MJ (2010) Validation of a disease-specific quality-of-life instrument for acoustic neuroma: the Penn Acoustic Neuroma Quality-of-Life Scale. Laryngoscope 120:1646–1654. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.20988
Silk PS, Lane JI, Driscoll CL (2009) Surgical approaches to vestibular schwannomas: what the radiologist needs to know. Radiographics 29:1955–1970. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.297095713
Silverstein H, Rosenberg SI, Flanzer JM, Wanamaker HH, Seidman MD (1993) An algorithm for the management of acoustic neuromas regarding age, hearing, tumor size, and symptoms. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 108:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1177/019459989310800101
Starnoni D, Daniel RT, Tuleasca C, George M, Levivier M, Messerer M (2018) Systematic review and meta-analysis of the technique of subtotal resection and stereotactic radiosurgery for large vestibular schwannomas: a “nerve-centered” approach. Neurosurg Focus 44:E4. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.12.Focus17669
Thai NLB, Mai NY, Vuong NL, Tin NM, Karam D, Refaey MA, Shahin KM, Soliman AL, Al Khudari R, Thuan TM, Sabbah GM, El-Qushayri AE, Karimzadeh S, Hirayama K, Huy NT (2021) Treatment for vestibular schwannoma: systematic review and single arm meta-analysis. Am J Otolaryngol 43:103337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2021.103337
Tuleasca C, George M, Schiappacasse L, Patin D, Fenu J, Maire R, Levivier M (2019) Gamma Knife radiosurgery for intravestibular and intracochlear schwannomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 161:63–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-018-3762-y
Wick CC, Arnaoutakis D, Barnett SL, Rivas A, Isaacson B (2017) Endoscopic transcanal transpromontorial approach for vestibular schwannoma resection: a case series. Otol Neurotol 38:e490–e494. https://doi.org/10.1097/mao.0000000000001588
Wu H, Zhang L, Han D, Mao Y, Yang J, Wang Z, Jia W, Zhong P, Jia H (2016) Summary and consensus in 7th International Conference on acoustic neuroma: an update for the management of sporadic acoustic neuromas. World J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2:234–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wjorl.2016.10.002
Zhang Y, Chen Y, Zou Y, Zhang W, Zhang R, Liu X, Lv Z, Yang K, Hu X, Xiao C, Liu W, Liu H (2013) Facial nerve preservation with preoperative identification and intraoperative monitoring in large vestibular schwannoma surgery. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 155:1857–1862. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-013-1815-9
H M (2018) Otolaryngology-head and neck surgery. Johns Hopkins. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/otolaryngology/specialty_areas/otology/conditions/acoustic-neuroma/treatment.html. Accessed 12 Dec 2020
Lee DJ, Westra WH, Staecker H, Long D, Niparko JK, Slattery WH, 3rd (2003) Clinical and histopathologic features of recurrent vestibular schwannoma (acoustic neuroma) after stereotactic radiosurgery. Otol Neurotol 24:650–660; discussion 660. https://doi.org/10.1097/00129492-200307000-00020
OECD (2022) Elderly population (indicator). https://data.oecd.org/pop/elderly-population.htm. Accessed 17 July 2022
Cubic centimeter to centimeter calculator. http://www.endmemo.com/cconvert/cm3cm.php.
Quality assessment tool for before-after (pre-post) studies with no control group. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/study-quality-assessment-tools. 2007
Sughrue ME, Kaur R, Rutkowski MJ, Kane AJ, Yang I, Pitts LH, Parsa AT (2010) A critical evaluation of vestibular schwannoma surgery for patients younger than 40 years of age. Neurosurgery 67:1646–1653; discussion 1653–1644. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e3181f8d3d3
Cohen-Gadol A (2021) Surgery for acoustic neuroma: retrosigmoid approach. Neurosurg Atlas. https://doi.org/10.18791/nsatlas.v5.ch08.1. Accessed 17 July 2022
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Ethics committee approval was not sought, as review and analyses were performed on published data.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Vinod Kumar Yakkala and Marco Mammi are co-first authors.
C. Eduardo Corrales, Timothy R. Smith, and Rania A. Mekary are co-senior authors.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Tumor - Schwannoma
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yakkala, V.K., Mammi, M., Lamba, N. et al. Audiovestibular symptoms and facial nerve function comparing microsurgery versus SRS for vestibular schwannomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Neurochir 164, 3221–3233 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-022-05338-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-022-05338-z