Abstract
Purpose
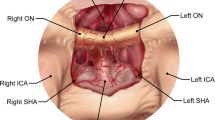
Suprasellar meningiomas usually present with visual deterioration, including decreased visual acuity and/or visual field defects. Suprasellar meningiomas have a close relationship with the optic apparatus, arteries of the anterior circulation, pituitary stalk and hypothalamus, which makes safe surgical resection a challenge especially with dissection around an already compromised optic apparatus. In this report 21 patients operated on for a suprasellar meningioma over a 4-year period are reviewed. Postoperative outcome and visual recovery are evaluated, including analysis of its determinants.
Methods
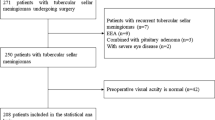
Over a 4-year period (2002–2006), patients surgically treated for suprasellar meningiomas were included in this retrospective study. All tumors were located at the tuberculum sellae and diaphragma sellae dura. Clinical and neuro-ophthalmological examinations, imaging studies, endocrinological evaluation and follow-up data were reviewed retrospectively. The influence of patient age, sex, duration of symptoms, extent of visual impairment, tumor size , extent into optic canal, consistency, operative respectability were analyzed as potential prognostic factors for postoperative visual outcome.
Results
Twenty-one patients were included in this retrospective study. Ages ranged from 25 to 65 years (mean: 43 years). All patients had visual acuity loss and visual field defects. Symptom duration ranged from 2 to 36 months (mean: 17 months). Tumor removal was complete in 17 patients, and subtotal resection was performed in four patients. There was one case of postoperative mortality. The follow-up duration ranged from 24 to 48 months (mean: 28 months). At the last follow-up 12 patients (60%) had achieved visual improvement, whereas vision was unchanged in eight patients (40%). None of the patients had visual deterioration during their follow-up. A univariate analysis of clinical and surgical parameters thought to be related to visual outcome showed that the duration of symptoms, preoperative visual status, tumor size and adherence to the internal carotid arteries and/or anterior cerebral artery had a significant impact on visual outcome.
Conclusion
The extent and duration of visual symptoms, size of the tumor and vascular adherence were prognostic factors affecting visual recovery after microsurgical resection of suprasellar meningiomas.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Mefty O, Smith RR (1991) Tuberculum sellae meningiomas. In: Al Mefty O (ed) Meningiomas. Raven Press, New York, pp 395–411
Andrews BT, Wilson CB (1988) Suprasellar meningiomas: the effect of tumor location on postoperative visual outcome. J Neurosurg 69:523–528
Bassiouni H, Asgari S, Stolke D (2006) Tuberculum sellae meningiomas: functional outcome in a consecutive series treated microsurgically. Surg Neurol 66:37–44
Benjamin V, Russell SM (2005) The microsurgical nuances of resecting tuberculum sellae meningiomas. Neurosurgery 56:411–417
Chicani CF, Miller NR (2003) Visual outcome in surgically treated suprasellar meningiomas. J Neuroopthalmol 23(1):3–10
DeDivitiis E, Esposito F, Cappabianca P, Cavallo LM, DeDivitiis O (2008) Tuberculum sellae meningiomas: high route or low route? A seires of 51 consecutive cases. Neurosurgery 62(3):556–563
Fahlbusch R, Schott W (2002) Pterional surgery of meningiomas of the tuberculum sellae and planum sphenoidale: surgical results with special consideration of ophthalmological and endocrinological outcomes. J Neurosurg 96:235–243
Goel A, Muzumdar D, Desai KI (2002) Tuberculum sellae meningioma: a report on the management basis of a surgical experience with 70 patients. Neurosurgery 51:1358–1364
Jallo GI, Benjamin V (2002) Tuberculum sellae meningiomas: microsurgical anatomy and surgical technique. Neurosurgery 51:1432–1440
Kim TW, Jung S, Jung TY, Kim IY, Kang SS, Kim SH (2008) Prognostic factors of postoperative visual outcomes in tuberculum sellae meningioma. Br J Neurosurg 22(2):231–234
Kinjo T, Al-Mefty O, Ciric I (1995) Diaphragma sellae meningiomas. Neurosurgery 36(6):1082–1092
Kitano M, Taneda M, Nakao Y (2007) Postoperative improvement in visual function in patients with tuberculum sellae meningiomas: results of extended transsphenoidal and transcranial approaches. J Neurosurg 107:337–346
Margalit NS, Lesser JB, Moche J, Sen C (2003) Meningiomas involving the optic nerve: technical aspects and outcomes for a series of 50 patients. Neurosurgery 53:523–532
Mathiesen T, Kihlstrom L (2006) Visual outcome of tuberculum sellae meningiomas after extradural optic nerve decompression. Neurosurgery 59:570–576
Mehrazin M, Mirfalah R (2008) Early postoperative visual outcome in microsurgically treated suprasellar meningiomas predict long-term visual outcome. Turk Neurosurg 18:380–386
Nakamura M, Roser F, Struck M, Vorkapic P, Samii M (2006) Tuberculum sellae meningiomas: clinical outcome considering different surgical approaches. Neurosurgery 59:1019–1029
Nozaki K, Kikuta KI, Takagi Y, Mineharu Y, Takahashi JA (2008) Effect of early optic canal unroofing on the outcome of visual functions in surgery for meningiomas of the tuberculum sellae and planum sphenoidale. Neurosurgery 62(4):839–846
Olivecrona H (1967) The suprasellar meningiomas. In: Olivecrona H, Tonnis W (eds) Handbuch der Neurochirurgie. Springer, Berlin, pp 167–172
Otani N, Muroi C, Yano H, Khan N, Pangalu A, Yonekawa Y (2006) Surgical management of tuberculum sellae meningiomas: role of selective extradural anterior clinoidectomy. Br J Neurosurg 20:129–138
Pamir MN, Ozduman K, Belirgen M, Kilic T, Ozek MM (2005) Outcome determinants of pterional surgery for tuberculum sellae meningiomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 147:1121–1130
Park CK, Jung HW, Yang SY, Seol HJ, Paek SH, Kim DG (2006) Surgically treated tuberculum sellae and diaphragm sellae meningiomas: the importance of short-term visual outcome. Neurosurgery 59:238–243
Puchner MJ, Fischer-Lampsatis RC, Herman HD, Freckmann N (1998) Suprasellar meningiomas: neurological and visual outcome at long-term follow-up in a homogenous series of patients treated microsurgically. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 140:1231–1238
Schick U, Hassler W (2005) Surgical management of tuberculum sellae meningiomas: involvement of the optic canal and visual outcome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76:977–983
Suri A, Narang KS, Sharma BS, Mahapatra AK (2008) Visual outcome after surgery in patients with suprasellar tumors and preoperative blindness. J Neurosurg 108(1):19–25
Yasargil MG (1996) Meningiomas. In: Yasargil MG (ed) Microneurosurgery. Georg Thieme, Stuttgart, pp 134–165
Zevgardis D, Medele RJ, Muller A, Hischa AC, Steiger HJ (2001) Meningiomas of the sellar region presenting with visual impairment: impact of various prognostic factors on surgical outcome in 62 patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 143:471–476
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galal, A., Faisal, A., Al-Werdany, M. et al. Determinants of postoperative visual recovery in suprasellar meningiomas. Acta Neurochir 152, 69–77 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-009-0492-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-009-0492-1