Abstract
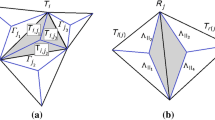
We apply the general framework developed by John et al. in Computing 64:307–321, 2000 to analyze the convergence of multi-level methods for mixed finite element discretizations of the generalized Stokes problem using the Scott–Vogelius element. The Scott–Vogelius element seems to be promising since discretely divergence-free functions are divergence-free pointwise. However, to satisfy the Ladyzhenskaya–Babuška–Brezzi stability condition, we have to deal in the multi-grid analysis with non-nested families of meshes which are derived from nested macro element triangulations. Additionally, the analysis takes into account an optional symmetric stabilization operator which suppresses spurious oscillations of the velocity provoked by a dominant reaction term. Usually, the generalized Stokes problems appears in semi-implicit splitting schemes for the unsteady Navier–Stokes equations, but the symmetric part of a stabilized discrete Oseen problem can be reguarded as a discrete generalized Stokes problem likewise.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold DN, Qin J (1992) Quadratic velocity/linear pressure Stokes elements. In: Advances in computer methods for partial differential equations VII, pp 28–34
Bank RE, Welfert BD, Yserentant H (1990) A class of iterative methods for solving saddle point problems. Numer Math 56: 645–666
Becker R, Braack M (2001) A finite element pressure gradient stabilization for the Stokes equations based on local projections. Calcolo 38: 173–199
Braack M, Burman E (2006) Local projection stabilization for the Oseen problem and its interpretation as a variational multiscale method. SIAM J Numer Anal 43: 2544–2566
Braess D, Sarazin R (1997) An efficient smoother for the Stokes problem. Appl Numer Math 23: 3–19
Braess D, Verfürth R (1990) Multigrid methods for nonconforming finite element methods. SIAM J Numer Anal 27: 979–986
Braess D, Dryja M, Hackbusch W (1999) A multigrid method for nonconforming FE-discretisations with applications to non-matching grids. Computing 63: 1–25
Bristeau MO, Glowinski R, Periaux J (1987) Numerical methods for the Navier–Stokes equations. Applications to the simulation of compressible and incompressible viscous flow. Comput Phys Reports 6: 73–187
Burman E, Hansbo P (2004) Edge stabilization for Galerkin approximations of convection-diffusion-reaction problems. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 193: 1437–1453
Burman E, Linke A (2007) Stabilized finite element schemes for incompressible flow using Scott–Vogelius elements. Appl Numer Math. doi:10.1016/j.apnum.2007.11.001 (accepted)
Burman E, Fernández MA, Hansbo P (2006) Continuous interior penalty finite element method for Oseen’s equations. SIAM J Numer Anal 44: 1248–1274
Ganesan S, Matthies G, Tobiska L (2008) Local projection stabilization of equal order interpolation applied to the Stokes problem. Math Comput 77: 2039–2060
Girault V, Raviart P-A (1986) Finite element methods for the Navier–Stokes equations. Springer, Berlin
John V, Matthies G (2001) Higher-order finite element discretizations in a benchmark problem for incompressible flows. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 37: 885–903
John V, Matthies G (2004) MooNMD—a program package based on mapped finite element methods. Comput Vis Sci 6: 163–170
John V, Tobiska L (2000) A coupled multigrid method for nonconforming finite element discretisations of the Stokes equation. Computing 64: 307–321
John V, Knobloch P, Matthies G, Tobiska L (2002) Non-nested multi-level solvers for finite element discretisations of mixed problems. Computing 68: 313–341
Manservisi S (2006) Numerical analysis of Vanka-type solvers for steady Stokes and Navier–Stokes flows. SIAM J Numer Anal 44: 2025–2056
Matthies G, Skrzypacz P, Tobiska L (2007) A unified convergence analysis for local projection stabilisations applied to the Oseen problem. M2AN Math Model Numer Anal 41: 713–742
Olshanskii M, Reusken A (2004) Grad-div stabilization for Stokes equations. Math Comput 73: 1699–1718
Ouazzi A, Turek S (2006) Efficient multigrid and data structures for edge-oriented FEM stabilization. In: Numerical mathematics and advanced applications. Springer, Berlin, pp 520–527
Qin J (1994) On the convergence of some low order mixed finite elements for incompressible fluids. PhD thesis, Pennsylvania State University
Sacchi Landriani G, Vandeven H (1989) Polynomial approximation of divergence-free functions. Math Comput 52: 103–130
Sarazin R (1996) Eine Klasse von effizienten Glättern vom Jacobi-Typ für das Stokes-Problem. PhD thesis, Ruhr-Universität Bochum
Schöberl J, Zulehner W (2003) On Schwarz-type smoothers for saddle point problems. Numer Math 95: 377–399
Scott L, Zhang S (1990) Finite element interpolation of nonsmooth functions satisfying boundary conditions. Math Comput 54: 483–493
Scott LR, Vogelius M (1985) Norm estimates for a maximal right inverse of the divergence operator in spaces of piecewise polynomials. Math Model Numer Anal 19: 111–143
Vanka S (1986) Block-implicit multigrid calculation of two-dimensional recirculating flows. Comp Methods Appl Mech Eng 59: 29–48
Vogelius M (1983) A right-inverse for the divergence operator in spaces of piecewise polynomials. Application to the p-version of the finite element method. Numer Math 41: 19–37
Zhang S (2005) A new family of stable mixed finite elements for the 3D Stokes equations. Math Comput 74: 543–554
Zulehner W (2000) A class of smoothers for saddle point problems. Computing 65: 227–246
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A. Linke has partially been funded by the DFG Research Center Matheon in Berlin.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Linke, A., Matthies, G. & Tobiska, L. Non-nested multi-grid solvers for mixed divergence-free Scott–Vogelius discretizations. Computing 83, 87–107 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00607-008-0016-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00607-008-0016-5
Keywords
- Multi-grid method
- Mixed finite element discretization
- Generalized Stokes problem
- Scott–Vogelius element
- Stabilized finite element methods