Abstract
A flexible electrochemiluminescence (ECL) hydrogel sensor exhibiting good self-healing was constructed. A transparent self-healing oxidized sodium alginate/hydrazide polyethylene glycol (OSA/PEG-DH) hydrogel was prepared by crosslinking dynamic covalent acylhydrazone bond. The introduction of 4-amino-DL-phenylalanine, a catalyst with good biocompatibility, allows rapid gelation and self-healing of hydrogel under mild conditions. Using the hydrogel as the sensing substrate, the ionic liquid (IL) 2-hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium chloride and the luminescent reagent N-(aminobutyl)-N-(ethylisoluminol) (ABEI) were simultaneously immobilized in the OSA/PEG-DH hydrogel to obtain the ABEI/IL/OSA/PEG-DH hydrogel. The ABEI/IL/OSA/PEG-DH hydrogel can be directly used as a semi-solid electrolyte for constructing a flexible ECL hydrogel sensor for the detection of H2O2, which acted as a coreactant of ABEI. The prepared flexible ECL sensor showed good self-healing performance, can restore ECL signal intensity within 20 min after physical damage, and showed high accuracy in the analysis of complex serum samples. This research shed new light on the development of flexible ECL sensor for bioanalytical applications.
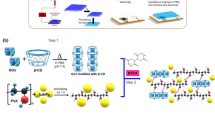
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Jin Z, Yang L, Shi S, Wang T, Duan G, Liu X, Li Y (2021) Flexible polydopamine bioelectronics. Adv Funct Mater 31(30):2103391
Yu Y, Nyein HYY, Gao W, Javey A (2020) Flexible electrochemical bioelectronics: the rise of in situ bioanalysis. Adv Mater 32(15):1902083
Wang Y, Xia Y, Xiang P, Dai Y, Gao Y, Xu H, Yu J, Gao G, Chen K (2022) Protein-assisted freeze-tolerant hydrogel with switchable performance toward customizable flexible sensor. Chem Eng J 428:131171
Kim J, Campbell AS, de Ávila BE-F, Wang J (2019) Wearable biosensors for healthcare monitoring. Nat Biotechnol 37(4):389–406
Ying B, Chen RZ, Zuo R, Li J, Liu X (2021) An anti-freezing, ambient-stable and highly stretchable ionic skin with strong surface adhesion for wearable sensing and soft robotics. Adv Funct Mater 31(42):2104665
Phan H-P, Zhong Y, Nguyen T-K, Park Y, Dinh T, Song E, Vadivelu RK, Masud MK, Li J, Shiddiky MJA, Dao D, Yamauchi Y, Rogers JA, Nguyen N-T (2019) Long-Lived, Transferred crystalline silicon carbide nanomembranes for implantable flexible electronics. ACS Nano 13(10):11572–11581
Yoon J, Lee SN, Shin MK, Kim H-W, Choi HK, Lee T, Choi J-W (2019) Flexible electrochemical glucose biosensor based on GOx/gold/MoS2/gold nanofilm on the polymer electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 140:111343
Li S, Liu Y, Ma Q (2019) Nanoparticle-based electrochemiluminescence cytosensors for single cell level detection, TrAC. Trends Anal Chem 110:277–292
Fu Y, Ma Q (2020) Recent developments in electrochemiluminescence nanosensors for cancer diagnosis applications. Nanoscale 12(26):13879–13898
Chen M-M, Cheng S-B, Ji K, Gao J, Liu Y-L, Wen W, Zhang X, Wang S, Huang W-H (2019) Construction of a flexible electrochemiluminescence platform for sweat detection. Chem Sci 10(25):6295–6303
Vu V-P, Sinh LH, Choa S-H (2020) Recent progress in self-healing materials for sensor arrays. ChemNanoMat 6(11):1522–1538
Kang J, Tok JBH, Bao Z (2019) Self-healing soft electronics. Nat Electron 2(4):144–150
Zhong R, Tang Q, Wang S, Zhang H, Zhang F, Xiao M, Man T, Qu X, Li L, Zhang W, Pei H (2018) Self-assembly of enzyme-like nanofibrous G-molecular hydrogel for printed flexible electrochemical sensors. Adv Mater 30(12):1706887
Chakraborty P, Guterman T, Adadi N, Yadid M, Brosh T, Adler-Abramovich L, Dvir T, Gazit E (2018) A self-healing, all-organic, conducting, composite peptide hydrogel as pressure sensor and electrogenic cell soft substrate. ACS Nano 13(1):163–175
Jiang X, Wang H, Yuan R, Chai Y (2018) Functional three-dimensional porous conductive polymer hydrogels for sensitive electrochemiluminescence in situ detection of H2O2 released from live cells. Anal Chem 90(14):8462–8469
Gao F, Teng H, Song J, Xu G, Luo X (2020) A flexible and highly sensitive nitrite sensor enabled by interconnected 3D porous polyaniline/carbon nanotube conductive hydrogels. Anal Methods 12(5):604–610
Tang L, Wu S, Qu J, Gong L, Tang J (2020) A review of conductive hydrogel used in flexible strain sensor. Materials 13(18):3947
Lu H, Zhang N, Ma M (2019) Electroconductive hydrogels for biomedical applications. WIREs Nanomed Nanobi 11(6):e1568
Yu X, Zhang H, Wang Y, Fan X, Li Z, Zhang X, Liu T (2022) Highly stretchable, ultra-soft, and fast self-healable conductive hydrogels based on polyaniline nanoparticles for sensitive flexible sensors. Adv Funct Mater 32(33):2204366
He X, Dong J, Zhang X, Bai X, Zhang C, Wei D (2022) Self-healing, anti-fatigue, antimicrobial ionic conductive hydrogels based on choline-amino acid polyionic liquids for multi-functional sensors. Chem Eng J 435:135168
Li G, Li C, Li G, Yu D, Song Z, Wang H, Liu X, Liu H, Liu W (2022) Development of conductive hydrogels for fabricating flexible strain sensors. Small 18(5):2101518
Han C, Guo W (2020) Fluorescent noble metal nanoclusters loaded protein hydrogel exhibiting anti-biofouling and self-healing properties for electrochemiluminescence biosensing applications. Small 16(45):2002621
Ding C, Li Y, Wang L, Luo X (2019) Ratiometric electrogenerated chemiluminescence cytosensor based on conducting polymer hydrogel loaded with internal standard molecules. Anal Chem 91(1):983–989
Guo X, Li Y, Li Y, Ye Z, Zhang J, Zhu T, Li F (2020) An L012@ PAni-PAAm hydrogel composite based-electrochemiluminescence biosensor for in situ detection of H2O2 released from cardiomyocytes. Electrochim Acta 354:136763
Liu Y, Hsu S-H (2018) Synthesis and biomedical applications of self-healing hydrogels. Front Chem 6(449):449
Wang L, Xu T, Zhang X (2021) Multifunctional conductive hydrogel-based flexible wearable sensors. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 134:116130
Chen J, Li S, Zhang Y, Wang W, Zhang X, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Bi H (2017) A reloadable self-healing hydrogel enabling diffusive transport of C-dots across gel–gel interface for scavenging reactive oxygen species. Adv Healthc Mater 6(21):1700746
Yang X, Liu G, Peng L, Guo J, Tao L, Yuan J, Chang C, Wei Y, Zhang L (2017) Highly efficient self-healable and dual responsive cellulose-based hydrogels for controlled release and 3D cell culture. Adv Funct Mater 27(40):1703174
Cao L, Cao B, Lu C, Wang G, Yu L, Ding J (2015) An injectable hydrogel formed by in situ cross-linking of glycol chitosan and multi-benzaldehyde functionalized PEG analogues for cartilage tissue engineering. J Mater Chem B 3(7):1268–1280
Gomes JM, Silva SS, Reis RL (2019) Biocompatible ionic liquids: fundamental behaviours and applications. Chem Soc Rev 48(15):4317–4335
Barfidokht A, Mishra RK, Seenivasan R, Liu S, Hubble LJ, Wang J, Hall DA (2019) Wearable electrochemical glove-based sensor for rapid and on-site detection of fentanyl. Sens Actuators B Chem 296:126422
Ciui B, Tertiş M, Cernat A, Săndulescu R, Wang J, Cristea C (2018) Finger-based printed sensors integrated on a glove for on-site screening of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factors. Anal. Chem. 90(12):7761–7768
Zhang T, Xing Y, Song Y, Gu Y, Yan X, Lu N, Liu H, Xu Z, Xu H, Zhang Z (2019) Aupt/mof–graphene: a synergistic catalyst with surprisingly high peroxidase-like activity and its application for H2O2 detection. Anal Chem 91(16):10589–10595
Atta NF, Gawad SAA, Galal A, Razik AA, El-Gohary AR (2021) Efficient electrochemical sensor for determination of H2O2 in human serum based on nano iron-nickel alloy/carbon nanotubes/ionic liquid crystal composite. J Electroanal Chem 881:114953
Fu M, Liang Y, Lv X, Li C, Yang YY, Yuan P, Ding X (2021) Recent advances in hydrogel-based anti-infective coatings. J Mater Sci Technol 85:169–183
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (201874005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Bai, Y., Zhao, X. et al. Conductive and self-healing hydrogel for flexible electrochemiluminescence sensor. Microchim Acta 190, 123 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05706-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05706-1