Abstract
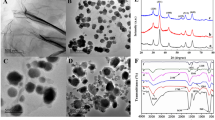
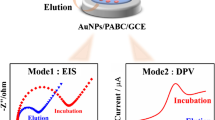
A molecularly imprinted paper-based analytical device (MIP-μPAD) was developed for the sensing of bisphenol A (BPA). The platform was screen-printed onto a filter paper support, where the electrodes and the fluorescence μPADs were designed. Owing to its dual electrochemical and fluorescence responses, molecularly imprinted curcumin nanoparticles were used to sense BPA. The μPAD design was characterized by transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy, and electrochemical techniques. The sensor design comprised a wide linear range from 1 to 200 μg L−1 with limits of detection of 0.47 ± 0.2 and 0.62 ± 0.3 μg L−1 (LOD, S/N = 3) for electrochemical and fluorescence sensing, respectively. Furthermore, the system showed good analytical performance such as selectivity, stability, and reproducibility. The feasibility of the MIP-μPAD was demonstrated for the sensing of BPA in seawater, foods, and polycarbonate plastic packaged water with recovery values of 97.2 and 101.8%.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vandenberg LN, Hauser R, Marcus M, Olea N, Welshons WV (2007) Human exposure to bisphenol A (BPA). Reprod Toxicol 24:139–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2007.07.010
Lin X, Cheng C, Terry P, Chend J, Cui H, Wu J (2017) Rapid and sensitive detection of bisphenol A from serum matrix. Biosens Bioelectron 91:104–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.12.024
Yang Q, Wu X, Peng H, Fu L, Song X, Li J, Xiong H, Chen L (2018) Simultaneous phase-inversion and imprinting based sensor for highly sensitive and selective detection of bisphenol A. Talanta 176:595–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.08.075
Vandenberg LN, Maffini MV, Sonnenschein C, Rubin BS, Soto AM (2009) Bisphenol-A and the great divide: a review of controversies in the field of endocrine disruption. Endocr Rev 30:75–95. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2008-0021
Lopardo L, Petrie B, Proctor K, Youdan J, Barden R, Kasprzyk-Hordern B (2019) Estimation of community-wide exposure to bisphenol A via water fingerprinting. Environ Int 125:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.12.048
Huang YQ, Wong CKC, Zheng JS, Bouwman H, Barra R, Wahlström B, Neretin L, Wong MH (2012) Bisphenol A (BPA) in China: a review of sources, environmental levels, and potential human health impacts. Environ Int 42:91–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2011.04.010
Jorge R, Thomas W (2015) Determination of bisphenols in beverages by mixed-mode solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1422:230–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2015.10.046
Kawaguchi M, Ito R, Endo N, Okanouchi N, Sakui N, Saito K, Nakazawa H (2006) Liquid phase microextraction with in situ derivatization for measurement of bisphenol A in river water sample by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1110:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2006.01.061
Miao W, Wei B, Yang R, Wu C, Lou D, Jiang W, Zhou Z (2014) Highly specific and sensitive detection of bisphenol A in water samples using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay employing a novel synthetic antigen. New J Chem 38:669–675. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3NJ01094E
Xue F, Wu J, Chu H, Mei Z, Ye Y, Liu J, Zhang R, Peng C, Zheng L, Chen W (2013) Electrochemical aptasensor for the determination of bisphenol A in drinking water. Microchim Acta 180:109–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-012-0909-z
Ren X, Cheshari EC, Qi J, Li X (2018) Silver microspheres coated with a molecularly imprinted polymer as a SERS substrate for sensitive detection of bisphenol A. Microchim Acta 185:242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2772-z
Ballesteros-Gómez A, Ruiz FJ, Rubio S, Pérez-Bendito D (2007) Determination of bisphenols a and F and their diglycidyl ethers in wastewater and river water by coacervative extraction and liquid chromatography-fluorimetry. Anal Chim Acta 603:51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2007.09.048
Goulart LA, Gonçalves R, Correa AA, Pereira EC, Mascaro LH (2018) Synergic effect of silver nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes on the simultaneous voltammetric determination of hydroquinone, catechol, bisphenol A and phenol. Microchim Acta 185:12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2540-5
Yin H, Zhou Y, Ai S, Chen Q, Zhu X, Liu X, Zhou L (2010) Sensitivity and selectivity determination of BPA in real water samples using PAMAM dendrimer and CoTe quantum dots modified glassy carbon electrode. J Hazard Mater 174:236–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.041
Fizir M, Richa A, He H, Touil S, Brada M, Fizir L (2020) A mini review on molecularly imprinted polymer based halloysite nanotubes composites: innovative materials for analytical and environmental applications. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 19:241–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-020-09537-x
Üzek R, Sari E, Şenel S, Denizli A, Merkoçi A (2019) A nitrocellulose paper strip for fluorometric determination of bisphenol A using molecularly imprinted nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 186:218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3323-y
Kamel AH, Jiang X, Li P, Liang R (2018) A paper-based potentiometric sensing platform based on molecularly imprinted nanobeads for determination of bisphenol A. Anal Methods 10:3890–3895. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8AY01229F
Wu Y, Liu Y, Gao K, Xia H, Luo M, Wang X, Ye L, Shi Y, Lu B (2015) Monitoring bisphenol A and its biodegradation in water using a fluorescent molecularly imprinted chemosensor. Chemosphere 119:515–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.07.017
Iqbal A, Tian Y, Wang X, Gong D, Guo Y, Iqbal K, Wang Z, Liu W, Qin W (2016) Carbon dots prepared by solid state method via citric acid and 1,10-phenanthroline for selective and sensing detection of Fe2+ and Fe3+. Sensors Actuators B 237:408–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.06.126
Wu X, Zhang Z, Li J, You H, Li Y, Chen L (2015) Molecularly imprinted polymers-coated gold nanoclusters for fluorescent detection of bisphenol A. Sensors Actuators B 211:507–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.01.115
Martinez AW, Phillips ST, Whitesides GM, Carrilho E (2010) Diagnostics for the developing world: microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Anal Chem Acta 82:3–10. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac9013989
Morbioli GG, Mazzu-Nascimento T, Stockton AM, Carrilho E (2017) Technical aspects and challenges of colorimetric detection with microfluidic paper-based analytical devices (μPADs)-a review. Anal Chim Acta 970:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.03.037
Weng X, Neethirajan S (2017) Aptamer-based fluorometric determination of norovirus using a paper-based microfluidic device. Microchim Acta 184:4545–4552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2467-x
Bhardwaj J, Devarakonda S, Kumar S, Jang J (2017) Development of a paper-based electrochemical immunosensor using an antibody-single walled carbon nanotubes bio-conjugate modified electrode for label-free detection of foodborne pathogens. Sensors Actuators B Chem 253:115–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.06.108
Kong Q, Wang Y, Zhang L, Ge S, Yu J (2017) A novel microfluidic paper-based colorimetric sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer membranes for highly selective and sensitive detection of bisphenol A. Sensors Actuators B Chem 243:130–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.11.146
Jemmeli D, Marcoccio E, Moscone D, Dridi C, Arduini F (2020) Highly sensitive paper-based electrochemical sensor for reagent free detection of bisphenol A. Talanta 216:120924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.120924
Pandit R, Gaikwad S, Agarkar G, Gade A, Rai M (2015) Curcumin nanoparticles: physico-chemical fabrication and its in vitro efficacy against human pathogens. 3. Biotech 5(6):991–997. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-015-0302-9
Zhang J, Yang Z, Liu Q, Liang H (2019) Electrochemical biotoxicity detection on a microfluidic paper-based analytical device via cellular respiratory inhibition. Talanta 202:384–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.05.031
Cinti S, Arduini F, Vellucci G, Cacciotti I, Nanni F, Moscone D (2014) Carbon black assisted tailoring of Prussian blue nanoparticles to tune sensitivity and detection limit towards H2O2 by using screen-printed electrode. Electrochem Commun 47:63–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2014.07.018
Kumar S, Bhushan P, Bhattacharya S (2019) Fluid transport mechanisms in paper-based microfluidic devices. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-0489-1_2
Butmee P, Tumcharern G, Saejueng P, Stankovic D, Ortner A, Jitcharoen J, Kalcher K, Samphao A (2019) A direct and sensitive electrochemical sensing platform based on ionic liquid functionalized graphene nanoplatelets for the detection of bisphenol A. Jeac 833:370–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.12.014
Tang RH, Liu LN, Zhang SF, He X, Li XJ, Xu F, Ni YH, Li F (2019) A review on advances in methods for modification of paper supports for use in point-of-care testing. Microchim Acta 186:521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3626-z
Mejri A, Mars A, Elfil H, Hamzaoui AH (2019) Reduced graphene oxide nanosheets modified with nickel disulfide and curcumin nanoparticles for non-enzymatic electrochemical sensing of methyl parathion and 4-nitrophenol. Microchim Acta 186:704. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3853-3
Fan H, Li Y, Wu D, Ma H, Mao K, Fan D, Du B, Li H, Wei Q (2012) Electrochemical bisphenol A sensor based on N-doped graphene sheets. Anal Chim Acta 711:24–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2011.10.051
Zheng Z, Du Y, Wang Z, Feng Q, Wang C (2013) Pt/graphene-CNTs nanocomposite based electrochemical sensors for the determination of endocrine disruptor bisphenol A in thermal printing papers. Analyst 138:693–701. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2AN36569C
Funding
The authors are grateful to the Tunisian Ministry of High Education and Scientific Research for the financial support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 2389 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mars, A., Mejri, A., Hamzaoui, A.H. et al. Molecularly imprinted curcumin nanoparticles decorated paper for electrochemical and fluorescence dual-mode sensing of bisphenol A. Microchim Acta 188, 94 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04753-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04753-w