Abstract
A method is described to enhance the sensitivity of an immunochromatographic assay for clenbuterol (CLE) by making use of dually-labeled gold nanoparticles (GNPs), background fluorescence blocking, and immunomagnetic separation. The GNPs were labeled with biotinylated antibody and streptavidin, respectively, and dually labeled GNPs were obtained via the biotin-streptavidin interaction to amplify the detection signal. The fluorescent signal was blocked by dually labeled GNPs and decreased as the dually labeled GNPs aggregation increases on nitrocellulose membrane, which derived from fluorescent polyvinylchloride card. However, fluorescence (measured at excitation/emission wavelengths of 518/580 nm) recovers when CLE reacts with dually labeled GNPs. Immunomagnetic separation was first applied for sample pretreatment. This can offset the matrix effect and improves the sensitivity and accuracy of the assay. Under the optimal conditions, the limits of detection of CLE visually were 0.25 μg·L−1. In addition, clenbuterol can be quantified in swine urine with a 0.03 μg·L−1 detection limit. This is 60-fold lower than current immunochromatography. Response is linear in the 0.06–0.59 μg·L−1 concentration range, and the recoveries from spiked swine urine range from 81 to 115%.”

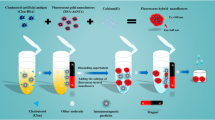
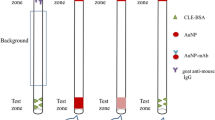
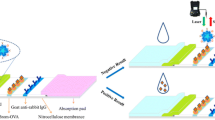
Schematic presentation of the strategies for improving sensitivity of immunochromatographic assay. It includes immunomagnetic separations, dually-labeled gold nanoparticles and background fluorescence blocking. The assay was applied to detect clenbuterol (CLE) in swine urine with an excellent performance.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbosa J, Cruz C, Martins J, Manuel Silva J, Neves C, Alves C, Ramos F, Noronha da Silveira MI (2005) Food poisoning by clenbuterol in Portugal. Food Addit Contam 22:563–566. https://doi.org/10.1080/02652030500135102
Cai Y, Kang K, Liu Y, Wang Y, He X (2018) Development of a lateral flow immunoassay of C-reactive protein detection based on red fluorescent nanoparticles. Anal Biochem 556:129–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AB.2018.06.017
Chen J, Park B, Eady M (2017) Simultaneous detection and serotyping of salmonellae by Immunomagnetic separation and label-free surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Food Anal Methods 10:3181–3193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-0870-x
Chen X, Xu Y, Yu J, Li J, Zhou X, Wu C, Ji Q, Ren Y, Wang L, Huang Z, Zhuang H, Piao L, Head R, Wang Y, Lou J (2014) Antigen detection based on background fluorescence quenching immunochromatographic assay. Anal Chim Acta 841:44–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2014.07.025
Cho IH, Bhunia A, Irudayaraj J (2015) Rapid pathogen detection by lateral-flow immunochromatographic assay with gold nanoparticle-assisted enzyme signal amplification. Int J Food Microbiol 206:60–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2015.04.032
Dong S, Liu Y, Zhang X, Xu C, Liu X, Zhang C (2018) Development of an immunochromatographic assay for the specific detection of bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) Cry1Ab toxin. Anal Biochem 567:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2018.08.014
Dou L, Zhao B, Bu T, Zhang W, Huang Q, Yan L, Huang L, Wang Y, Wang J, Zhang D (2018) Highly sensitive detection of a small molecule by a paired labels recognition system based lateral flow assay. Anal Bioanal Chem 410:3161–3170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1003-0
Feng F, Zheng J, Qin P, Han T, Zhao D (2017) A novel quartz crystal microbalance sensor array based on molecular imprinted polymers for simultaneous detection of clenbuterol and its metabolites. Talanta 167:94–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TALANTA.2017.02.001
Fu Q, Liang J, Lan C, Zhou K, Shi C, Tang Y (2014) Development of a novel dual-functional lateral-flow sensor for on-site detection of small molecule analytes. Sensors Actuators B Chem 203:683–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.06.043
Garssen GJ, Geesink GH, Hoving-Bolink AH, Verplanke JC (1995) Effects of dietary clenbuterol and salbutamol on meat quality in veal calves. Meat Sci 40:337–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/0309-1740(94)00034-5
Hermanson GT (2013) Bioconjugate Techniques: Third Edition
Huang Z, Cui X, Xie Q-Y, Liu DF, Lai WH (2016) Short communication: a novel method using immunomagnetic separation with a fluorescent nanobeads lateral flow assay for the rapid detection of low-concentration Escherichia coli O157:H7 in raw milk. J Dairy Sci 99:9581–9585. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2016-11780
Liu D, Huang Y, Wang S, Liu K, Chen M, Xiong Y, Yang W, Lai W (2015) A modified lateral flow immunoassay for the detection of trace aflatoxin M1 based on immunomagnetic nanobeads with different antibody concentrations. Food Control 51:218–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.11.036
Liu J, Fan Y, Kong Z, Wang Y, Luo J, Xu S, Jin H, Cai X (2018) Smartphone-based rapid quantitative detection of luteinizing hormone using gold immunochromatographic strip. Sensors Actuators, B Chem 259:1073–1081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.12.161
Liu R, Liu L, Song S, et al (2017) Development of an immunochromatographic strip for the rapid detection of 10 β-agonists based on an ultrasensitive monoclonal antibody
Parr MK, Opfermann G, Schäänzer W (2009) Analytical methods for the detection of clenbuterol. Bioanalysis
Pei X, Wang Q, Li X, Xie J, Xie S, Peng T, Wang C, Sun Y, Jiang H (2016) Provision of ultrasensitive quantitative gold Immunochromatography for rapid monitoring of olaquindox in animal feed and water samples. Food Anal Methods 9:1919–1927. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0360-y
PENG T, ZHANG FS, YANG WC et al (2014) Lateral-flow assay for rapid quantitative detection of Clorprenaline residue in swine urine. J Food Prot 77:1824–1829. https://doi.org/10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-14-103
Prezelj A, Obreza A, Pecar S (2003) Abuse of Clenbuterol and its detection. Curr Med Chem 10:281–290. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867033368330
Shan S, Lai W, Xiong Y, Wei H, Xu H (2015) Novel strategies to enhance lateral flow immunoassay sensitivity for detecting foodborne pathogens. J Agric Food Chem 63:745–753. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf5046415
Shellaiah M, Simon T, Venkatesan P, Sun KW, Ko FH, Wu SP (2018) Nanodiamonds conjugated to gold nanoparticles for colorimetric detection of clenbuterol and chromium(III) in urine. Microchim Acta 185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2611-7
Sun Y, Xie J, Peng T, Wang J, Xie S, Yao K, Wang C, Sun S, Xia X, Jiang H (2017) A new method based on time-resolved Fluoroimmunoassay for the detection of streptomycin in Milk. Food Anal Methods 10:2262–2269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-0797-2
Taranova NA, Urusov AE, Sadykhov EG, Zherdev AV, Dzantiev BB (2017) Bifunctional gold nanoparticles as an agglomeration-enhancing tool for highly sensitive lateral flow tests: a case study with procalcitonin. Microchim Acta 184:4189–4195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2355-4
Wang J, Cao F, He S, Xia Y, Liu X, Jiang W, Yu Y, Zhang H, Chen W (2018a) FRET on lateral flow test strip to enhance sensitivity for detecting cancer biomarker. Talanta. 176:444–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.07.096
Wang J, Zhang L, Huang Y, Dandapat A, Dai L, Zhang G, Lu X, Zhang J, Lai W, Chen T (2017) Hollow au-ag nanoparticles labeled Immunochromatography strip for highly sensitive detection of Clenbuterol. Sci Rep 7. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41419
Wang R, Zhang W, Wang P, Su X (2018b) A paper-based competitive lateral flow immunoassay for multi β-agonist residues by using a single monoclonal antibody labelled with red fluorescent nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185:191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2730-9
Xiao M, Fu Q, Shen H, Chen Y, Xiao W, Yan D, Tang X, Zhong Z, Tang Y (2018) A turn-on competitive immunochromatographic strips integrated with quantum dots and gold nano-stars for cadmium ion detection. Talanta. 178:644–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.10.002
Yan H, Xu D, Meng H, et al (2014) Food poisoning by clenbuterol in China. Qual Assur Saf Crop Foods
Zhang Q, Qu Q, Chen S, Liu X, Li P (2017) A double-label time-resolved fluorescent strip for rapidly quantitative detection of carbofuran residues in agro-products. Food Chem 231:295–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.02.016
Zhang Y, Li M, Cui Y, Hong X, du D (2018) Using of tyramine signal amplification to improve the sensitivity of ELISA for aflatoxin B1 in edible oil samples. Food Anal Methods 11:2553–2560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-018-1235-9
Zhao B, Huang Q, Dou L, Bu T, Chen K, Yang Q, Yan L, Wang J, Zhang D (2018) Prussian blue nanoparticles based lateral flow assay for high sensitive determination of clenbuterol. Sensors Actuators B Chem 275:223–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2018.08.029
Zhou J, Zhu K, Xu F, Wang W, Jiang H, Wang Z, Ding S (2014) Development of a microsphere-based fluorescence immunochromatographic assay for monitoring lincomycin in milk, honey, beef, and swine urine. J Agric Food Chem 62:12061–12066. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf5029416
Funding
This study was supported financially by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology of People’s Republic of China (2017YFF0211003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Yuyang Zeng and Demei Liang are co-author.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 179 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, Y., Liang, D., Zheng, P. et al. Immunochromatographic fluorometric determination of clenbuterol with enhanced sensitivity. Microchim Acta 186, 225 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3326-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3326-8