Abstract
The authors describe a selective and sensitive method for the colorimetric determination of Cd(II) by using silver nanoparticles capped with chalcone carboxylic acid (CCA) as an optical indicator probe. The addition of Cd(II) ions causes particle aggregation and this is accompanied by a color change from yellow to orange, with absorption peaks shifting from 396 to 522 nm. This assay enables selective detection of Cd(II), while other metal ions such as Al(III), Ca(II), Co(II), bichromate, Cu(II), Fe(III), Mn(II), Ni(II), Cr(III), Zn(II), Mg(II), Pb(II) and Hg(II) do not significantly interfere at moderate levels. The visually detectable limit of detection is 0.23 μM, and the instrumental detection limit is 0.13 μM. A linear relationship, between the absorbances ratio at 522 and 396 nm and Cd(II) concentration, was obtained in the 0.227 to 3.18 μM Cd(II) concentration range. The colorimetric method was successfully applied to the determination of Cd(II) in spiked drinking water and lake water. The results were in good agreement with results by inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry.

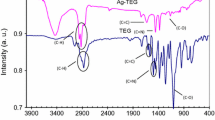
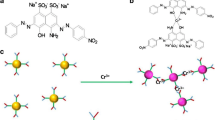
Schematic of a selective and sensitive method for the colorimetric determination of Cd(II) by using silver nanoparticles capped with chalcone carboxylic acid as an optical indicator probe. The addition of Cd(II) ions causes particle aggregation and this is accompanied by a color change from yellow to orange.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mendes A, Duda G, Nascimento C, Silva M (2006) Bioavailability of cadmium and lead in a soil amended with phosphorus fertilizers. Sci Agric 63:328–332
Chaney RL, Ryan JA, Li YM, Brown SL (1999) Cadmium in soils and plants, ed. McLaughlin MJ and Singh BR, Kluwer, Boston, p 219
Sung Y, Wu S (2014) Colorimetric detection of cd(II) ions based on di-(1H-pyrrol-2-yl)methanethione functionalized gold nanoparticles. Sensors Actuators B Chem 201:86–91
Jin T, Lu J, Nordberg M (1998) Toxicokinetics and biochemistry of cadmium with special emphasis on the role of metallothionein. Neurotoxicology 19:529–535
Jiang G, Xu L, Song S, Zhu C, Wu Q, Zhang L, Wu L (2008) Effects of long-term low-dose cadmium exposure on genomic DNA methylation in human embryo lung fibroblast cells. Toxicology 244:49–55
Goyer R, Liu J, Waalkes M (2004) Cadmium and cancer of prostate and testis. Biometals 17:555–558
Godt J, Scheidig F, Grosse-Siestrup C, Esche V, Brandenburg P, Reich A, Groneberg DA (2006) The toxicity of cadmium and resulting hazards for human health. J Occup Med Toxicol 1:1–6
Jane AM, Matin MS, Amy T, John MH, Polly AN (2006) Cadmium exposure and breast cancer risk. J Natl Cancer Inst 98(12):869–873
Violaine V, Dominique L, Philippe H (2003) Cadmium, lung and prostate cancer: a systematic review of recent epidemiological data. J Toxicol environ health, Part B 6:227–256
Akesson A, Julin B, Wolk A (2008) Long-term dietary cadmium intake and postmenopausal endometrial cancer incidence: a population-based prospective cohort study. Cancer Res 68:6435–6441
WHO (2008) Cadmium, in: guidelines for drinking-water quality. World Health Organization, Geneva, 3rd ed, 317–319
Parham H, Pourreza N, Rahbar N (2009) Solid phase extraction of lead and cadmium using solid sulfur as a new metal extractor prior to determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. J Hazard Mater 163:588–592
Zougagh M, Torres AG, Cano Pavon JM (2002) Determination of cadmium in water by ICP-AES with on-line adsorption preconcentration using DPTH-gel and TS-gel microcolumns. Talanta 56:753–761
Yang Y, Cheng T, Zhu W, Xu Y, Qian X (2010) Highly selective and sensitive near-infrared fluorescent sensors for cadmium in aqueous solution. Org Lett 13:264–267
Yin J, Wu T, Song J, Zhang Q, Liu S, Xu R, Duan H (2011) SERS-active nanoparticles for sensitive and selective detection of cadmium ion (Cd2+). Chem Mater 23:4756–4764
Kim HN, Ren WX, Kim JS, Yoon J (2012) Fluorescent and colorimetric sensors for detection of lead, cadmium, and mercury ions. Chem Soc Rev 41:3210–3244
Jin W, Huang P, Wu F, Ma LH (2015) Ultrasensitive colorimetric assay of cadmium ion based on silver nanoparticles functionalized with 5-sulfosalicylic acid for wide practical applications. Analyst 140:3507–3513
Sener G, Uzun L, Denizli A (2014) Colorimetric sensor array based on gold nanoparticles and amino acids for identification of toxic metal ions in water. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:18395–18400
Sener G, Uzun L, Denizli A (2014) Lysine-promoted colorimetric response of gold nanoparticles: a simple assay for ultrasensitive mercury(II) detection. Anal Chem 86:514–520
Saha K, Agasti SS, Kim C, Li X, Rotello VM (2012) Gold nanoparticles in chemical and biological sensing. Chem Rev 112:2739–2779
Lou T, Chen Z, Wang Y, Chen L (2011) Blue-to-red colorimetric sensing strategy for Hg2+ and Ag+ via redox-regulated surface chemistry of gold nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3:1568–1573
Chai F, Wang C, Wang T, Li L, Su Z (2010) Colorimetric detection of Pb2+ using glutathione functionalized gold nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2:1466–1470
Wu X, Tang WX, Hou C, Zhang C, Zhu NN (2014) Colorimetric and bare-eye detection of alkaline earth metal ions based on the aggregation of silver nanoparticles functionalized with thioglycolic acid. Microchim Acta 181:991–998
Guo Y, Zhang Y, Shao H, Wang Z, Wang X, Jiang X (2014) Label-free colorimetric detection of cadmium ions in rice samples using gold nanoparticles. Anal Chem 86:8530–8534
Li H, Yao Y, Han C, Zhan J (2009) Triazole-ester modified silver nanoparticles: click synthesis and Cd2+ colorimetric sensing. Chem Commun 32:4812–4814
Wu Y, Zhan S, Wang L, Zhou P (2014) Selection of a DNA aptamer for cadmium detection based on cationic polymer mediated aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Analyst 139:1550–1561
Wang W, Efrima S, Regev O (1998) Directing oleate stabilized nanosized silver colloids into organic phases. Langmuir 14:602–610
Lee JS, Jean AKRL, Hurst SJ, Mirkin CA (2007) Silver nanoparticle–oligonucleotide conjugates based on DNA with triple cyclic disulfide moieties. Nano Lett 7:2112–2115
Thompson DG, Enright A, Faulds K, Smith WE, Graham D (2008) Ultrasensitive DNA detection using oligonucleotide–silver nanoparticle conjugates. Anal Chem 80:2805–2810
Li HB, Li FY, Han CP, Cui ZM, Xie GY, Zhang AQ (2010) Highly sensitive and selective tryptophan colorimetric sensor based on 4,4-bipyridine-functionalized silver nanoparticles. Sensors Actuators B Chem 145:194–199
Xu YB, Dong YJ, Jiang X, Zhu NN (2013) Colorimetric detection of trivalent chromium in aqueous solution using tartrate-capped silver nanoparticles as probe. J Nanosci Nanotechno 13:6820–6825
Wu XY, Xu YB, Dong YJ, Jiang X, Zhu NN (2013) Colorimetric determination of hexavalent chromium with ascorbic acid capped silver nanoparticles. Anal Methods 5:560–565
Shimizu GKH, Enright GD, Ratcliffe CI, Rego GS, Reid JL, Ripmeester JA (1998) Silver sulfonates: an unexplored class of layered solids. Chem Mater 10:3282–3283
Jaliehvand F, Leung BO, Mah V (2009) Cadmium(II) complex formation with cysteine and penicillamine. Inorg Chem 48:5758–5771
Shi ZH, Han QX, Yang LZ, Yang H, Tang XL, Dou W, Li ZQ, Zhang YG, Shao YL, Guan LP, Liu WS (2015) A highly selective two-photon fluorescent probe for detection of cadmium(II) based on intramolecular electron transfer and its imaging in living cells. Chem Eur J 21:290–297
Gu Y, Li N, Gao MM, Wang ZL, Xiao DL, Li Y, Jia HN, He H (2015) Microwave-assisted synthesis of BSA-modified silver nanoparticles as a selective fluorescent probe for detection and cellular imaging of cadmium(II). Microchim Acta 182:1255–1261
Wang ZX, Guo YX, Ding SN (2015) Fluorometric determination of cadmium(II) and mercury(II) using nanoclusters consisting of a gold-nickel alloy. Microchim Acta 182:2223–2231
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the program of the Food Safety and Nutrition Innovation Team of Shanghai Normal University (DXL123).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 302 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Y., Ding, L., Jin, X. et al. Silver nanoparticles capped with chalcon carboxylic acid as a probe for colorimetric determination of cadmium(II). Microchim Acta 184, 3357–3362 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2358-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2358-1