Abstract
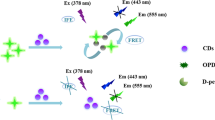
Carbon nanodots modified with triethylenetetramine (referred to as TCDs) are shown to be viable fluorescent probes for relay recognition of Cu(II) ion and glutathione (GSH). The assay is based on an “on-off-on” mechanism where the “on-off” effect, i.e. quenching by Cu(II) by up to 67%, is exploited to quantify it in concentrations as low as 3.4 nM. The unique quenching of fluorescence (measured at excitation/emission wavelengths of 380/470 nm; quantum yield 16%) is attributed to the fairly selective capture of Cu(II) by the amino and amide groups on the surface of the TCDs. On addition of GSH to the quenched TCD/Cu(II) complex, fluorescence is restored. This effect enables GSH to be quantified in the 0.2 to 175 μM concentration range, with a 0.11 μM detection limit. The turn-on response to GSH is highly selective over other natural amino acids and common anions. Furthermore, the TCDs were successfully applied to image Cu(II) and GSH in living yeast cells.

Carbon nanodots modified with triethylenetetramine show strong blue fluorescence which is quenched by Cu(II) but restored on addition of glutathione. Both Cu(II) (down to 3.4 nM) and glutathione (down to 110 nM) can be detected via these effects.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hola K, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Giannelis EP, Zboril R, Rogach AL (2014) Carbon dots-emerging light emitters for bioimaging, cancer therapy and optoelectronics. Nano Today 9:590–603
Xu MH, He GL, Li ZH, He FJ, Gao F, Su YJ, Zhang LY, Yang Z, Zhang YF (2014) A green heterogeneous synthesis of N-doped carbon dots and their photoluminescence applications in solid and aqueous states. Nanoscale 6:10307–10315
Yan FY, Kong DP, Luo YM, Ye QH, He JJ, Guo XF, Chen L (2016) Carbon dots serve as an effective probe for the quantitative determination and for intracellular imaging of mercury(II). Microchim Acta 183:1611–1618
Zhu SJ, Meng QN, Wang L, Zhang JH, Song YB, Jin H, Zhang K, Sun HC, Wang HY, Yang B (2013) Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, probes, and bioimaging. Angew Chem 125:4045–4049
Qu SN, Wang XY, Lu QP, Liu XY, Wang LJ (2012) A biocompatible fluorescent ink based on water- soluble luminescent carbon nanodots. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:12215–12218
Cao L, Sahu S, Anilkumar P, Bunker CE, Xu J, Shiral Fernando KA, Wang P, Guliants EA, Tackett KN, Sun Y-P (2011) Carbon nanoparticles as visible-light photocatalysts for efficient CO2 conversion and beyond. J Am Chem Soc 133:4754–4757
Wang HL, Zhou GD, Gai HW, Chen XQ (2012) A fluorescein-based probe with high selectivity to cysteine over homocysteine and glutathione. Chem Commun 48:8341–8343
Wang FX, Hao QL, Zhang YH, Xu YJ, Lei W (2016) Fluorescence quenchometric method for determination of ferric ion using boron-doped carbon dots. Microchim Acta 183:273–279
Wang YF, Hu A (2014) Carbon quantum dots: synthesis, properties and applications. J Mater Chem C 2:6921–6939
Chinen AB, Guan CM, Ferrer JR, Barnaby SN, Merkel TJ, Mirkin CA (2015) Nanoparticle probes for the detection of cancer biomarkers, cells, and tissues by fluorescence. Chem Rev 115:10530–10574
Qu SN, Chen H, Zheng XM, Cao JS, Liu XY (2013) Ratiometric fluorescent nanoprobe based on water soluble carbon nanodots with multiple sensing capacities. Nanoscale 5:5514–5518
Liu S, Tian JQ, Wang L, Zhang YW, Qin XY, Luo YL, Asiri AM, Al-Youbi AO, Sun XP (2012) Hydrothermal treatment of grass: a low-cost, green route to nitrogen-doped, carbon-rich, photoluminescent polymer nanodots as an effective fluorescent sensing platform for label-free detection of Cu(II) ions. Adv Mater 24:2037–2041
Gu JJ, Hu DH, Wang WN, Zhang QH, Meng Z, Jia XD, Xi K (2015) Carbon dot cluster as an efficient “off-on” fluorescent probe to detect Au(III) and glutathione. Biosens Bioelectron 68:27–33
Wang B, Chen YF, Wu YY, Weng B, Liu YS, Li CM (2016) Synthesis of nitrogen- and iron-containing carbon dots, and their application to colorimetric and fluorometric determination of dopamine. Microchim Acta 183:2491–2500
Gao Z, Wang LB, Su RX, Huang RL, Qi W, He ZM (2015) A carbon dot-based “off-on” fluorescent probe for highly selective and sensitive detection of phytic acid. Biosens Bioelectron 70:232–238
Zheng M, Xie ZG, Qu D, Li D, Du P, Jing XB, Sun ZC (2013) On-off-on fluorescent carbon dot nanoprobe for recognition of chromium(VI) and ascorbic acid based on the inner filter effect. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:13242–13247
Zuo PL, Lu XH, Sun ZG, Guo YH, He H (2016) A review on syntheses, properties, characterization and bioanalytical applications of fluorescent carbon dots. Microchim Acta 183:519–542
Wang XD, Wang D, Guo YL, Yang CD, Iqbal A, Liu WS, Qin WW, Yan D, Guo HC (2015) Imidazole derivative-functionalized carbon dots: using as a fluorescent probe for detecting water and imaging of live cells. Dalton Trans 44:5547–5554
Sun Y-P, Zhou B, Lin Y et al (2006) Quantum-sized carbon dots for bright and colorful photoluminescence. J Am Chem Soc 128:7756–7757
Wei WL, Xu C, Ren JS, Xu BL, Qu XG (2012) Sensing metal ions with ion selectivity of a crown ether and fluorescence resonance energy transfer between carbon dots and grapheme. Chem Commun 48:1284–1286
Cayuela A, Kennedy SR, Soriano ML, Jones CD, Valcárcel M, Steed JW (2015) Fluorescent carbon dot-molecular salt hydrogels. Chem Sci 6:6139–6146
Zhu SJ, Song YB, Zhao XH, Shao JR, Zhang JH, Yang B (2015) The photoluminescence mechanism in carbon dots (graphene quantum dots, carbon nanodots andpolymer dots): current state and future perspective. Nano Res 8:355–381
Zhu AW, Qu Q, Shao XL, Kong B, Tian Y (2012) Carbon-dot-based dual-emission nanohybrid produces a ratiometric fluorescent probe for in vivo imaging of cellular copper ions. Angew Chem 124:7297–7301
Zhao AD, Chen ZW, Zhao CQ, Gao N, Ren JS, Qu XG (2015) Recent advances in bioapplications of C-dots. Carbon 85:309–327
Salinas-Castillo A, Ariza-Avidad M, Pritz C, Camprubí-Robles M, Fernández B, Ruedas-Rama MJ, Megia-Fernández A, Lapresta-Fernández A, Santoyo-Gonzalez F, Schrott-Fischer A (2013) Carbon dots for copper detection with down and upconversion fluorescent properties as excitation sources. Chem Commun 49:1103–1105
Dong YQ, Wang RX, Li GL, Chen CQ, Chi YW, Chen GN (2012) Polyamine-functionalized carbon quantum dots as fluorescent probes for selective and sensitive detection of copper ions. Anal Chem 84:6220–6224
Liu J-M, Lin L-P, Wang X-X, Lin S-Q, Cai W-L, Zhang L-H, Zheng Z-Y (2012) Highly selective and sensitive detection of Cu(II) with lysine enhancing bovine serum albumin modified-carbon dots fluorescent probe. Analyst 137:2637–2642
Rao HB, Liu W, Lu ZW, Wang YY, Ge HW, Zou P, Wang XX, He H, Zeng XY, Wang YJ (2016) Silica-coated carbon dots conjugated to CdTe quantum dots: a ratiometric fluorescent probe for copper(II). Microchim Acta 183:581–588
Guo Y, Yang LL, Li WW, Wang XF, Shang YH, Li BX (2016) Carbon dots doped with nitrogen and sulfur and loaded with copper(II) as a “turn-on” fluorescent probe for cysteine, glutathione and homocysteine. Microchim Acta 183:1409–1416
Anderson ME (1998) Glutathione: an overview of biosynthesis and modulation. Chem Biol Interact 111:1–14
Ullah H, Khan MF, Jan SU, Hashmat F (2016) Depletion of GSH in human blood plasma and cytosolic fraction during cadmium toxicity is temperature and pH dependent. Pak J Pharm Sci 29:89–95
Zhang HT, Liu RC, Liu J, Li L, Wang P, Yao SQ, Xu ZT, Sun HY (2016) A minimalist fluorescent probe for differentiating Cys, Hcy and GSH in live cells. Chem Sci 7:256–260
Lakowicz JR (2006) Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy. Springer, New York, pp 54–55
Qian ZS, Chai LJ, Huang YY, Tang C, Shen JJ, Chen JR, Feng H (2015) A real-time fluorescent assay for the detection of alkaline phosphatase activity based on carbon quantum dots. Biosens Bioelectron 68:675–680
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21176125), the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province of China (B201313, B201419), and the Science Research Project of Heilongjiang Province Education Department, China (12541861, 1254G066).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 405 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, R., Guo, X., Jia, L. et al. A fluorescent “on-off-on” assay for selective recognition of Cu(II) and glutathione based on modified carbon nanodots, and its application to cellular imaging. Microchim Acta 184, 1143–1150 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2076-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2076-8