Abstract
Purpose
Systemic damage in acute pancreatitis (AP) can be characterized by oxidative stress and the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Roflumilast has been shown to be a potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant agent. In the present study, we aimed to investigate the effect of roflumilast in cerulein-induced AP.
Methods
Thirty-two male rats were divided into four groups: group 1 (sham), group 2 (Roflumilast), group 3 (AP), and group 4 (AP + Roflumilast). AP was induced by injecting 4 × 75 μg/kg of body weight at an interval of 1 h. Rats were killed after 12 h following the last cerulein administration. AP was confirmed by measuring the serum amylase level and inflammatory features.
Results
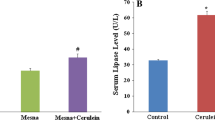
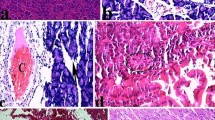
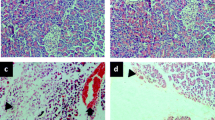
Morphological changes were observed in the pancreas. Amylase levels were higher in the AP and AP + Roflumilast groups than the sham and Roflumilast groups. The serum levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 increased in the AP group, whereas they decreased in the Roflumilast group. The total oxidant activity (TOA) was higher and the total antioxidant capacity (TAC) was lower in the AP group. The administration of roflumilast decreased the TOA and increased the TAC in comparison with the AP group (p < 0.05 for both).
Conclusions
Roflumilast significantly decreases oxidative stress and inflammatory mediators in the plasma, pancreas, and lung in cerulein-induced AP rats.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Working Group IAP/APA Acute Pancreatitis Guidelines. IAP/APA evidence-based guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2013;13(4 Suppl 2):e1–15.
Hammer HF. An update on pancreatic pathophysiology (do we have to rewrite pancreatic pathophysiology?). Wien Med Wochenschr. 2014;164(3–4):57–62.
Onder A, Kapan M, Gümüş M, Yüksel H, Böyük A, Alp H, et al. The protective effects of curcumin on intestine and remote organs against mesenteric ischemia/reperfusion injury. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2012;23(2):141–7.
Böyük A, Onder A, Kapan M, Gümüş M, Fιrat U, Başaralι MK, et al. Ellagic acid ameliorates lung injury after intestinal ischemia-reperfusion. Pharmacogn Mag. 2011;7(27):224–8.
Gümüş M, Yüksel H, Evliyaoğlu O, Kapan M, Böyük A, Önder A, et al. Effects of ellagic acid on copper, zinc, and biochemical values in serum and liver of experimental cholestatic rats. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2011;143(1):386–93.
Romero FJ, Bosch-Morell F, Romero MJ, Jareno EJ, Romero B, Marin N, et al. Lipid peroxidation products and antioxidants in human disease. Environ Health Perspect. 1998;106(5):1229–34.
Okita K, Mizuguchi T, Shigenori O, Ishii M, Nishidate T, Ueki T, et al. Pancreatic regeneration: basic research and gene regulation. Surg Today. 2015.
Esrefoglu M. Experimental and clinical evidence of antioxidant therapy in acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(39):5533–41.
Bukowczan J, Warzecha Z, Ceranowicz P, Kusnierz-Cabala B, Tomaszewska R, Dembinski A. Pretreatment with obestatin reduces the severity of ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute pancreatitis in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;760:113–21.
Kapan M, Gumus M, Onder A, Firat U, Basarali MK, Boyuk A, et al. The effects of ellagic acid on the liver and remote organs’ oxidative stress and structure after hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury caused by pringle maneuver in rats. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2012;113(5):274–81.
Kılıç E, Türkoğlu A, Keleş A, Ekinci A, Kesgin S, Gümüş M. The antioxidant effects of pomegranate extract on local and remote organs in a mesenteric ischemia and reperfusion model. Redox Rep. 2015 May 26.
Gul M, Aliosmanoglu I, Uslukaya O, Firat U, Yüksel H, Gümüs M, et al. The protective effect of ellagic acid on lung damage caused by experimental obstructive jaundice model. Acta Chir Belg. 2013;13(4):285–9.
Oguz A, Kapan M, Onder A, Kilic E, Gumus M, Basarali MK, et al. The effects of curcumin on the liver and remote organs after hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury formed with Pringle manoeuvre in rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013;17(4):457–66.
Kwak HJ, Park KM, Choi HE, Chung KS, Lim HJ, Park HY. PDE4 inhibitor, roflumilast protects cardiomyocytes against NO-induced apoptosis via activation of PKA and Epac dual pathways. Cell Signal. 2008;20(5):803–14.
Takahashi T, Tang T, Lai NC, Roth DM, Rebolledo B, Saito M, et al. Increased cardiac adenylyl cyclase expression is associated with increased survival after myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2006;114(5):388–96.
Rieder F, Siegmund B, Bundschuh DS, Lehr HA, Endres S, Eigler A. The selective phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor roflumilast and phosphodiesterase 3/4 inhibitor pumafentrine reduce clinical score and TNF expression in experimental colitis in mice. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(2):e56867.
Hatzelmann A, Schudt C. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory potential of the novel PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001;97(1):267–79.
Bundschuh DS, Eltze M, Barsig J, Wollin L, Hatzelmann A, Beume R. In vivo efficacy in airway disease models of roflumilast, a novel orally active PDE4 inhibitor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001;297(1):280–90.
Milara J, Lluch J, Almudever P, Freire J, Xiaozhong Q, Cortijo J. Roflumilast N-oxide reverses corticosteroid resistance in neutrophils from patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134(2):314–22.
Torphy TJ. Phosphodiesterase isozymes: molecular targets for novel antiasthma agents. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157(2):351–70.
Hatzelmann A, Morcillo EJ, Lungarella G, Adnot S, Sanjar S, Beume R, et al. The preclinical pharmacology of roflumilast–a selective, oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor in development for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2010;23(4):235–56.
Erel O. A novel automated method to measure total antioxidant response against potent free radical reactions. Clin Biochem. 2004;37(2):112–9.
Erel O. A new automated colorimetric method for measuring total oxidant status. Clin Biochem. 2005;38(12):1103–11.
Tüfek A, Tokgöz O, Aliosmanoglu I, Alabalik U, Evliyaoglu O, Çiftçi T, et al. The protective effects of dexmedetomidine on the liver and remote organs against hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. Int J Surg. 2013;11(1):96–100.
Schmidt J, Rattner DW, Lewandrowski K, Compton CC, Mandavilli U, Knoefel WT, et al. A better model of acute pancreatitis for evaluating therapy. Ann Surg. 1992;215(1):44–56.
Chatterjee PK, Cuzzocrea S, Brown PA, Zacharowski K, Stewart KN, Mota-Filipe H, et al. Tempol, a membrane-permeable radical scavenger, reduces oxidant stress-mediated renal dysfunction and injury in the rat. Kidney Int. 2000;58(2):658–73.
Camargo CA Jr, Madden JF, Gao W, Selvan RS, Clavien PA. Interleukin-6 protects liver against warm ischemia/reperfusion injury and promotes hepatocyte proliferation in the rodent. Hepatology. 1997;26(6):1513–20.
Frossard JL, Pastor CM. Experimental acute pancreatitis: new insights into the pathophysiology. Front Biosci. 2002;7:d275–87.
Feng C, Su X, Zhou X, Wang LL, Li B, Chen LI, et al. Early peritoneal lavage with ulinastatin improves outcome and enhances multi-organ protection in a model of severe acute pancreatitis. Exp Ther Med. 2015;9(4):1171–7.
Zhu L, Lu J, Yang J, Sun P. Early-phase peritoneal drainage and lavage in a rat model of severe acute pancreatitis. Surg Today. 2016;46(3):371–8.
Botoi G, Andercou A. Early and prolonged peritoneal lavage with laparoscopy in severe acute pancreatitis. Chirurgia (Bucur). 2009;104(1):49–53.
Giembycz MA. Can the anti-inflammatory potential of PDE4 inhibitors be realized: guarded optimism or wishful thinking? Br J Pharmacol. 2008;155(3):288–90.
Howes LG. Selective COX-2 inhibitors, NSAIDs and cardiovascular events—is celecoxib the safest choice? Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2007;3(5):831–45.
Dinarello CA. Anti-inflammatory agents: present and future. Cell. 2010;140(6):935–50.
Rabe KF. Update on roflumilast, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;163(1):53–67.
Kusterer K, Poschmann T, Friedemann A, Enghofer M, Zendler S, Usadel KH. Arterial constriction, ischemia-reperfusion, and leukocyte adherence in acute pancreatitis. Am J Physiol. 1993;265(1 Pt 1):G165–71.
Fink GW, Norman JG. Intrapancreatic interleukin-1beta gene expression by specific leukocyte populations during acute pancreatitis. J Surg Res. 1996;63(1):369–73.
Gilgenast O, Brandt-Nedelev B, Wiswedel I, Lippert H, Halangk W, Reinheckel T. Differential oxidative injury in extrapancreatic tissues during experimental pancreatitis: modification of lung proteins by 4-hydroxynonenal. Dig Dis Sci. 2001;46(4):932–7.
Bhatia M, Saluja AK, Hofbauer B, Frossard JL, Lee HS, Castagliuolo I, et al. Role of substance P and the neurokinin 1 receptor in acute pancreatitis and pancreatitis-associated lung injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(8):4760–5.
Martorana PA, Beume R, Lucattelli M, Wollin L, Lungarella G. Roflumilast fully prevents emphysema in mice chronically exposed to cigarette smoke. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;172(7):848–53.
Jones NA, Boswell-Smith V, Lever R, Page CP. The effect of selective phosphodiesterase isoenzyme inhibition on neutrophil function in vitro. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2005;18(2):93–101.
Mata M, Sarria B, Buenestado A, Cortijo J, Cerda M, Morcillo EJ. Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibition decreases MUC5AC expression induced by epidermal growth factor in human airway epithelial cells. Thorax. 2005;60(2):144–52.
Stebbins KJ, Provins L, Ellis JL. Aerosol activity of phosphodiesterase type IV inhibitors in a murine model of cigarette smoke induced pulmonary inflammation [abstract]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;167:A486.
Martin TJ. PDE4 inhibitors—a review of the recent patent literature. IDrugs. 2001;4(3):312–38.
Newton RC, Decicco CP. Therapeutic potential and strategies for inhibiting tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Med Chem. 1999;42(13):2295–314.
Vecchio D, Acquaviva A, Arezzini B, Tenor H, Martorana PA, Gardi C. Downregulation of NOX4 expression by roflumilast N-oxide reduces markers of fibrosis in lung fibroblasts. Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:745984.
Cortijo J, Iranzo A, Milara X, Mata M, Cerda-Nicolas M, Ruiz-Sauri A, et al. Roflumilast, a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, alleviates bleomycin-induced lung injury. Br J Pharmacol. 2009;156(3):534–44.
Sabatini F, Petecchia L, Boero S, Silvestri M, Klar J, Tenor H, et al. A phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, roflumilast N-oxide, inhibits human lung fibroblast functions in vitro. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2010;23(4):283–91.
Kikuchi N, Ishii Y, Morishima Y, Yageta Y, Haraguchi N, Yamadori T, et al. Aggravation of bleomycin-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in mice lacking peroxiredoxin I. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011;45(3):600–9.
Reid DJ, Pham NT. Roflumilast: a novel treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann Pharmacother. 2012;46(4):521–9.
Hermann R, Nassr N, Lahu G, Peterfai E, Knoerzer D, Herzog R, et al. Steady-state pharmacokinetics of roflumilast and roflumilast N-oxide in patients with mild and moderate liver cirrhosis. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2007;46(5):403–16.
Pinner NA, Hamilton LA, Hughes A. Roflumilast: a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor for the treatment of severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clin Ther. 2012;34(1):56–66.
Folch E, Gelpi E, Rosello-Catafau J, Closa D. Free radicals generated by xanthine oxidase mediate pancreatitis-associated organ failure. Dig Dis Sci. 1998;43(11):2405–10.
Dabrowski A, Gabryelewicz A. Oxidative stress. An early phenomenon characteristic of acute experimental pancreatitis. Int J Pancreatol. 1992;12(3):193–9.
Czako L, Takacs T, Varga IS, Tiszlavicz L, Hai DQ, Hegyi P, et al. Oxidative stress in distant organs and the effects of allopurinol during experimental acute pancreatitis. Int J Pancreatol. 2000;27(3):209–16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uslukaya, O., Turkoglu, A., Yazgan, U.C. et al. The effects of roflumilast on the pancreas and remote organs in a cerulein-induced experimental acute pancreatitis model in rats. Surg Today 46, 1435–1442 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-016-1329-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-016-1329-1